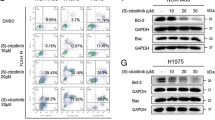
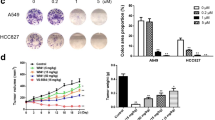
Abstract
Purpose
Paclitaxel is an anticancer drug for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, drug-resistance remains a major problem. Honokiol is a natural component which has been found to exhibit anti-tumor activity. Paclitaxel and honokiol have been reported to be able to induce paraptosis. The aim of this study was to investigate whether honokiol can reverse paclitaxel resistance by inducing paraptosis in NSCLC cells.
Methods
NSCLC cell lines H1650 (paclitaxel-sensitive), H1299 and H1650/PTX (intrinsic and acquired paclitaxel-resistant, respectively) were used to assess the cytotoxic effects of paclitaxel and honokiol. Light and transmission electron microscopy were performed to detect cytoplasmic vacuolation. In vitro cell viability and clonogenic survival assays, as well as in vivo xenograft assays were conducted to test synergistic killing effects of paclitaxel and honokiol on NSCLC cells. Western blotting, flow cytometry and immunofluorescence were performed to evaluate paraptosis-regulating mechanisms.
Results
We found that combination treatment with paclitaxel and honokiol synergistically killed H1650, H1299 and H1650/PTX cells by inducing paraptosis, which is characterized by cytoplasmic vacuolation. Moreover, paclitaxel/honokiol treatment resulted in a significant growth delay in H1299 xenograft tumors that showed extensive cytoplasmic vacuolation. Mechanistically, proteasomal inhibition-mediated endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and unfolded protein responses leading to ER dilation, and the disruption of intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis and mitochondrial Ca2+ overload resulting in mitochondrial disfunction, were found to be involved in paclitaxel/honokiol-induced paraptosis. Cellular protein light chain 3 (LC3) may play an important role in paclitaxel/honokiol induced cytoplasmic vacuolation and NSCLC cell death.
Conclusions
Combination of honokiol and paclitaxel may represent a novel strategy for the treatment of paclitaxel-resistant NSCLC.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.L. Siegel, K.D. Miller, A. Jemal, Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 65, 5–29 (2015)
N. Hanna, D. Johnson, S. Temin, S. Baker Jr., J. Brahmer, P.M. Ellis, G. Giaccone, P.J. Hesketh, I. Jaiyesimi, N.B. Leighl, G.J. Riely, J.H. Schiller, B.J. Schneider, T.J. Smith, J. Tashbar, W.A. Biermann, G. Masters, Systemic therapy for stage IV non–small-cell lung cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 35, 3484–3515 (2017)
M.A. Socinski, Update on taxanes in the first-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2, e691–e703 (2014)
L. Cortes-Dericks, D. Galetta, The therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in lung cancer: benefits, risks and challenges. Cell. Oncol. 42, 727–738 (2019)
A. Quintanal-Villalonga, S. Molina-Pinelo, Epigenetics of lung cancer: a translation perspective. Cell. Oncol. 42, 739–756 (2019)
J. Zhou, P. Giannakakou, Targeting microtubules for cancer chemotherapy. Curr. Med. Chem. Anti-Cancer Agents 5, 65–71 (2005)
J.J. Yeh, W.H. Hsu, J.J. Wang, S.T. Ho, A. Kao, Predicting chemotherapy response to paclitaxel-based therapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with p-glycoprotein expression. Respiration 70, 32–35 (2003)
G.M. Ajabnoor, T. Crook, H.M. Coley, Paclitaxel resistance is associated with switch from apoptotic to autophagic cell death in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cell. Death Dis. 3, e260 (2012)
X.F. Le, Bast, R.C. Jr., Src family kinases and paclitaxel sensitivity. Cancer Biol. Ther. 12, 260–269 (2011)
X. Peng, F. Gong, Y. Chen, Y. Jiang, J. Liu, M. Yu, S. Zjang, M. Wang, G. Xiao, H. Liao, Autophagy promotes paclitaxel resistance of cervical cancer cells: involvement of Warburg effect activated hypoxia-induced factor 1-α-mediated signaling. Cell Death Dis. 5, e1367 (2014)
G. Xi, X. Hu, B. Wu, H. Jiang, C.Y. Young, Y. Pang, H. Yuan, Autophagy inhibition promotes paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 307, 141–148 (2011)
A. Holleman, I. Chung, R.R. Olsen, B. Kwak, A. Mizokami, N. Saijo, A. Parissenti, Z. Duan, E.E. Voest, B.R. Zetter, miR-135a contributes to paclitaxel resistance in tumor cells both in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 30, 4386–4398 (2011)
L. Wang, H. Li, Y. Ren, S. Zou, W. Fang, X. Jiang, L. Jia, M. Li, X. Liu, X. Yuan, X. Yuan, G. Chen, J. Yang, C. Wu, Targeting HDAC with a novel inhibitor effectively reverses paclitaxel resistance in non-small cell lung cancer via multiple mechanisms. Cell Death Dis. 7, e20630 (2016)
