Abstract
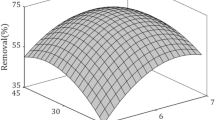
The potential use of sewage sludge as a precursor for the production of activated carbon was explored in this paper. After chemical activation with ZnCl2, three activated carbons were used to decontaminate synthetic solutions containing Bisphenol A and the results were compared with a commercial activated carbon. The effect of the impregnation ratio (activating agent/precursor) and the use of CO2 during the second carbonisation on the textural properties and Bisphenol A adsorption performance of the activated carbons were studied. The highest specific surface area achieved was 730 m2/g, obtained with an impregnation ratio of 2:1 with the use of CO2.The kinetics of Bisphenol A adsorption were successfully described by both pseudo-second-order and Elovich models, while the adsorption isotherms were well fitted to the Freundlich model. The prepared activated carbon had excellent adsorption efficiency toward Bisphenol A with a maximum adsorption of 285.8 mg/g which was closer to the retention amount of the commercial one. The best adsorption conditions for Bisphenol A removal were obtained by applying response surface methodology (RSM) coupled with Box-Behnken design (BBD) onto AC-Industrial2. Under these conditions, 657.76 mg/g can be reached. Thus, these optimum conditions were therefore applied for bisphenol A removal from real effluents and the obtained results are very promising.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of the current study are available within the article.
References
Bhadra, B.N.; Lee, J.K.; Cho, C.W.; Jhung, S.H.: Remarkably efficient adsorbent for the removal of bisphenol A from water: Bio-MOF-1-derived porous carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 343, 225–234 (2018)
Dong, S.; Rene, E.R.; Zhao, L.; Xiaoxiu, L.; Ma, M.: Design and preparation of functional azo linked polymers for the adsorptive removal of bisphenol A from water: performance and analysis of the mechanism. Environ. Res. 206, 112601 (2021)
Fenichel, P.; Chevalier, N.; Brucker-Davis, F.: Bisphenol A: an endocrine and metabolic disruptor. Ann. Endocrinol. 74(3), 211–220 (2013)
Geueke, B.: Dossier—bisphenol A food packaging forum (2014). https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.33495
Goldinger, D.M.; Demierre, A.-L.; Zoller, O.; Rupp, H.; Reinhard, H.; Magnin, R.; Becker, T.W.; Bourqui-Pittet, M.: Endocrine activity of alternatives to BPA found in thermal paper in Switzerland. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 71(3), 453–462 (2015)
Dodson, R.E.; Nishioka, M.; Standley, L.J.; Perovich, L.J.; Brody, J.G.; Rudel, R.A.: Endocrine disruptors and asthma-associated chemicals in consumer products. Environ. Health Perspect. 120(7), 935–943 (2012)
Manfo, F.P.T.; Jubendradass, R.; Nantia, E.A.; Moundipa, P.F.; Mathur, P.P.: Adverse effects of bisphenol A on male reproductive function. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 228, 57–82 (2013)
Karnam, S.; Ghosh, R.; Mondal, S.; Mondal, M.: Evaluation of subacute bisphenol-A toxicity on male reproductive system. Vet. World 8(6), 738–744 (2015)
Gonsioroski, A.; Mourikes, V.E.; Flaws, J.A.: Endocrine disruptors in water and their effects on the reproductive system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21(6), 1929–1995 (2020)
Wang, N.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, C.; Wang, H.; Huang, P.; Wang, B.; Su, M.; Jiang, F.; Fang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Q.: Influence of bisphenol A on thyroid volume and structure independent of iodine in school children. PLoS ONE 10(10), e0141248 (2015)
Steinmetz, R.; Brown, N.G.; Allen, D.L.; Bigsby, R.M.; Ben-Jonathan, N.: The environmental estrogen bisphenol A stimulates prolactin release in vitro and in vivo. Endocrinology 138(5), 1780–1786 (1997)
