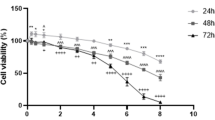
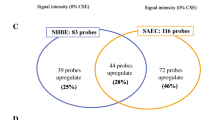
Abstract
Background
Humidifier disinfectants (HDs), including polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate (PHMG-p), are commonly used in Korea to prevent microbial growth. Epidemiological studies show that PHMG-p causes severe lung injury, accompanied by pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. Several studies have examined humidifier disinfectant-associated lung injuries, but few have examined potential carcinogenic activity of PHMG-p. Our previous studies have shown that PHMG-p can induce lung cancer. However, gene expression changes in squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) caused by PHMG-p have not yet been studied.
Objectives
We aimed to determine the PHMG-p-induced changes in transcription levels of genes involved in SCC development and progression in primary bronchial/tracheal epithelial cells (PBTE cells).
Results
Genetic alterations induced by PHMG-p were designated as fold change (FC) values of greater than 2 or less than 0.5. RNA sequencing analysis revealed that two genes were upregulated and sixteen genes were downregulated in the short-term PHMG-p exposure group. Fourteen genes were upregulated and 3 genes were downregulated in the long-term PHMG-p exposure group.
Conclusion
Our data show that PHMG-p induces genetic changes associated with SCC progression in PBTE cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bikkavilli RK et al (2015) Wnt7a is a novel inducer of β-catenin-independent tumor-suppressive cellular senescence in lung cancer. Oncogene 34:5317–5328
Chatterjee S, Sinha S, Kundu CN (2021) Nectin cell adhesion molecule-4 (NECTIN-4): a potential target for cancer therapy. Eur J Pharmacol 911:174516
Cui H et al (2015) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 induces a pro-tumourigenic increase of miR-210 in lung adenocarcinoma cells and their exosomes. Oncogene 34:3640–3650
Delpeut S, Noyce RS, Richardson CD (2014) The tumor-associated marker, PVRL4 (nectin-4), is the epithelial receptor for morbilliviruses. Viruses 6:2268–2286
Fessart D et al (2021) Extracellular AGR2 triggers lung tumour cell proliferation through repression of p21CIP1. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Mol Cell Res 1868:118920
Gentleman RC et al (2004) Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol 5:1–16
Hatakeyama J, Wald JH, Printsev I, Ho H-YH, Carraway KL (2014) Vangl1 and Vangl2: planar cell polarity components with a developing role in cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 21:R345–R356
He J, Fu Y, Hu J, Chen J, Lou G (2021) Hypomethylation-mediated AGR2 overexpression facilitates cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Manag Res 13:5177
Jeon B-H, Park YJ (2012) Frequency of humidifier and humidifier disinfectant usage in gyeonggi provine. Environ Health Toxicol 27
Jeong MH, Kim HR, Park YJ, Chung KH (2019) Akt and Notch pathways mediate polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via ZEB2. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 380:114691
Jeong S-H et al (2021) MTF1 is essential for the expression of MT1B, MT1F, MT1G, and MT1H induced by PHMG, but not CMIT, in the human pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells. Toxics 9:203
Ji Z, Pan X, Shang Y, Ni D-T, Wu F-L (2019) KIF18B as a regulator in microtubule movement accelerates tumor progression and triggers poor outcome in lung adenocarcinoma. Tissue Cell 61:44–50
Jin SW, Lee GH, Pham HT, Choi JH, Jeong HG (2019) Polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate damages tight junctions and the F-actin architecture by activating calpain-1 via the P2RX7/Ca2+ signaling pathway. Cells 9:59
Ju Q et al (2020) Genome-wide analysis of prognostic-related lncRNAs, miRNAs and mRNAs forming a competing endogenous RNA network in lung squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 146:1711–1723
Ju YJ et al (2021) A comprehensive study of deaths due to exposure to humidifier disinfectant in Korea: focusing on medical records, assessment of exposure to humidifier disinfectants, and causes of death. Epidemiol Health 43:e2021091. https://doi.org/10.4178/epih.e2021091
Kim C et al (2021a) Evaluation of the long-term effect of polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate in a rat lung model using conventional chest computed tomography with histopathologic analysis. PLoS ONE 16:e0256756