L.E. Fried, J. Arbiser, Honokiol, a multifunctional antiangiogenic and antitumor agent. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 11, 1139–1148 (2009)
S. Arora, S. Singh, G.A. Piazza, C.M. Contreras, J. Panyam, Singh, Honokiol, a novel natural agent for cancer prevention and therapy. Curr. Mol. Med. 12, 1244–1252 (2012)
J. Pan, Y. Lee, Q. Zhang, D. Xiong, W.C. Tina, Y. Wang, M. Yon, Honokiol decreases lung cancer metastasis through inhibition of the STAT3 signaling pathway. Cancer Prev. Res. 10, 133–141 (2017)
R.J. Leeman-Neill, Q. Cai, S.C. Joyce, S.M. Thomas, N.E. Bhola, D.B. Neill, J.L. Arbiser, J.R. Grandis, Honokiol inhibits epidermal growth factor receptor signaling and enhances the antitumor effects of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 16, 2571–2579 (2010)
W. Tian, Y. Deng, L. Li, H. He, J. Sun, D. Xu, Honokiol synergizes chemotherapy drugs in multidrug resistant breast cancer cells via enhanced apoptosis and additional programmed necrotic death. Int. J. Oncol. 42, 721–732 (2013)
X. Wang, J.J. Beitler, H. Wang, M.J. Lee, W. Huang, L. Koenig, S. Nannapaneni, A.R. Amin, M. Bonner, H.J. Shin, Z.G. Chen, J.L. Arbiser, D.M. Shin, Honokiol enhances paclitaxel efficacy in multi-drug resistant human cancer model through the induction of apoptosis. PLoS One 9, e86369 (2014)
Y. Wang, X. Zhu, Z. Yang, X. Zhao, Honokiol induces caspase-independent paraptosis via reactive oxygen species production that is accompanied by apoptosis in leukemia cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 430, 876–882 (2013)
Y. Wang, Z. Yang, X. Zhao, Honokol induces paraptosis and apoptosis and exhibits schedule-dependent synergy in combination with imatinib in human leukemia cells. Toxicol. Mech. Meth. 20, 34–41 (2010)
T. Chen, X. Wang, L. Sun, L. Wang, D. Xiang, M. Mok, Taxol induces caspase-independent cytoplasmic vacuolization and cell death through endoplasmic reticulum (ER) swelling in ASTC-a-1 cells. Cancer Lett. 270, 164–172 (2008)
Q. Sun, T. Chen, X. Wang, X. Wei, Taxol induces paraptosis independent of both protein synthesis and MAPK pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 222, 421–432 (2010)
Y. Wang, Y. Zhou, Z. Zheng, J. Li, Y. Yan, W. Wu, Sulforaphane metabolites reduce resistance to paclitaxel via microtubule disruption. Cell Death Dis. 9, 1134 (2018)
C.-H. Dai, Y. Shu, P. Chen, J.-N. Wu, L.-H. Zhu, R.-X. Yuan, W.-G. Long, Y.-M. Zhu, J. Li, YM155 sensitizes non-small cell lung cancers to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors through the mechanism of autophagy induction. BBA-Mol. Basis Dis. 1864, 3786–3798 (2018)
P. Chen, H.-P. Huang, Y. Wang, J. Jin, W.-G. Long, K. Chen, X.H. Zhao, C.-G. Chen, J. Li, Curcumin overcome primary gefitinib resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer cells through inducing autophagy- related cell death. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 38, 254 (2019)
B.M. Ram, G. Ramakrishna, Endoplasmic reticulum vacuolation and unfolded protein response leading to paraptosis like cell death in cyclosporine A treated cancer cervix cells is mediated by cyclophilin B inhibition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1843, 2497–2512 (2014)
M.J. Yoon, E.H. Kin, J.H. Lin, T.K. Kwon, K.S. Choi, Superoxide anion and proteaomal dysfunction contribute to curcumin-induced paraptosis of malignant breast cancer cells. Free Raolical Biol. Med. 48, 713–726 (2010)
M. Hirabayashi, K. Inoue, K. Tanaka, K. Nakadate, Y. Ohsawa, Y. Kamei, A.H. Popiel, A. Sinohara, A. Iwamatsu, Y. Kimura, Y. Uchiyama, S. Hori, A. Kakizuka, VCP/p97 in abnormal protein aggregates, cytoplasmic vacuoles, and cell death, phenotypes relevant to neurodegeneration. Cell Death Differ. 8, 977–984 (2001)
R. Kar, P.K. Singha, M. Venkatachalan, P. Saikumar, A novel role for MAPI LC3 in nonautophagic cytoplasmic vacuolation death of cancer cells. Oncogene 28, 2556–2568 (2009)
P.K. Singha, S. Pandeswara, M.A. Venkatachalam, P. Saikumar, Manumycin A inhibits triple-negative breast cancer growth through LC3-mediated cytoplasmic vacuolation death. Cell Death Dis. 4, e457 (2013)
M. Yoo, E.H. Kim, T.K. Kwon, S.A. Park, K.S. Choi, Simultaneous mitochondrial Ca2+ overload and proteasomal inhibition are responsible for the induction of paraptosis in malignant breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 324, 197–209 (2012)
J. Xue, R. Li, X. Zhao, C. Ma, X. Lv, L. Li, P. Liu, Morusin induces paraptosis-like cell death through mitochondrial calcium overload and disfunction in epithelial ovarian cancer. Chem. Biol. Interact. 283, 59–74 (2018)