Han, C.; Hong, Y.-C.: Bisphenol A, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases: epidemiological, laboratory, and clinical trial evidence. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 18(2), 11–16 (2016)
Dehghani, M.H.; Ghadermazi, M.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sadighara, P.; Jahed-Khaniki, G.; Heibati, B.; McKay, G.: Adsorptive removal of endocrine disrupting bisphenol A from aqueous solution using chitosan. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 4(3), 2647–2655 (2016)
Di Donato, M.; Cernera, G.; Giovannelli, P.; Galasso, G.; Bilancio, A.; Migliaccio, A.; Castoria, G.: Recent advances on bisphenol-A and endocrine disruptor effects on human prostate cancer. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 457, 35–42 (2017)
Guo, W.; Hu, W.; Pan, J.; Zhou, H.; Guan, W.; Wang, X.; Dai, J.; Xu, L.: Selective adsorption and separation of BPA from aqueous solution using novel molecularly imprinted polymers based on kaolinite/Fe3O4 composites. Chem. Eng. J. 171(2), 603–611 (2011)
Bhatnagar, A.; Anastopoulos, I.: Adsorptive removal of bisphenol A (BPA) from aqueous solution: a review. Chemosphere 168, 885–902 (2017)
Akhtar, J.; Amin, N.A.S.; Shahzad, K.: A review on removal of pharmaceuticals from water by adsorption. Desalin. Water. Treat. 57(27), 12842–12860 (2015)
Umar, M.; Roddick, F.; Fan, L.; Aziz, H.A.: Application of ozone for the removal of bisphenol A from water and wastewater: a review. Chemosphere 90(8), 2197–2207 (2013)
Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Xu, J.: Progress in the biological and chemical treatment technologies for emerging contaminant removal from wastewater: a critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 323, 274–298 (2017)
Zhang, Y.; Causserand, C.; Aimar, P.; Cravedi, J.P.: Removal of bisphenol A by a nanofiltration membrane in view of drinking water production. Water Res. 40(20), 3793–3799 (2006)
Bensouilah, R.; Hammedi, T.; Ouakouak, A.; Ghorbel, A.; Ksibi, Z.: Comparative study of the efficiency of different noble metals supported on zirconium oxide in the catalytic wet air oxidation of bisphenol-A solution. Chem. Phys. Lett. 761, 138022 (2020)
Rastegari, M.; Saeedi, M.; Mollahosseini, A.; Ayatynia, M.: Phenan-threne sorption onto kaolinite; heavy metals and organic matter effects. Int. J. Environ. Res. 10(3), 441–448 (2016)
Prete, M.C.; Tarley, C.R.T.: Bisphenol A adsorption in aqueous medium by investigating organic and inorganic components of hybrid polymer (Polyvinylpyridine/SiO2/APTMS). Chem. Eng. J. 367, 102–114 (2019)
Wang, Y.; Pan, C.; Chu, W.; Vipin, A.; Sun, L.: Environmental remediation applications of carbon nanotubes and graphene oxide: adsorption and catalysis. Nanomaterials 9(3), 439–464 (2019)
Marsh, H.; Heintz, E.A.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.: Introduction to Carbon Technologies; University of Alicante: Alicante, Spain, 669 (Eds.) (1997)
Bansal, R.C.; Donnet. J.-B.; Stoeckli. F.: Active Carbon; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA (1988)
Supong, A.; Bhomick, P.C.; Baruah, M.; Pongener, C.; Sinha, U.B.; Sinha, D.: Adsorptive removal of Bisphenol A by biomass activated carbon and insights into the adsorption mechanism through density functional theory calculations. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 13, 100159–100172 (2019)
Hadi, P.; Xu, M.; Ning, C.; Lin, C.S.K.; McKay, G.: A critical review on preparation, characterization and utilization of sludge-derived activated carbons for wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 260, 895–906 (2015)
Raheem, A.; Sikarwar, V.S.; He, J.; Dastyar, W.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Wang, W.; Zhao, M.: Opportunities and challenges in sustainable treatment and resource reuse of sewage sludge: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 337, 616–641 (2018)
Mu’azu, N.; Jarrah, N.; Zubair, M.; Alagha, O.: Removal of phenolic compounds from water using sewage sludge-based activated carbon adsorption: a review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 14(10), 1094–1128 (2017)
