Abstract
Background
Myricetin, a flavonoid, has anti-inflammation effects and can improve pancreatic β cells dysfunction. However, the role of myricetin in severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) and the precise mechanism remain unclear.
Objectives
This study aimed to investigate how myricetin affects pancreatic damage induced by SAP.
Results
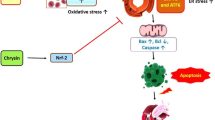
Myricetin substantially reduced the expression of lipase and amylase, and ameliorated pancreatic damage induced by SAP. Moreover, myricetin inhibited the release of several inflammatory relevant cytokines including tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and IL-10, alleviated apoptosis of pancreatic alveolar cells, and ameliorated microcirculatory dysfunction in SAP rats. Furthermore, myricetin inhibited the acetylation of forkhead box protein O1(FOXO1) and the phosphorylation of NF-kB.
Conclusion
Myricetin improves SAP-induced pancreatic injury through suppressing microcirculation dysfunction, overactive inflammatory response, and cell apoptosis. In addition, myricetin deregulates acetylated FOXO1 and phosphorylated nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB), which may be the potential mechanism for SAP alleviation.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article. The datasets used and/or analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Fan Z, Tang D, Wu Q, Huang Q, Song J (2022) Long Q (2022) Scopoletin inhibits PDGF-BB-induced proliferation and migration of airway smooth muscle cells by regulating NF-κB signaling pathway. Allergol Immunopathol 50(1):92–988
Ji S, Zhan Q (2022) Momordica charantia polysaccharides alleviate diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome by regulating intestinal inflammation and barrier via NF-κB pathway. Allergol Immunopathol 50(3):62–70
Jung HY et al (2017) Myricetin improves endurance capacity and mitochondrial density by activating SIRT1 and PGC-1alpha. Sci Rep 7:6237
Karunakaran U et al (2019) Myricetin prevents thapsigargin-induced CDK5-P66Shc signalosome mediated pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction. Free Radic Biol Med 141:59–66
Kinnala PJ et al (2001) Pancreatic tissue perfusion in experimental acute pancreatitis. Eur J Surg 167:689–694
Lv C et al (2020) CTRP3 ameliorates cerulein-induced severe acute pancreatitis in mice via SIRT1/NF-kappaB/p53 axis. Biosci Rep 40:BSR20200092
Matsumoto M et al (2020) Efficacy of recombinant human-soluble thrombomodulin for severe acute pancreatitis in a rat experimental model. Pancreas 49:503–508
Rong Y et al (2021) Resveratrol suppresses severe acute pancreatitis-induced microcirculation disturbance through targeting SIRT1-FOXO1 axis. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:8891544
Shi C et al (2018) SRT1720 ameliorates sodium taurocholate-induced severe acute pancreatitis in rats by suppressing NF-kappaB signalling. Biomed Pharmacother 108:50–57
Song X et al (2021) Myricetin: a review of the most recent research. Biomed Pharmacother 134:111017
Sun Y et al (2018) Role of p-MKK7 in myricetin-induced protection against intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Pharmacol Res 129:432–442
Sun WL et al (2021) Myricetin supplementation decreases hepatic lipid synthesis and inflammation by modulating gut microbiota. Cell Rep 36:109641
Wang N et al (2017) Resveratrol protects against L-arginine-induced acute necrotizing pancreatitis in mice by enhancing SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of p53 and heat shock factor 1. Int J Mol Med 40:427–437
Wang J et al (2021) Protective effect of Dachengqi decoction on the pancreatic microcirculatory system in severe acute pancreatitis by down-regulating HMGB-TLR-4-IL-23-IL-17A mediated neutrophil activation by targeting SIRT1. Gland Surg 10:3030–3044
Wang T et al (2022) Antioxidative myricetin-enriched nanoparticles towards acute liver injury. J Mater Chem B 10:7875–7883
Wang S, Liu B, Liu J, Gu Y (2022) TRIM27 suppresses inflammation injuries in pediatric pneumonia by targeting TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Allergol Immunopathol 50(2):33–39
Yu J et al (2012) Changes of inflammation and apoptosis in adrenal gland after experimental injury in rats with acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Inflammation 35:11–22
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and the experiments were performed by Ke Ren. Data collection and analysis were performed by Jinfeng Lin and Yadong Wang. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Xiaoyan Ji and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author Ke Ren declares that he/she has no conflict of interest; author Jinfeng Lin declares that he/she has no conflict of interest; author Yadong Wang declares that he/she has no conflict of interest; author Xiaoyan Ji declares that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Ethical approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee of Affiliated Nantong Third Hospital of Nantong University (Nantong Third People’s Hospital), and the ethics Approval Number is P20210426-002.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.




Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, K., Lin, J., Wang, Y. et al. Myricetin alleviates pancreatic microcirculation and inflammation in rats with severe acute pancreatitis through FOXO1 and NF-κB pathways. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-023-00388-5
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-023-00388-5