Abstract
Background
Carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning affects several vital organs; however, the long-term damage to lungs has not been well investigated.
Objective
This study investigated the morphological changes and the associated molecules 6 weeks after CO poisoning in rat models. Rats in the CO poisoning group were exposed to 1500 ppm CO in a gas chamber for 3 h. After 6 weeks, the rats in the control and CO poisoning groups were sacrificed. Pathological changes were assessed using hematoxylin and eosin staining. Western blotting and antibody arrays for inflammatory signaling molecules were performed using lung homogenates. Complete blood counts and Krebs Von Den Lungen (KL)-6 levels were compared among rats in the control group and those immediately and 6 weeks after CO poisoning using blood sampling from an indwelling catheter.
Results
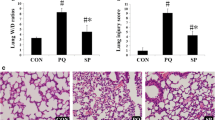
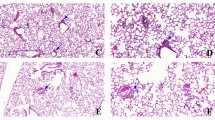
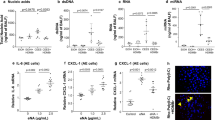
CO-poisoned lungs showed emphysematous changes with increased mean linear intercept (p = 0.0007). SERPINA1, IL-13, CD44, and GDF7 levels were significantly decreased, whereas TGFβ, ɑ-SMA, MMP9, and NF-κB levels were significantly increased in the CO-poisoned lungs. KL-6 serum levels were significantly higher in the CO-poisoned rats (p < 0.0001).
Conclusion
This is the first study to demonstrate the long-term effects and emphysematous changes in CO-poisoned lung models. We recommend long-term monitoring following CO poisoning.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within this article.
References
Agustí A, Hogg JC (2019) Update on the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med 381:1248–1256. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1900475
Aloisio E, Braga F, Puricelli C, Panteghini M (2021) Prognostic role of Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6) measurement in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Chem Lab Med 59:1400–1408. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2021-0199
Althaus M et al (2009) Carbon monoxide rapidly impairs alveolar fluid clearance by inhibiting epithelial sodium channels. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 41:639–650. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2008-0458OC
Bathoorn E et al (2007) Anti-inflammatory effects of inhaled carbon monoxide in patients with COPD: a pilot study. Eur Respir J 30:1131–1137. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00163206
Bhatt SP et al (2017) Computed tomography measure of lung at risk and lung function decline in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 196:569–576. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201701-0050OC
Bodduluri S et al (2017) Biomechanical CT metrics are associated with patient outcomes in COPD. Thorax 72:409–414. https://doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2016-209544
Boutten A et al (2004) Decreased expression of interleukin 13 in human lung emphysema. Thorax 59:850–854. https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.2004.025247
Briassoulis G et al (2006) Circulating levels of KL-6 in acute respiratory distress syndrome sepsis or traumatic brain injury in critically ill children. Pediatr Pulmonol 41:790–795. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppul.20465
Demirdöğen E et al (2022) Serum Krebs von den Lungen-6: promising biomarker to differentiate CPFE from IPF. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 39:e2022035. https://doi.org/10.36141/svdld.v39i4.11344
Dong P et al (2022) Growth differentiation factor 7 prevents sepsis-induced acute lung injury in mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2022:3676444. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3676444
Fein A et al (1980) Carbon monoxide effect on alveolar epithelial permeability. Chest 78:726–731. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.78.5.726
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (2021) Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease 2022 report. https://goldcopd.org/archived-reports/
Hampson NB, Piantadosi CA, Thom SR, Weaver LK (2012) Practice recommendations in the diagnosis, management, and prevention of carbon monoxide poisoning. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 186:1095–1101. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201207-1284CI
Henry CR et al (2006) Myocardial injury and long-term mortality following moderate to severe carbon monoxide poisoning. JAMA 295:398–402. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.295.4.398
Hodge S et al (2007) Smoking alters alveolar macrophage recognition and phagocytic ability: implications in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 37:748–755. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2007-0025OC
Hoetzel A et al (2007) Carbon monoxide in sepsis. Antioxid Redox Signal 9:2013–2026. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2007.1762
Hoetzel A et al (2009) Carbon monoxide prevents ventilator-induced lung injury via caveolin-1. Crit Care Med 37:1708–1715. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e31819efa31
Holm Nielsen S et al (2019) Serological assessment of activated fibroblasts by alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA): a noninvasive biomarker of activated fibroblasts in lung disorders. Transl Oncol 12:368–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2018.11.004
Huang CC et al (2022) Association between carbon monoxide poisoning and adrenal insufficiency: a nationwide cohort study. Sci Rep 12:16219. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-20584-y
Kim YJ et al (2018) Analysis of the development and progression of carbon monoxide poisoning-related acute kidney injury according to the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) criteria. Clin Toxicol (phila) 56:759–764. https://doi.org/10.1080/15563650.2018.1424890
Kohno N et al (1989) New serum indicator of interstitial pneumonitis activity. sialylated carbohydrate antigen KL-6. Chest 96:68–73. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.96.1.68
Kohno N et al (1993) KL-6, a mucin-like glycoprotein, in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with interstitial lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis 148:637–642. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm/148.3.637
Kokuho N et al (2015) Diagnostic values for club cell secretory protein (CC16) in serum of patients of combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. COPD 12:347–354. https://doi.org/10.3109/15412555.2014.948994
Kwak K et al (2021) Association between carbon monoxide intoxication and incidence of ischemic stroke: a retrospective nested case-control study in South Korea. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 30:105496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.105496
Lederer DJ et al (2009) Circulating KL-6, a biomarker of lung injury, in obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur Respir J 33:793–796. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00150708