Im, U.-S.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.H.; mi Lee, S.; Lee, B.-R.; Peck, D.-H.; Jung, D.-H.: Preparation of activated carbon from needle coke via two-stage steam activation process. Mater. Lett. 237, 22–25 (2018)
Guo, S.; Peng, J.; Li, W.; Yang, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Xia, H.: Effects of CO2 activation on porous structures of coconut shell-based activated carbons. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255(20), 8443–8449 (2009)
Brito, M.J.P.; Veloso, C.M.; Bonomo, R.C.F.; Fontan, R.D.C.I.; Santos, L.S.; Monteiro, K.A.: Activated carbons preparation from yellow mombin fruit stones for lipase immobilization. Fuel Process. Technol. 156, 421–428 (2017)
Hock, P.E.; Zaini, M.A.A.: Activated carbons by zinc chloride activation for dye removal: a commentary. Acta. Chim. Slov. 11(2), 99–106 (2018)
Sanz-Santos, E.; Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; Ceballos, L.; Larriba, M.; Águeda, V.I.; García, J.: Application of sludge-based activated carbons for the effective adsorption of neonicotinoid pesticides. Appl. Sci. 11(7), 3087–3102 (2021)
Kumar, A.; Jena, H.M.: Preparation and characterization of high surface area activated carbon from Fox nut (Euryale ferox) shell by chemical activation with H3PO4. Results Phys. 6, 651–658 (2016)
Smisek, M.; Cerny, S.: Active Carbon: Manufacture, Properties and Applications. Elsevier, New York (1970)
Box, G.E.P.; Hunter, W.G.; Hunter, J.S.: Statistics for Experimenters. Wiley, New York (1978)
Montgomery, D.C.: Design and Analysis of Experiments, 3rd edn., p. 270. Wiley, New York (1991)
Box, G.E.P.; Wilson, K.B.: On the experimental attainment of optimum conditions. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 13(1), 1–38 (1951)
Box, G.E.P.; Behnken, D.W.: Some new three level designs for the study of quantitative variables. Technometrics 2(4), 455–475 (1960)
Montgomery, D.C.: Design and Analysis of Experiments. Wiley, Singapore (2001)
Montgomery, D.C.: Design and Analysis of Experiments, 4th edn. Wiley, New York (1997)
Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W.: Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure. Appl. Chem. 87(9–10), 1051–1069 (2015)
Chen, R.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Lu, M.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Ma, W.; Wang, S.: Preparation and characterization of activated carbons from tobacco stem by chemical activation. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 67(6), 713–724 (2017)
Mohanty, K.; Das, D.; Biswas, M.N.: Preparation and characterization of activated carbons from Sterculia alata nutshell by chemical activation with zinc chloride to remove phenol from wastewater. Adsorption 12(2), 119–132 (2006)
Rojas-Morales, J.L.; Gutiérrez-González, E.C.; de Jesús Colina-Andrade, G.: Obtaining and characterization of activated carbon obtained sludge treatment plant wastewater from a poultry industry. Ing. Investig. Tecnol. 17(4), 453–462 (2016) (ISSN 2594-0732)
Liou, T.-H.: Development of mesoporous structure and high adsorption capacity of biomass-based activated carbon by phosphoric acid and zinc chloride activation. Chem. Eng. J. 158(2), 129–142 (2010)
Streit, A.F.M.; Côrtes, L.N.; Druzian, S.P.; Godinho, M.; Collazzo, G.C.; Perondi, D.; Dotto, G.L.: Development of high quality activated carbon from biological sludge and its application for dyes removal from aqueous solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 660, 277–287 (2019)
Wu, C.; Li, L.; Zhou, H.; Ai, J.; Zhang, H.; Tao, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W.: Effects of chemical modification on physicochemical properties and adsorption behavior of sludge-based activated carbon. J. Enviro. Sci. 100, 340–352 (2021)