Kim C et al (2021b) Evaluation of polyhexamethylene guanidine-induced lung injuries by chest CT, pathologic examination, and RNA sequencing in a rat model. Sci Rep 11:1–12
Kim H-C, Kim H, Mun E-C, Lee Y, Park S (2021c) Need for individual-based evaluation to determine the association between humidifier disinfectants and health injuries. Ann Occup Environ Med 33
Kim H-R, Hwang G-W, Naganuma A, Chung K-H (2016) Adverse health effects of humidifier disinfectants in Korea: lung toxicity of polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate. J Toxicol Sci 41:711–717
Kim S-W et al (2007) Proteomics-based identification of proteins secreted in apical surface fluid of squamous metaplastic human tracheobronchial epithelial cells cultured by three-dimensional organotypic air-liquid interface method. Can Res 67:6565–6573
Kim W-Y, Hong S-B (2017) Humidifier disinfectant-associated lung injury: six years after the tragic event. Tuberculos Respir Disease 80:351–357
Koh HM et al (2019) Prognostic role of S100A8 and S100A9 protein expressions in non-small cell carcinoma of the lung. J Pathol Transl Med 53:13–22
Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2012) Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9:357–359
Lee H et al (2022) Analysis of lung cancer-related genetic changes in long-term and low-dose polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate (PHMG-p) treated human pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol 23:1–15
McCarroll J, Wong SW, Hsu K, Geczy CL, Tedla N (2022) Intranasal delivery of recombinant S100A8 protein delays lung cancer growth by remodeling the lung immune microenvironment. Front Immunol 1874
Miao T-w, Yang D-q, Chen F-y, Zhu Q, Chen X (2022) A ferroptosis-related gene signature for overall survival prediction and immune infiltration in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Biosci Rep 42:BSR20212835
Mokhlesi A, Talkhabi M (2020) Comprehensive transcriptomic analysis identifies novel regulators of lung adenocarcinoma. J Cell Commun Signal 14:453–465
Ohkubo Y et al (2010) Combining carbon ion radiotherapy and local injection of α-galactosylceramide–pulsed dendritic cells inhibits lung metastases in an in vivo murine model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78:1524–1531
Park D-U et al (2017) Types of household humidifier disinfectant and associated risk of lung injury (HDLI) in South Korea. Sci Total Environ 596:53–60
Park JS, Park YJ, Kim HR, Chung KH (2019) Polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate-induced ROS-mediated DNA damage caused cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in lung epithelial cells. J Toxicol Sci 44:415–424
Peinado-Serrano J et al (2022) A six-gene prognostic and predictive radiotherapy-based signature for early and locally advanced stages in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancers 14:2054
Puissegur M et al (2011) miR-210 is overexpressed in late stages of lung cancer and mediates mitochondrial alterations associated with modulation of HIF-1 activity. Cell Death Differ 18:465–478
Puvirajesinghe TM et al (2016) Identification of p62/SQSTM1 as a component of non-canonical Wnt VANGL2–JNK signalling in breast cancer. Nat Commun 7:1–15
Quinlan AR, Hall IM (2010) BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 26:841–842
Rodón L et al (2019) The CREB coactivator CRTC2 promotes oncogenesis in LKB1-mutant non–small cell lung cancer. Science advances 5:eaaw6455
Ryu SH et al (2019) Humidifier disinfectant and use characteristics associated with lung injury in Korea. Indoor Air 29:735–747
Savini A et al (2015) Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung: clinical criteria for treatment strategy. J Cancer Metastas Treatment 1:90–93
Shi S et al (2018) CRTC2 promotes non-small cell lung cancer A549 migration and invasion in vitro. Thoracic Cancer 9:136–141
Shi X et al (2022) Integrative pan cancer analysis reveals the importance of CFTR in lung adenocarcinoma prognosis. Genomics 114:110279
Song C et al (2020) A prognostic nomogram combining immune-related gene signature and clinical factors predicts survival in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol 10:1300
Song JA et al (2014) Polyhexamethyleneguanidine phosphate induces severe lung inflammation, fibrosis, and thymic atrophy. Food Chem Toxicol 69:267–275
Su W et al (2016) miR-135b reverses chemoresistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells by downregulation of FZD1. Biomed Pharmacother 84:123–129
