Abstract
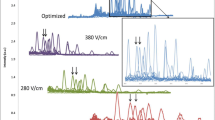
Electrospray (ESI) ionization efficiencies (IE) of a set of 10 compounds differing by chemical nature, extent of ionization in solution (basicity), and by hydrophobicity (tetrapropylammonium and tetraethylammonium ion, triethylamine, 1-naphthylamine, N,N-dimethylaniline, diphenylphthalate, dimethylphtahalate, piperidine, pyrrolidine, pyridine) have been measured in seven mobile phases (three acetonitrile percentages 20%, 50%, and 80%, and three different pH-adjusting additives, 0.1% formic acid, 1 mM ammonia, pH 5.0 buffer combination) using the relative measurement method. MS parameters were optimized separately for each ion. The resulting relative IE data were converted into comparable logIE values by anchoring them to the logIE of tetrapropylammonium ion taking into account the differences of ionization in different solvents and thereby making the logIE values of the compounds comparable across solvents. The following conclusions were made from analysis of the data. The compounds with pK a values in the range of the solution pH values displayed higher IE at lower pH. The sensitivity of IE towards pH depends on hydrophobicity being very strong with pyridine, weaker with N,N-dimethylaniline, and weakest with 1-naphthylamine. IEs of tetraalkylammonium ions and triethylamine were expectedly insensitive towards solution pH. Surprisingly high IEs of phthalate esters were observed. The differences in solutions with different acetonitrile content and similar pH were smaller compared with the pH effects. These results highlight the importance of hydrophobicity in electrospray and demonstrate that high hydrophobicity can sometimes successfully compensate for low basicity.

ᅟ


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cech, N.B., Enke, C.G.: Practical implications of some recent studies in electrospray ionization fundamentals. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 20, 362–387 (2001)
Kebarle, P., Tang, L.: From ions in solution to ions in the gas phase. Anal. Chem. 65, 972–986 (1993)
Chalcraft, K.R., Lee, R., Mills, C., Britz-McKibbin, P.: Virtual quantification of metabolites by capillary electrophoresis-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry: predicting ionization efficiency without chemical standards. Anal. Chem. 81, 2506–2515 (2009)
Ehrmann, B., Henriksen, T., Cech, N.B.: Relative importance of basicity in the gas phase and in solution for determining selectivity in electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 19, 719–728 (2008)
Konermann, L., Ahadi, E., Rodriguez, A.D., Vahidi, S.: Unraveling the mechanism of electrospray ionization. Anal. Chem. 85, 2–9 (2013)
Tang, L., Kebarle, P.: Dependence of ion intensity in electrospray mass spectrometry on the concentration of the analytes in the electrosprayed solution. Anal. Chem. 65, 3654–3668 (1993)
Constantopoulus, T.L., Jackson, G.S., Enke, C.G.: Effects of salt concentration on analyte response using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 10, 625–634 (1999)
Kruve, A., Kaupmees, K., Liigand, J., Oss, M., Leito, I.: Sodium adduct formation efficiency in ESI source. J. Mass Spectrom. 48, 695–702 (2013)
Yang, X.Y., Qu, Y., Yuan, Q., Wan, P., Du, Z., Chen, D., Wong, C.: Effect of ammonium on liquid- and gas-phase protonation and deprotonation in electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Analyst 138, 659–665 (2012)
van Berkel, G.J., McLuckey, S.A., Glish, G.L.: Electrochemical origin of radical cations observed in electrospray ionization mass spectra. Anal. Chem. 64, 1586–1593 (1992)
Dole, M., Mack, L.L., Hines, R.L., Mobley, R.C., Ferguson, L.D., Alice, M.B.: Molecular beams of macroions. J. Chem. Phys. 49, 2240–2249 (1968)
Iribarne, J., Thomson, B.: On the evaporation of small ions from charged droplets. J. Chem. Phys. 64, 2287–2294 (1976)
Kebarle, P., Peschke, M.: On the mechanisms by which the charged droplets produced by electrospray lead to gas phase ions. Anal. Chim. Acta. 406, 11–35 (2000)