Zhang, J.; Shao, J.; Jin, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H.: Sludge-based biochar activation to enhance Pb(II) adsorption. Fuel 252, 101–108 (2019)
Khoshbouy, R.; Takahashi, F.; Yoshikawa, K.: Preparation of high surface area sludge-based activated hydrochar via hydrothermal carbonization and application in the removal of basic dye. Environ. Res. 175, 457–467 (2019)
Giles, C.H.; MacEwan, T.H.; Nakhwa, S.N.; Smith, D.: Studies in adsorption. Part XI. A system of classification of solution adsorption isotherms, and its use in diagnosis of adsorption mechanisms and in measurement of specific surface areas of solids. J. Chem. Soc. 846, 3973–3993 (1960)
Acosta, R.; Nabarlatz, D.; Sánchez-Sánchez, A.; Jagiello, J.; Gadonneix, P.; Celzard, A.; Fierro, V.: Adsorption of bisphenol A on KOH-activated tyre pyrolysis char. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 6(1), 823–833 (2018)
Fazeli Zafar, F.; Barati, B.; Rasoulzadeh, H.; Sheikhmohammadi, A.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.: Adsorption kinetics analysis and optimization of Bisphenol A onto magnetic activated carbon with shrimp shell based precursor. Biomass Bioenergy 166, 106604 (2022)
Gómez-Serrano, V.; Adame-Pereira, M.; Alexandre-Franco, M.; Fernández-González, C.: Adsorption of bisphenol A by activated carbon developed from PET waste by KOH activation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28, 24342–24354 (2020)
Zbair, M.; Ainassaari, K.; Drif, A.; Ojala, S.; Bottlinger, M.; Pirilä, M.; Keiski, L.R.; Bensitel, M.; Brahmi, R.: Toward new benchmark adsorbents: preparation and characterization of activated carbon from argan nut shell for bisphenol A removal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 25(2), 1869–1882 (2017)
Hacıosmanoğlu, G.G.; Doğruel, T.; Gençc, S.; Oner, E.T.; Can, Z.S.: Adsorptive removal of bisphenol A from aqueous solutions using phosphonated levan. J. Hazard. Mater. 374, 43–49 (2019)
Mohammadi, A.A.; Dehghani, M.H.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Yaghmaian, K.; Es’haghi, Z.: Adsorptive removal of endocrine disrupting compounds from aqueous solutions using magnetic multi-wall carbon nanotubes modified with chitosan biopolymer based on response surface methodology: functionalization, kinetics, and isotherms studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 155(15), 1019–1029 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Comunidad de Madrid through the Industrial PhD Projects (under Grant Numbers IND2017/AMB-7720 and IND2019/AMB-17114) and REMTAVARES-CM Network (under Grant Number S2018/EMT-4341) and The European Social Fund. Also, the authors thank the project PID 2020-116478RB-I00 supported by MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 and gratefully acknowledge the financial support furnished by the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MO helped in writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, conceptualization, validation, investigation, methodology, formal analysis and software. ES-S was involved in writing—review and editing, conceptualization, investigation, formal analysis and software. FF, SÁ-T and MKY contributed to writing—review and editing, conceptualization, methodology and supervision. BH performed writing—review and editing, conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis and software. ML helped in writing—review and editing. JG was involved in resources, project administration, funding acquisition and validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to report.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ounis, M., Sanz-Santos, E., Fakhfakh, F. et al. Optimisation of Adsorption Removal of Bisphenol A Using Sludge-Based Activated Carbons: Application of Response Surface Methodology with a Box–Behnken Design. Arab J Sci Eng 49, 497–514 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08203-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08203-y