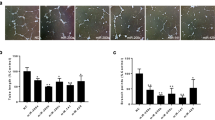
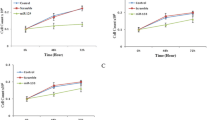
Abstract
Angiogenesis is an important biological process associated with plethora of physiological and patho-physiological conditions. Recent data suggests that fine balance between anti-angiogenic microRNA (miRNA) and pro-angiogenicmiRNA drive the process of neovascularization. Many of these miRNAs act via G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) which regulates diverse physiological processes including angiogenesis. Aberrant GPCR expression and signaling through G-protein often results into uncontrolled angiogenesis, tumor development and metastasis. In this review, we discuss the new emerging insights of GPCR-miRNA network and their interaction in angiogenic pathways leading to the cancer progression. Alongside we have focused on the GPCR mediated angiogenic processes which are controlled by anti-angiogenicmiRNAs and the influence of deregulation of these miRNAs on cancer angiogenesis. Through an extensive literature survey, we identified 7 distinct miRNAs, which are playing important role in regulating angiogenesis. Through network analysis with predicted targets for reported miRNAs and pathway enrichment, 25 major cell signaling pathways associated with tumor-angiogenesis could be identified, further reinforcing the relevance of the miRNAs in the process.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Adair TH, Montani JP. Angiogenesis, Integrated Systems Physiology: from Molecule to Function to Disease. San Rafael, CA: Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences; 2010.
Adams D, Koike H, Slama M, Coelho T. Hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis: a model of medical progress for a fatal disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15:387–404.
Allen AM. Role of angiotensin in the rostral ventrolateral medulla in the development and maintenance of hypertension. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2011;11:117–23.
Allen AM, Zhuo J, Mendelsohn FA. Localization and function of angiotensin AT1 receptors. Am J Hypertens. 2000;13:31S-S38.
Bandres E, Agirre X, Bitarte N, Ramirez N, Zarate R, et al. Epigenetic regulation of microRNA expression in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2009;125:2737–43.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97.
Bockenhauer S, Furstenberg A, Yao XJ, Kobilka BK, Moerner WE. Conformational dynamics of single G protein-coupled receptors in solution. J Phys Chem B. 2011;115:13328–38.
Brusevold IJ, Tveteraas IH, Aasrum M, Odegard J, Sandnes DL, Christoffersen T. Role of LPAR3, PKC and EGFR in LPA-induced cell migration in oral squamous carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:432.
Burger JA, Kipps TJ. Chemokine receptors and stromal cells in the homing and homeostasis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002;43:461–6.
Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat Med. 2003;9:653–60.
Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature. 2005;438:932–6.
Chen DB, Zheng J. Regulation of placental angiogenesis. Microcirculation. 2014;21:15–25.
Chen Q, Zhong T. The association of CXCR4 expression with clinicopathological significance and potential drug target in prostate cancer: a meta-analysis and literature review. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015;9:5115–22.
Chen SU, Lee H, Chang DY, Chou CH, Chang CY, et al. Lysophosphatidic acid mediates interleukin-8 expression in human endometrial stromal cells through its receptor and nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent pathway: a possible role in angiogenesis of endometrium and placenta. Endocrinology. 2008;149:5888–96.
Chen T, Yang YJ, Li YK, Liu J, Wu PF, et al. Chronic administration tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside promotes hippocampal memory and synaptic plasticity and activates ERKs, CaMKII and SIRT1/miR-134 in vivo. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;190:74–82.
Chiang YY, Chen KB, Tsai TH, Tsai WC. Lowered cancer risk with ACE inhibitors/ARBs: a population-based cohort study. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2014;16:27–33.
Chung AS, Ferrara N. Developmental and pathological angiogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011;27:563–84.
Cory S, Adams JM. The Bcl2 family: regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:647–56.
Cunningham SA, Waxham MN, Arrate PM, Brock TA. Interaction of the Flt-1 tyrosine kinase receptor with the p85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Mapping of a novel site involved in binding. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:20254–7.
De Francesco EM, Sotgia F, Clarke RB, Lisanti MP, Maggiolini M. G protein-coupled receptors at the crossroad between physiologic and pathologic angiogenesis: old paradigms and emerging concepts. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(12):2713.
de Gasparo M, Catt KJ, Inagami T, Wright JW, Unger T. International union of pharmacology. XXIII The angiotensin II receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2000;52:415–72.
Deshayes F, Nahmias C. Angiotensin receptors: a new role in cancer? Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2005;16:293–9.
Di Liberto V, Mudo G, Belluardo N. Crosstalk between receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) in the brain: Focus on heteroreceptor complexes and related functional neurotrophic effects. Neuropharmacology. 2019;152:67–77.