T.E. Gunter, S.S. Sheu, Characteristic and possible functions of mitochondrial Ca2+ transport mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1787, 1291–1308 (2009)
M.A. Matlib, Z. Zhou, S. Knight, S. Ahmed, K.M. Choi, J. Krause-Bauer, R. Phillips, R. Altschuld, Y. Katsube, N. Sperelakis, D.M. Bers, Oxygen-bridged dinuclear ruthenium amine complex specifically inhibits Ca uptake into mitochondria in vitro and in situ in single cardiac myocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 10223–10231 (1998)
S. Horwitz, Taxol (paclitaxel): Mechanisms of action. Ann. Oncol. 5, S3–S6 (1994)
H. Hua, W. Chen, L. Shen, Q. Sheng, L. Teng, Honokiol augments the anti-cancer effect of oxaliplatin in colon cancer cells. Acta Biochem. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai) 45, 773–779 (2013)
M.Y. Bonner, I. Karlsson, M. Rodolfo, R.S. Arnold, E. Vergani, J.L. Arbiser, Honokiol bis-dichloroacetate (Honokiol DCA) demonstrates activity in vemurafenib- resistant melanoma in vivo. Oncotarget 7, 12857–12868 (2016)
H. Zahredding, K.L. Borden, Mechanisms and insights into drug resistance in cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 4, 28 (2013)
S. Mansilla, L. Llovera, J. Portugal, Chemotherapeutic targeting of cell death pathways. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 12, 226–238 (2012)
S. Sperandio, I. de Belle, D.E. Bredesen, An alternative, nonapoptotic form of programmed cell death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97, 14376–14381 (2000)
W.B. Wang, L.X. Feng, Q.X. Yue, W.Y. Wu, S.H. Guan, B.H. Jiang, M. Yang, X. Liu, D.A. Guo, Paraptosis accompanied by autophagy and apoptosis was induced by celastrol, a natural compound with influence on proteasome, ER stress and Hep90. J. Cell. Physiol. 227, 2196–2206 (2012)
S. Sperandio, K. Poksay, I. Belle, M.J. Lafuente, B. Liu, J. Nasir, D.E. Bredesen, Paraptosis: mediation by MAP kinase and inhibition by AIP-1/Alix. Cell Death Differ. 11, 1066–1075 (2004)
E.G. Mimnaugh, W. Xu, M. Vos, X. Yuan, L. Neckers, Endoplasmic reticulum vacuolization and valosin-containing protein relocolization result from simultaneous Hsp90 inhibition by geldanamycin and proteasome inhibition by velcade. Mol.Cancer Res. 4, 667–681 (2006)
Y. Fu, J. Li, A.S. Lee, GRR78/Bip inhibits endoplasmic reticulum BIK and protects human breast cancer cells against estrogen starvation-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 67, 3734–3740 (2007)
N. Al-Furoukh, A. Ianni, H. Nolte, S. Hölper, M. Krüger, S. Wanrooij, T. Braun, CIpX stimulates the mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt) in mammalian cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1853, 2580–2591 (2015)
J. Moscat, M.T. Diaz-Meco, p62 at the crossroads of autophagy, apoptosis, and cancer. Cell 137, 1001–1004 (2009)
S. Pankiv, T.H. Clausen, T. Lamark, A. Brech, J.A. Bruun, H. Outzen, A. Øvervatn, G. Bjørkøy, T. Johansen, p62/SQSTM1 binds directly to Atg8/LC3 to facilitate degradation of ubiquitinated protein aggregates by autophagy. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 24131–24145 (2007)
V.I. Korolchuk, A. Mansilla, F.M. Menzies, D.C. Rubinsztein, Autophagy, inhibition compromises degradation of ubiquitin-proteasome pathway substrates. Mol. Cell 33, 517–527 (2009)
B. Zhivotovsky, S. Orrenius, Calcium and cell death mechanisms: a perspective from the cell death community. Cell Calcium 50, 211–221 (2011)
S. Orrenius, V. Gogvadze, B. Zhivotovsky, Calcium and mitochondria in the regulation of cell death. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 460, 72–81 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Institute of Medical Science of Jiangsu University for their technical assistance and instrument support.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the National Youth Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81402485).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All experimental procedures were conducted in accordance with the Chinese legislation regarding experimental animals and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Jiangsu University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 1.67 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, XQ., Ren, J., Wang, Y. et al. Synergistic killing effect of paclitaxel and honokiol in non-small cell lung cancer cells through paraptosis induction. Cell Oncol. 44, 135–150 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-020-00557-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-020-00557-x