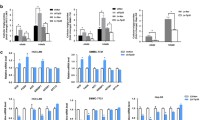
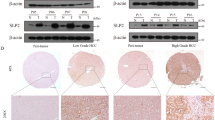
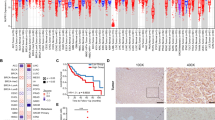
Abstract
Purpose
The detailed molecular mechanisms of aberrant lipid metabolism in HCC remain unclear. Herein, we focused on the potential role of DDX39B in aberrant lipogenesis and malignant development in HCC.
Methods
DDX39B expression in HCC and para-cancer tissues was measured by immunohistochemistry. CCK-8, colony formation and Transwell assays were utilized to detect HCC cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro. Oil red O and Nile red staining and triglyceride and cholesterol detection were used to measure lipogenesis. Coimmunoprecipitation was used to detect interactions between DDX39B and SREBP1. Immunofluorescence assays were performed to investigate the impact of DDX39B on SREBP1 nuclear translocation. A luciferase assay was used to explore the transcriptional activity of SREBP1. The subcutaneous and orthotopic xenograft models in nude mice were generated to verify the contribution of the DDX39B/SREBP1 axis to tumor growth, lung metastasis and lipid synthesis in vivo.
Results
DDX39B is upregulated in HCC tissues and predicts a worse prognosis. Upregulated DDX39B contributes to the proliferation, metastasis and lipogenesis of HCC cells. Mechanistically, DDX39B directly interacts with SREBP1, and silencing DDX39B impairs the stabilization of the SREBP1 protein through FBXW7-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of SREBP1. Furthermore, DDX39B deficiency decreases the nuclear translocation and activation of SREBP1 and transcription of SREBP1 downstream genes, resulting in reduced lipid accumulation.
Conclusions
Our study reveals a novel mechanism by which DDX39B facilitates the malignant progression of HCC via activation of SREBP1-mediated de novo lipogenesis, implicating DDX39B as both a potential predictor of recurrence and prognosis and a promising therapeutic target.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this manuscript (and its supplementary information files) or available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
H. Sung, J. Ferlay, R.L. Siegel, M. Laversanne, I. Soerjomataram, A. Jemal, F. Bray, Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 71, 209–249 (2021)
J.M. Llovet, R. Montal, D. Sia, R.S. Finn, Molecular therapies and precision medicine for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 15, 599–616 (2018)
C.R. de Lope, S. Tremosini, A. Forner, M. Reig, J. Bruix, Management of HCC. J. Hepatol. 56(Suppl 1), S75-87 (2012)
J.D. Yang, J.K. Heimbach, New advances in the diagnosis and management of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMJ 371, m3544 (2020)
J.D. Yang, P. Hainaut, G.J. Gores, A. Amadou, A. Plymoth, L.R. Roberts, A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 16, 589–604 (2019)
M. Muller, T.G. Bird, J.C. Nault, The landscape of gene mutations in cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 72, 990–1002 (2020)
D. Hanahan, R.A. Weinberg, Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144, 646–674 (2011)
M.T. Snaebjornsson, S. Janaki-Raman, A. Schulze, Greasing the wheels of the cancer machine: the role of lipid metabolism in cancer. Cell Metab. 31, 62–76 (2020)
A.J. Hoy, S.R. Nagarajan, L.M. Butler, Tumour fatty acid metabolism in the context of therapy resistance and obesity. Nat. Rev. Cancer 21, 753–766 (2021)
L. Gu, Y. Zhu, X. Lin, B. Lu, X. Zhou, F. Zhou, Q. Zhao, E.V. Prochownik, Y. Li, The IKKbeta-USP30-ACLY axis controls lipogenesis and tumorigenesis. Hepatology 73, 160–174 (2021)
N. Yahagi, H. Shimano, K. Hasegawa, K. Ohashi, T. Matsuzaka, Y. Najima, M. Sekiya, S. Tomita, H. Okazaki, Y. Tamura, Y. Iizuka, K. Ohashi, R. Nagai, S. Ishibashi, T. Kadowaki, M. Makuuchi, S. Ohnishi, J. Osuga, N. Yamada, Co-ordinate activation of lipogenic enzymes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 41, 1316–1322 (2005)
L. Che, P. Paliogiannis, A. Cigliano, M.G. Pilo, X. Chen, D.F. Calvisi, Pathogenetic, prognostic, and therapeutic role of fatty acid synthase in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 9, 1412 (2019)
