Abstract
Background
Endotrophin is the cleavage product COL6. Recent findings indicate that endotrophin is actively involved in inflammation, angiogenesis, and fibrosis. It also seems to play a critical role in obesity-induced systemic insulin resistance by increasing chronic inflammation and fibrosis in adipose tissues. In this study, we aimed to reveal the relationship between human adipose tissue, inflammation, and insulin resistance (IR).
Methods
The study included 51 IR patients and 37 healthy controls. The presence of IR was based on Homeostatic model of assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) level of 2, 7, or higher. Fasting plasma samples were obtained from the patients and the control group.
Results
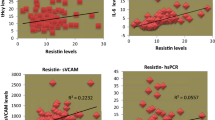
The IR patients had a higher HOMA-IR, waist circumference, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), fasting insulin (FI), and triglyceride levels than the control subjects (p < 0.05). Endotrophin and CRP levels were significantly higher in patients with IR than controls (23.12 ± 18.32 ng/mL; 11.20 ± 6.60 ng/mL p < 0,001; 5.5 ± 3.37 ng/L; 1.97 ± 0.89 ng/L p < 0.001). The serum endotrophin level showed a positive correlation with HOMA-IR (r = 0.359; p < 0.001), waist circumference (r = 0.214; p < 0.05), FI (r = 0.386; p < 0.001), and CRP level (r = 0.251; p < 0.05)
Conclusion
The serum endotrophin level was higher in patients with IR, independently of BMI, fasting glucose, and all other factors. Therefore, we foresee that high levels of endotrophin may be a new biomarker for early diagnosis of metabolic worsening in overweight and obesity. We also found a positive correlation between endotrophin and CRP. This indicates that endotrophin is closely related to inflammatory processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun K, Kusminski CM, Scherer PE. Adipose tissue remodeling and obesity. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:2094–101.
Rajala MW, Scherer PE. Minireview: the adipocyte–at the crossroads of energy homeostasis, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Endocrinology. 2003;144:3765–73.
Park J, Scherer PE. Endotrophin—a novel factor linking obesity with aggressive tumor growth. Oncotarget. 2012;3(12):1487–8. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.796.
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL, Ferrante AW Jr. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Investig. 2003;112:1796–808.
Gordon S. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:23–35.
Spencer M, et al. Adipose tissue macrophages in insulin-resistant subjects are associated with collagen VI and fibrosis and demonstrate alternative activation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010;299:E1016–27.
Greenberg AS, Obin MS. Obesity and the role of adipose tissue in inflammation and metabolism. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006;83:461S–5S.
Pasarica M, et al. Adipose tissue collagen VI in obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:5155–62.
Gara SK, Grumati P, Urciuolo A, et al. Three novel collagen VI chains with high homology to the alpha3 chain. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:10658–70.
Colombatti A, Mucignat MT, Bonaldo P. Secretion and matrix assembly of recombinant type VI collagen. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:13105–11.
Sun K, Park J, Gupta OT, et al. Endotrophin triggers adipose tissue fibrosis and metabolic dysfunction. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3485.
Park J, Morley TS, Scherer PE. Inhibition of endotrophin, a cleavage product of collagen VI, confers cisplatin sensitivity to tumours. EMBO Mol Med. 2013;5:935–48.
Park J, Scherer PE. Adipocyte-derived endotrophin promotes malignant tumor progression. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:4243–56.
Türkiye Endokrinoloji ve Metabolizma Derneği. Metabolik Sendrom Kılavuzu. Ankara. 2009 s:8/http://temd.org.tr/admin/uploads/tbl_yayinlar/metabolik_sendrom.pdf
Hotamisligil GS. IThe role of TNFalpha and TNF receptors in obesity and insulin resistance. J Intern Med. 1999;245:621–625. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2796.1999.00490.x.’..
Di Gregorio GB, Yao-Borengasser A, Rasouli N, Varma V, Lu T, Miles LM, et al. Expression of CD68 and macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 genes in human adipose and muscle tissues: association with cytokine expression, insulin resistance, and reduction by pioglitazone. Diabetes. 2005;54:2305–13.
Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D, Chou CJ, et al. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2003;112:1821–30.
Lawler HM, Underkofler CM, Kern PA, Erickson C, Bredbeck B, Rasouli N, Adipose Tissue Hypoxia, Inflammation, and Fibrosis in Obese Insulin-Sensitive and Obese Insulin-Resistant Subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016;101:1422–1428. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2015-4125
Khan T. Metabolic dysregulation and adipose tissue fibrosis: role of collagen VI. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29(6):1575–91.
Dankel SN, Svärd J, Matthä S, et al. COL6A3 expression in adipocytes associates with insulin resistance and depends on PPARγ and adipocyte size. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014;22:1807–13.
Haffner SM. Insulin resistance, inflammation, and the prediabetic state. Am J Cardiol. 2003;92:18J–26J.
Festa A, D’Agostino R Jr, Howard G, Mykkänen L, Tracy RP, Haffner SM. Chronic subclinical inflammation as part of the insulin resistance syndrome: the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study (IRAS). Circulation. 2000;102:42–7.
Pradhan AD, Cook NR, Buring JE, Manson JE, Ridker PM. C-reactive protein is independently associated with fasting insulin in nondiabetic women. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003;23:650–5.
Tanigaki K, Vongpatanasin W, Barrera JA, Atochin DN, Huang PL, Bonvini E, et al. C-reactive protein causes insulin resistance in mice through Fcgamma receptor IIB-mediated inhibition of skeletal muscle glucose delivery. Diabetes. 2013;62:721–31. https://doi.org/10.2337/db12-0133.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Determination of inflammation-associated biomarkers will help to understand the pathophysiology of IR.
• Endotrophin, the alpha 3 chain of type VI collagen, plays a critical role in obesity-induced systemic insulin resistance by increasing chronic inflammation and fibrosis in adipose tissues.
• Endotrophin level was higher in patients with IR, independently of BMI, fasting glucose, and all other factors.
• Endotrophin can be used either during the follow-up or in treatment of inflammation and IR.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aydin Yoldemir, Ş., Arman, Y., Akarsu, M. et al. The relationship between insulin resistance, obesity, and endotrophin. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 40, 191–195 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-019-00780-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-019-00780-9