Lee CG et al (2001) Interleukin-13 induces tissue fibrosis by selectively stimulating and activating transforming growth factor beta(1). J Exp Med 194:809–821. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.194.6.809
Lippi G et al (2012) Pathophysiology, clinics, diagnosis and treatment of heart involvement in carbon monoxide poisoning. Clin Biochem 45:1278–1285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2012.06.004
Lungarella G, Cavarra E, Lucattelli M, Martorana PA (2008) The dual role of neutrophil elastase in lung destruction and repair. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40:1287–1296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2007.12.008
Martinez FJ et al (2022) Treatment trials in young patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and pre–chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients: time to move forward. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 205:275–287. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.202107-1663SO
McKenzie AN et al (1993) Interleukin 13, a T-cell-derived cytokine that regulates human monocyte and B-cell function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:3735–3739. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.90.8.3735
Morris DG et al (2003) Loss of integrin alpha(v)beta6-mediated TGF-beta activation causes Mmp12-dependent emphysema. Nature 422:169–173. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01413
Park YJ et al (2019) Effects of β-Sitosterol from corn silk on TGF-β1-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition in lung alveolar epithelial cells. J Agric Food Chem 67:9789–9795. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b02730
Rose JJ et al (2017) Carbon monoxide poisoning: pathogenesis, management, and future directions of therapy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 195:596–606. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201606-1275CI
Ryter SW, Choi AM (2006) Therapeutic applications of carbon monoxide in lung disease. Curr Opin Pharmacol 6:257–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2006.03.002
Sakai M, Kubota T, Ohnishi H, Yokoyama A (2013) A novel lung injury animal model using KL-6-measurable human MUC1-expressing mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 432:460–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.01.123
Sato H et al (2004) KL-6 levels are elevated in plasma from patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Eur Respir J 23:142–145. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.03.00070303
Schuliga M (2015) NF-kappaB signaling in chronic inflammatory airway disease. Biomolecules 5:1266–1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5031266
Stockley RA, Halpin DMG, Celli BR, Singh D (2019) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease biomarkers and their interpretation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 199:1195–1204. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201810-1860SO
Strnad P, McElvaney NG, Lomas DA (2020) Alpha(1)-antitrypsin deficiency. N Engl J Med 382:1443–1455. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1910234
Teder P et al (2002) Resolution of lung inflammation by CD44. Science (1979) 296:155–158. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1069659
Thom SR et al (2004) Delayed neuropathology after carbon monoxide poisoning is immune-mediated. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:13660–13665. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0405642101
Warburton D, Shi W, Xu B (2013) TGF-β-Smad3 signaling in emphysema and pulmonary fibrosis: an epigenetic aberration of normal development? Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 304:L83-85. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00258.2012
Wei KY et al (2021) Carbon monoxide poisoning and chronic kidney disease risk: a nationwide, population-based study. Am J Nephrol 52:292–303. https://doi.org/10.1159/000515383
Wewers M (1989) Pathogenesis of emphysema: assessment of basic science concepts through clinical investigation. Chest 95:190–195. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.95.1.190
Wilson MR et al (2010) Efficacy and safety of inhaled carbon monoxide during pulmonary inflammation in mice. PLoS ONE 5:e11565. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0011565
Wohnhaas CT et al (2021) Cigarette smoke specifically affects small airway epithelial cell populations and triggers the expansion of inflammatory and squamous differentiation associated basal cells. Int J Mol Sci 22:7646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147646
Xu L, Bian W, Gu XH, Shen C (2017) Differing expression of cytokines and tumor markers in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema compared to emphysema and pulmonary fibrosis. COPD 14:245–250. https://doi.org/10.1080/15412555.2017.1278753
Yu N et al (2018) Treatment with eucalyptol mitigates cigarette smoke-induced lung injury through suppressing ICAM-1 gene expression. Biosci Rep 38:20171636. https://doi.org/10.1042/bsr20171636
Zheng T et al (2000) Inducible targeting of IL-13 to the adult lung causes matrix metalloproteinase- and cathepsin-dependent emphysema. J Clin Invest 106:1081–1093. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci10458
Acknowledgement
We thank Prof. Hyun Kim and Prof. Sang-Ha Kim for supporting this study.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, which is funded by the Korean government (Ministry of Science and Information and Communications Technology, grant no. NRF-2021R1A2C200492211).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SJL, JYL, and WYL: contributed to conceptualization; JYL: was responsible for methodology, software, and formal analysis; JYL and MK: were responsible for validation, resources, and data curation; SJL, TK, MK, and JYL: did investigation; SJL and JYL: were involved in visualization and writing—original draft preparation; TK, YSC, MK, and WYL: contributed to writing—review and editing; WYL: was involved in supervision and project administration; YSC: performed funding acquisition. All the authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
Seok Jeong Lee declares that she has no conflict of interest. Taeyeong Kim declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yong Sung Cha declares that he has no conflict of interest. Min Kim declares that she has no conflict of interest. Ji Yong Lee declares that she has no conflict of interest. Won-Yeon Lee declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine (YWC-210308-1, 7-Apr-2022) and conducted according to the National Institutes of Health Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.J., Kim, T., Cha, Y.S. et al. Alveolar damage and development of emphysema in rats with carbon monoxide poisoning. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-023-00405-7
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-023-00405-7