Di Tommaso P, Moretti S, Xenarios I, Orobitg M, Montanyola A, et al. T-Coffee: a web server for the multiple sequence alignment of protein and RNA sequences using structural information and homology extension. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:W13–7.
Edward Zhou X, Melcher K, Eric XuH. Structural biology of G protein-coupled receptor signaling complexes. Protein Sci. 2019;28:487–501.
Egami K, Murohara T, Shimada T, Sasaki K, Shintani S, et al. Role of host angiotensin II type 1 receptor in tumor angiogenesis and growth. J Clin Invest. 2003;112:67–75.
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs - microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:259–69.
Ferrara N. The role of VEGF in the regulation of physiological and pathological angiogenesis. EXS. 2005;94:209–31.
Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009;29:789–91.
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003;9:669–76.
Finan C, Gaulton A, Kruger FA, Lumbers RT, Shah T, et al. The druggable genome and support for target identification and validation in drug development. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9(383):eaag1166.
Fu HL, Wu DP, Wang XF, Wang JG, Jiao F, et al. Altered miRNA expression is associated with differentiation, invasion, and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) in patients from Huaian, China. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013;67:657–68.
Fujita M, Hayashi I, Yamashina S, Itoman M, Majima M. Blockade of angiotensin AT1a receptor signaling reduces tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;294:441–7.
Gavard J, Gutkind JS. VEGF controls endothelial-cell permeability by promoting the beta-arrestin-dependent endocytosis of VE-cadherin. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:1223–34.
Ge YZ, Xu LW, Xu Z, Wu R, Xin H, et al. Expression profiles and clinical significance of microRNAs in papillary renal cell carcinoma: a STROBE-compliant observational study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94:e767.
Gerber HP, McMurtrey A, Kowalski J, Yan M, Keyt BA, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates endothelial cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3’-kinase/Akt signal transduction pathway. Requirement for Flk-1/KDR activation. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:30336–43.
Giray BG, Emekdas G, Tezcan S, Ulger M, Serin MS, et al. Profiles of serum microRNAs; miR-125b-5p and miR223-3p serve as novel biomarkers for HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 2014;41:4513–9.
Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, van Dongen S, Enright AJ. miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:D154–8.
Grisshammer R. New approaches towards the understanding of integral membrane proteins: a structural perspective on G protein-coupled receptors. Protein Sci. 2017;26:1493–504.
Haller F, von Heydebreck A, Zhang JD, Gunawan B, Langer C, et al. Localization- and mutation-dependent microRNA (miRNA) expression signatures in gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GISTs), with a cluster of co-expressed miRNAs located at 14q32.31. J Pathol. 2010;220:71–86.
Hallersund P, Elfvin A, Helander HF, Fandriks L. The expression of renin-angiotensin system components in the human gastric mucosa. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2011;12:54–64.
Hellstrom M, Phng LK, Hofmann JJ, Wallgard E, Coultas L, et al. Dll4 signalling through Notch1 regulates formation of tip cells during angiogenesis. Nature. 2007;445:776–80.
Hersi HM, Raulf N, Gaken J, Folarin N, Tavassoli M. MicroRNA-9 inhibits growth and invasion of head and neck cancer cells and is a predictive biomarker of response to plerixafor, an inhibitor of its target CXCR4. Mol Oncol. 2018;12:2023–41.
Hirota T, Date Y, Nishibatake Y, Takane H, Fukuoka Y, et al. Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) expression is negatively regulated by certain microRNAs in human lung tissues. Lung Cancer. 2012;77:16–23.
Hooper AJ, Burnett JR. Anti-PCSK9 therapies for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2013;13:429–35.
Huang W, Masureel M, Qu Q, Janetzko J, Inoue A, et al. Structure of the neurotensin receptor 1 in complex with beta-arrestin 1. Nature. 2020;579:303–8.
Hui Y, Li Y, Jing Y, Feng JQ, Ding Y. miRNA-101 acts as a tumor suppressor in oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting CX chemokine receptor 7. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8:4902–11.
Insel PA, Tang CM, Hahntow I, Michel MC. Impact of GPCRs in clinical medicine: monogenic diseases, genetic variants and drug targets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1768:994–1005.
Ishii I, Fukushima N, Ye X, Chun J. Lysophospholipid receptors: signaling and biology. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:321–54.
Jiang X, Du L, Wang L, Li J, Liu Y, et al. Serum microRNA expression signatures identified from genome-wide microRNA profiling serve as novel noninvasive biomarkers for diagnosis and recurrence of bladder cancer. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:854–62.