Leito, I., Herodes, K., Huopolainen, M., Virro, K., Künnapas, A., Kruve, A., Tanner, R.: Towards the electrospray ionization mass spectrometry ionization efficiency scale of organic compounds. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 22, 379–384 (2008)
Cech, N.B., Krone, J.P., Enke, C.G.: Predicting electrospray response from chromatographic retention time. Anal. Chem. 73, 208–213 (2001)
Cech, N.B., Enke, C.G.: Relating electrospray ionization response to nonpolar character of small peptides. Anal. Chem. 72, 2717–2723 (2000)
Oss, M., Kruve, A., Herodes, K., Leito, I.: Electrospray ionization efficiency scale of organic compounds. Anal. Chem. 82, 2865–2872 (2010)
Huffman, B.A., Poltash, M.L., Hughey, C.A.: Effect of polar protic and polar aprotic solvents on negative-ion electrospray ionization and chromatographic separation of small acidic molecules. Anal. Chem. 84, 9942–950 (2012)
Amad, M.H., Cech, N.B., Jackson, G.S., Enke, C.G.: Importance of gas-phase proton affinities in determining the electrospray ionization response for analytes and solvents. J. Mass Spectrom. 35, 784–789 (2000)
Henriksen, T., Juhler, R.K., Svensmark, B., Cech, N.B.: The relative influences of acidity and polarity on responsiveness of small organic molecules to analysis with negative ion electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS). J. Am. Mass Spectrom. 16, 446–455 (2005)
Nguyen, T.B., Nizkorodov, S.A., Laskin, A., Laskin, J.: An approach toward quantification of organic compounds in complex environmental samples using high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 5, 72–80 (2013)
Zhou, S., Hamburger, M.: Effects of solvent composition on molecular ion response in electrospray mass spectrometry: investigation of the ionization prozess. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 9, 1516–1521 (1995)
Girod, M., Dagancy, X., Antoine, R., Dugourd, P.: Relation between charge state distributions of peptide anions and pH changes in the electrospray plume. A mass spectrometry and optical spectroscopy investigations. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 308, 41–48 (2011)
Girod, M., Dagancy, X., Boutou, V., Broyer, M., Antoine, R., Dugourd, P., Mordehai, A., Love, C., Werlich, M., Fjeldsted, J., Stafford, G.: Profiling an electrospray plume by laser-induced fluorescence and Fraunhofer diffraction combined to mass spectrometry: influence of size and composition of droplets on charge-state distributions of electrosprayed proteins. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14, 9389–9396 (2012)
Ahadi, E., Konermann, L.: Ejection of solvated ions from electrosprayed methanol/water nanodroplets studied by molecular dynamics simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 9354–9363 (2011)
Kaljurand, I., Kütt, A., Sooväli, L., Rodima, T., Mäemets, V., Leito, I., Koppel, I.: Extension of the self-consistent spectrophotometric basicity scale in acetonitrile to a full span of a 28 pK(a) units: Unification of different basicity scales. J. Org. Chem. 70, 1019–1028 (2005)
Sooväli, L., Kaljurand, I., Kütt, A., Leito, I.: Uncertainity estimation in measurement of pK(a) values in nonaqueous media: a case study on basicity scale in acetonitrile medium. Anal. Chim. Acta. 566, 290–303 (2006)
Greenspan, P., Fowler, S.: Spectrofluorometric studies of the lipid probe, nile red. J. Lipid Res. 26, 781–789 (1985)
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by PUT 34 from Estonian Research Council as well as the institutional funding IUT20-14 (TLOKT14014I) from the Ministry of Education and Research of Estonia, and carried out in part at the High Performance Computing Center of the University of Tartu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 464 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liigand, J., Kruve, A., Leito, I. et al. Effect of Mobile Phase on Electrospray Ionization Efficiency. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 25, 1853–1861 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-014-0969-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-014-0969-x