X. Zuo, Z. Chen, W. Gao, Y. Zhang, J. Wang, J. Wang, M. Cao, J. Cai, J. Wu, X. Wang, M6A-mediated upregulation of LINC00958 increases lipogenesis and acts as a nanotherapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 13, 5 (2020)
J. Fleckner, M. Zhang, J. Valcarcel, M.R. Green, U2AF65 recruits a novel human DEAD box protein required for the U2 snRNP-branchpoint interaction. Genes Dev. 11, 1864–1872 (1997)
H.H. Yoo, I.K. Chung, Requirement of DDX39 DEAD box RNA helicase for genome integrity and telomere protection. Aging Cell 10, 557–571 (2011)
Z. Xu, X. Li, H. Li, C. Nie, W. Liu, S. Li, Z. Liu, W. Wang, J. Wang, Suppression of DDX39B sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to DNA-damaging chemotherapeutic agents via destabilizing BRCA1 mRNA. Oncogene 39, 7051–7062 (2020)
A. Gnjec, K.J. D’Costa, S.M. Laws, R. Hedley, K. Balakrishnan, K. Taddei, G. Martins, A. Paton, G. Verdile, S.E. Gandy, G.A. Broe, W.S. Brooks, H. Bennett, O. Piguet, P. Price, J. Miklossy, J. Hallmayer, P.L. McGeer, R.N. Martins, Association of alleles carried at TNFA -850 and BAT1 -22 with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflammation 5, 36 (2008)
A. Quinones-Lombrana, A. Lopez-Soto, F.J. Ballina-Garcia, M. Alperi-Lopez, R. Queiro-Silva, A. Lopez-Vazquez, C. Lopez-Larrea, S. Gonzalez, BAT1 promoter polymorphism is associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. J. Rheumatol. 35, 741–744 (2008)
V.R. Mendonca, L.C. Souza, G.C. Garcia, B.M. Magalhaes, M.V. Lacerda, B.B. Andrade, M.S. Goncalves, M. Barral-Netto, DDX39B (BAT1), TNF and IL6 gene polymorphisms and association with clinical outcomes of patients with Plasmodium vivax malaria. Malar. J. 13, 278 (2014)
G. Zhao, H. Yuan, Q. Li, J. Zhang, Y. Guo, T. Feng, R. Gu, D. Ou, S. Li, K. Li, P. Lin, DDX39B drives colorectal cancer progression by promoting the stability and nuclear translocation of PKM2. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 7, 275 (2022)
Q. Tu, X. Liu, X. Yao, R. Li, G. Liu, H. Jiang, K. Li, Q. Chen, X. Huang, Q. Chang, G. Xu, H. Zhu, P. Shi, B. Zhao, RETSAT associates with DDX39B to promote fork restarting and resistance to gemcitabine based chemotherapy in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res.: CR 41, 274 (2022)
M. An, H. Zheng, J. Huang, Y. Lin, Y. Luo, Y. Kong, M. Pang, D. Zhang, J. Yang, J. Chen, Y. Li, C. Chen, T. Lin, Aberrant nuclear export of circNCOR1 underlies SMAD7-Mediated lymph node metastasis of bladder cancer. Can. Res. 82, 2239–2253 (2022)
Y. Guo, Q. Li, G. Zhao, J. Zhang, H. Yuan, T. Feng, D. Ou, R. Gu, S. Li, K. Li, P. Lin, Loss of TRIM31 promotes breast cancer progression through regulating K48- and K63-linked ubiquitination of p53. Cell Death Dis. 12, 945 (2021)
K. Li, C. Mo, D. Gong, Y. Chen, Z. Huang, Y. Li, J. Zhang, L. Huang, Y. Li, F.V. Fuller-Pace, P. Lin, Y. Wei, DDX17 nucleocytoplasmic shuttling promotes acquired gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells via activation of beta-catenin. Cancer Lett. 400, 194–202 (2017)
K. Li, G. Zhao, H. Yuan, J. Zhang, Q. Li, D. Gong, P. Lin, Upregulated expression of DDX5 predicts recurrence and poor prognosis in breast cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 229, 153736 (2022)
M. Morishita, W. Ariyoshi, T. Okinaga, M. Usui, K. Nakashima, T. Nishihara, A. actinomycetemcomitans LPS enhances foam cell formation induced by LDL. J. Dent. Res. 92, 241–246 (2013)
E.C. Jensen, Quantitative analysis of histological staining and fluorescence using ImageJ. Anat. Rec. (Hoboken) 296, 378–381 (2013)
M. Yuan, D.M. Kremer, H. Huang, S.B. Breitkopf, I. Ben-Sahra, B.D. Manning, C.A. Lyssiotis, J.M. Asara, Ex vivo and in vivo stable isotope labelling of central carbon metabolism and related pathways with analysis by LC–MS/MS. Nat. Protoc. 14, 313–330 (2019)
M.T. Bengoechea-Alonso, J. Ericsson, A phosphorylation cascade controls the degradation of active SREBP1. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 5885–5895 (2009)
D. Eberle, B. Hegarty, P. Bossard, P. Ferre, F. Foufelle, SREBP transcription factors: master regulators of lipid homeostasis. Biochimie 86, 839–848 (2004)
K. Li, G. Zhao, J. Ao, D. Gong, J. Zhang, Y. Chen, J. Li, L. Huang, R. Xiang, J. Hu, P. Lin, Y. Wei, ZNF32 induces anoikis resistance through maintaining redox homeostasis and activating Src/FAK signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 442, 271–278 (2018)