Sun N et al (2022) A novel immune checkpoints-based signature to predict prognosis and response to immunotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma. J Transl Med 20:1–15
Sun Q et al (2022b) Prognostic value and oncogenic effects of ubiquitin-specific protease 43 in lung squamous cell carcinoma. The Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine
Vitt A et al (2015) Antimicrobial activity of polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate in comparison to chlorhexidine using the quantitative suspension method. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 14:1–9
Wang J, Yang Q, Tang M, Liu W (2022) Validation and analysis of expression, prognosis and immune infiltration of WNT gene family in non-small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol 12
Wang R, Wang X, Zhang J, Liu Y (2021) LINC00942 promotes tumor proliferation and metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma via FZD1 upregulation. Technol Cancer Res Treat 20:1533033820977526
Werynska B et al (2013) Metallothionein 1F and 2A overexpression predicts poor outcome of non-small cell lung cancer patients. Exp Mol Pathol 94:301–308
Xiong Y, Mingzhen L, Zhang P, Zhang L, Yue Y (2017) Study on genetype in lung squamous carcinoma by high-throughput of transcriptome sequence. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi 20
Xu F et al (2020a) A TP53-associated gene signature for prediction of prognosis and therapeutic responses in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Oncoimmunology 9:1731943
Xu Z et al (2020b) Circ-IGF1R inhibits cell invasion and migration in non-small cell lung cancer. Thoracic Cancer 11:875–887
Xue Y et al (2021) Long noncoding RNAs PTPRG Antisense RNA 1 targets cyclin D1 to facilitate cell proliferation in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Biotherap Radiopharm
Yang J-W et al (2022) Tissue-level alveolar epithelium model for recapitulating SARS-CoV-2 infection and cellular plasticity. Commun Biol 5:1–12
Yang Y et al (2019) Evidence for an oncogenic role of HOXC6 in human non-small cell lung cancer. PeerJ 7:e6629
Zhang H et al (2022) QKI-6 Suppresses Cell Proliferation, Migration, and EMT in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Frontiers in Oncology 12
Zhang Q-X et al (2021) The roles of risk model based on the 3-XRCC genes in lung adenocarcinoma progression. Transl Cancer Res 10:4413
Zhang W et al (2018) TRIM58/cg26157385 methylation is associated with eight prognostic genes in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep 40:206–216
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Environment Research (NIER) funded by the Ministry of Environment (MOE) of the Republic of Korea (grant number NIER-2022-04-03-001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PYH and JSH analyzed the RNA sequencing data, searched references to genes and wrote this manuscript. KC, NYJ, KJ, PEK, and BYW performed the data analysis. LH1 performed RT-qPCR. KJY, CJY, LYS, and PSA contributed to searching references to this study. LH2 designed this study and edited the manuscript. LJH supervised the study and acquired the funding source. (LH1: Hyejin Lee, LH2: Hong Lee).
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yoon Hee Park declares that there are no conflicts of interest. Sang Hoon Jeong declares that there are no conflicts of interest. Hyejin Lee declares that there are no conflicts of interest. Cherry Kim declares that there are no conflicts of interest. Yoon Jeong Nam declares that there are no conflicts of interest. Ja Young Kang declares that there are no conflicts of interest. Jin Young Choi declares that there are no conflicts of interest. Yu-Seon Lee declares that there are no conflicts of interest. Su a Park declares that there are no conflicts of interest. Jaeyoung Kim declares that there are no conflicts of interest. Eun-Kee Park declares that there are no conflicts of interest. Yong-Wook Baek declares that there are no conflicts of interest. Hong Lee declares that there are no conflicts of interest. Ju-Han Lee declares that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Park, Y.H., Jeong, S.H., Lee, H. et al. Gene expression related to lung cancer altered by PHMG-p treatment in PBTE cells. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 19, 205–217 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-022-00319-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-022-00319-w