E. Desjonqueres, C. Campani, F. Marra, J. Zucman-Rossi, J.C. Nault, Preneoplastic lesions in the liver: Molecular insights and relevance for clinical practice. Liver Int. 42, 492–506 (2022)
I. Kindrat, V. Tryndyak, A. de Conti, S. Shpyleva, T.K. Mudalige, T. Kobets, A.M. Erstenyuk, F.A. Beland, I.P. Pogribny, MicroRNA-152-mediated dysregulation of hepatic transferrin receptor 1 in liver carcinogenesis. Oncotarget 7, 1276–1287 (2016)
F. Fornari, L. Gramantieri, M. Ferracin, A. Veronese, S. Sabbioni, G.A. Calin, G.L. Grazi, C. Giovannini, C.M. Croce, L. Bolondi, M. Negrini, MiR-221 controls CDKN1C/p57 and CDKN1B/p27 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 27, 5651–5661 (2008)
S. Zhang, J. Li, Y. Jiang, Y. Xu, C. Qin, Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) suppresses metastastic potential of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res.: CR 28, 71 (2009)
A.K. Walker, F. Yang, K. Jiang, J.Y. Ji, J.L. Watts, A. Purushotham, O. Boss, M.L. Hirsch, S. Ribich, J.J. Smith, K. Israelian, C.H. Westphal, J.T. Rodgers, T. Shioda, S.L. Elson, P. Mulligan, H. Najafi-Shoushtari, J.C. Black, J.K. Thakur, L.C. Kadyk, J.R. Whetstine, R. Mostoslavsky, P. Puigserver, X. Li, N.J. Dyson, A.C. Hart, A.M. Naar, Conserved role of SIRT1 orthologs in fasting-dependent inhibition of the lipid/cholesterol regulator SREBP. Genes Dev. 24, 1403–1417 (2010)
H. Shimano, R. Sato, SREBP-regulated lipid metabolism: convergent physiology - divergent pathophysiology. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 13, 710–730 (2017)
W. Shao, P.J. Espenshade, Expanding roles for SREBP in metabolism. Cell Metab. 16, 414–419 (2012)
H. Shimano, J.D. Horton, R.E. Hammer, I. Shimomura, M.S. Brown, J.L. Goldstein, Overproduction of cholesterol and fatty acids causes massive liver enlargement in transgenic mice expressing truncated SREBP-1a. J. Clin. Invest. 98, 1575–1584 (1996)
J.D. Horton, I. Shimomura, M.S. Brown, R.E. Hammer, J.L. Goldstein, H. Shimano, Activation of cholesterol synthesis in preference to fatty acid synthesis in liver and adipose tissue of transgenic mice overproducing sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2. J. Clin. Invest. 101, 2331–2339 (1998)
M.T. Bengoechea-Alonso, J. Ericsson, A phosphorylation cascade controls the degradation of active SREBP1. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 5885–5895 (2009)
A. Sundqvist, M.T. Bengoechea-Alonso, X. Ye, V. Lukiyanchuk, J. Jin, J.W. Harper, J. Ericsson, Control of lipid metabolism by phosphorylation-dependent degradation of the SREBP family of transcription factors by SCF(Fbw7). Cell Metab. 1, 379–391 (2005)
J.D. Horton, N.A. Shah, J.A. Warrington, N.N. Anderson, S.W. Park, M.S. Brown, J.L. Goldstein, Combined analysis of oligonucleotide microarray data from transgenic and knockout mice identifies direct SREBP target genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 12027–12032 (2003)
X. Zhao, L. Zhao, H. Yang, J. Li, X. Min, F. Yang, J. Liu, G. Huang, Pyruvate kinase M2 interacts with nuclear sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1a and thereby activates lipogenesis and cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 293, 6623–6634 (2018)
F. Kapadia, A. Pryor, T.H. Chang, L.F. Johnson, Nuclear localization of poly(A)+ mRNA following siRNA reduction of expression of the mammalian RNA helicases UAP56 and URH49. Gene 384, 37–44 (2006)
D. Nakata, S. Nakao, K. Nakayama, S. Araki, Y. Nakayama, S. Aparicio, T. Hara, A. Nakanishi, The RNA helicase DDX39B and its paralog DDX39A regulate androgen receptor splice variant AR-V7 generation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 483, 271–276 (2017)
T. Yamazaki, N. Fujiwara, H. Yukinaga, M. Ebisuya, T. Shiki, T. Kurihara, N. Kioka, T. Kambe, M. Nagao, E. Nishida, S. Masuda, The closely related RNA helicases, UAP56 and URH49, preferentially form distinct mRNA export machineries and coordinately regulate mitotic progression. Mol. Biol. Cell 21, 2953–2965 (2010)
C. Huang, D. Liang, D.C. Tatomer, J.E. Wilusz, A length-dependent evolutionarily conserved pathway controls nuclear export of circular RNAs. Genes Dev. 32, 639–644 (2018)
T. Zhang, Z. Ma, L. Liu, J. Sun, H. Tang, B. Zhang, Y. Zou, H. Li, DDX39 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis through activating Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Cell Death Dis. 9, 675 (2018)
J. Wang, R. Ling, Y. Zhou, X. Gao, Y. Yang, C. Mao, D. Chen, SREBP1 silencing inhibits the proliferation and motility of human esophageal squamous carcinoma cells via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 20, 2855–2869 (2020)
J.M. Llovet, J. Zucman-Rossi, E. Pikarsky, B. Sangro, M. Schwartz, M. Sherman, G. Gores, Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2, 16018 (2016)
T. Gangadhar, R.L. Schilsky, Molecular markers to individualize adjuvant therapy for colon cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 7, 318–325 (2010)
F. Andre, N. Ismaila, K.H. Allison, W.E. Barlow, D.E. Collyar, S. Damodaran, N.L. Henry, K. Jhaveri, K. Kalinsky, N.M. Kuderer, A. Litvak, E.L. Mayer, L. Pusztai, R. Raab, A.C. Wolff, V. Stearns, Biomarkers for adjuvant endocrine and chemotherapy in early-stage breast cancer: ASCO guideline update. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 40, 1816–1837 (2022)
A.M.M. Eggermont, C.U. Blank, M. Mandala, G.V. Long, V. Atkinson, S. Dalle, A. Haydon, M. Lichinitser, A. Khattak, M.S. Carlino, S. Sandhu, J. Larkin, S. Puig, P.A. Ascierto, P. Rutkowski, D. Schadendorf, R. Koornstra, L. Hernandez-Aya, M. Maio, A.J.M. van den Eertwegh, J.J. Grob, R. Gutzmer, R. Jamal, P. Lorigan, N. Ibrahim, S. Marreaud, A.C.J. van Akkooi, S. Suciu, C. Robert, Adjuvant Pembrolizumab versus Placebo in Resected Stage III Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 378, 1789–1801 (2018)
R. Pinyol, R. Montal, L. Bassaganyas, D. Sia, T. Takayama, G.Y. Chau, V. Mazzaferro, S. Roayaie, H.C. Lee, N. Kokudo, Z. Zhang, S. Torrecilla, A. Moeini, L. Rodriguez-Carunchio, E. Gane, C. Verslype, A.E. Croitoru, U. Cillo, M. de la Mata, L. Lupo, S. Strasser, J.W. Park, J. Camps, M. Sole, S.N. Thung, A. Villanueva, C. Pena, G. Meinhardt, J. Bruix, J.M. Llovet, Molecular predictors of prevention of recurrence in HCC with sorafenib as adjuvant treatment and prognostic factors in the phase 3 STORM trial. Gut 68, 1065–1075 (2019)
J.D. Schwartz, M. Schwartz, J. Mandeli, M. Sung, Neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy for resectable hepatocellular carcinoma: review of the randomised clinical trials. Lancet Oncol. 3, 593–603 (2002)
S. Schumann, B.R. Jackson, I. Yule, S.K. Whitehead, C. Revill, R. Foster, A. Whitehouse, Targeting the ATP-dependent formation of herpesvirus ribonucleoprotein particle assembly as an antiviral approach. Nat. Microbiol. 2, 16201 (2016)
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82072933, 82272892, and 82103525); 1·3·5 project for disciplines of excellence Clinical Research Incubation Project, West China Hospital, Sichuan University (2020HXFH007); and Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (2022YFS0216).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LP, LK and FTY conceived this work; LK and FTY designed the experiments. FTY, LSQ and ZG developed the methodology, performed in vitro and in vivo experiments and analyzed the data; LQ, YH, ZJ, GR and ODQ contributed to the in vivo experiments; GYF, KQM and WQJ prepared Table 1 and Table 2; FTY and LK wrote the manuscript; LK and LP revised the manuscript. LP supervised this work. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Informed consent was obtained from patients, and this study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Outdo Biotech Company. Animal studies were conducted with approval from the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of West China Hospital Sichuan University.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could inappropriately influence the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, T., Li, S., Zhao, G. et al. DDX39B facilitates the malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via activation of SREBP1-mediated de novo lipid synthesis. Cell Oncol. 46, 1235–1252 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-023-00807-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-023-00807-8