Jiang X, Wang J, Deng X, Xiong F, Zhang S, et al. The role of microenvironment in tumor angiogenesis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39:204.
Kamat AA, Merritt WM, Coffey D, Lin YG, Patel PR, et al. Clinical and biological significance of vascular endothelial growth factor in endometrial cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:7487–95.
Kang Y, Zhou XE, Gao X, He Y, Liu W, et al. Crystal structure of rhodopsin bound to arrestin by femtosecond X-ray laser. Nature. 2015;523:561–7.
Kaur H, Carvalho J, Looso M, Singh P, Chennupati R, et al. Single-cell profiling reveals heterogeneity and functional patterning of GPCR expression in the vascular system. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15700.
Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Hirajima S, Kawaguchi T, Miyamae M, et al. Plasma microRNA profiles: identification of miR-25 as a novel diagnostic and monitoring biomarker in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2014;111:1614–24.
Kryczek I, Lange A, Mottram P, Alvarez X, Cheng P, et al. CXCL12 and vascular endothelial growth factor synergistically induce neoangiogenesis in human ovarian cancers. Cancer Res. 2005;65:465–72.
Lages E, Guttin A, El Atifi M, Ramus C, Ipas H, et al. MicroRNA and target protein patterns reveal physiopathological features of glioma subtypes. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e20600.
Lappano R, Rigiracciolo D, De Marco P, Avino S, Cappello AR, et al. Recent advances on the role of G protein-coupled receptors in hypoxia-mediated signaling. AAPS J. 2016;18:305–10.
Law IKM, Padua DM, Iliopoulos D, Pothoulakis C. Role of G protein-coupled receptors-microRNA interactions in gastrointestinal pathophysiology. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017;313:G361–72.
Lee MJ, Thangada S, Claffey KP, Ancellin N, Liu CH, et al. Vascular endothelial cell adherens junction assembly and morphogenesis induced by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Cell. 1999;99:301–12.
Lee MJ, Van Brocklyn JR, Thangada S, Liu CH, Hand AR, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate as a ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor EDG-1. Science. 1998;279:1552–5.
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120:15–20.
Li GC, Qin XL, Song HH, Li YN, Qiu YY, et al. Upregulated microRNA-15b alleviates ovarian cancer through inhitbition of the PI3K/Akt pathway by targeting LPAR3. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:22331–42.
Li J, Wang Y, Luo J, Fu Z, Ying J, et al. miR-134 inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting FOXM1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2012;586:3761–5.
Lobov IB, Renard RA, Papadopoulos N, Gale NW, Thurston G, et al. Delta-like ligand 4 (Dll4) is induced by VEGF as a negative regulator of angiogenic sprouting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:3219–24.
Lujambio A, Calin GA, Villanueva A, Ropero S, Sanchez-Cespedes M, et al. A microRNA DNA methylation signature for human cancer metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:13556–61.
Ma Z, Yu YR, Badea CT, Kovacs JJ, Xiong X, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 regulates endothelial function through beta-arrestin 1. Circulation. 2019;139:1629–42.
Madden SL, Cook BP, Nacht M, Weber WD, Callahan MR, et al. Vascular gene expression in nonneoplastic and malignant brain. Am J Pathol. 2004;165:601–8.
Maehama T, Taylor GS, Dixon JE. PTEN and myotubularin: novel phosphoinositide phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2001;70:247–79.
McCusker EC, Bane SE, O’Malley MA, Robinson AS. Heterologous GPCR expression: a bottleneck to obtaining crystal structures. Biotechnol Prog. 2007;23:540–7.
Medina PP, Slack FJ. microRNAs and cancer: an overview. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:2485–92.
Miao Z, Luker KE, Summers BC, Berahovich R, Bhojani MS, et al. CXCR7 (RDC1) promotes breast and lung tumor growth in vivo and is expressed on tumor-associated vasculature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:15735–40.
Mooers BH. Simplifying and enhancing the use of PyMOL with horizontal scripts. Protein Sci. 2016;25:1873–82.
Nagahashi M, Ramachandran S, Kim EY, Allegood JC, Rashid OM, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate produced by sphingosine kinase 1 promotes breast cancer progression by stimulating angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2012;72:726–35.
Natarajan K, Berk BC. Crosstalk coregulation mechanisms of G protein-coupled receptors and receptor tyrosine kinases. Methods Mol Biol. 2006;332:51–77.
Noguchi R, Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Yoshii J, Ikenaka Y, et al. Combination of interferon-beta and the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, perindopril, attenuates murine hepatocellular carcinoma development and angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:6038–45.
Nolan DJ, Ciarrocchi A, Mellick AS, Jaggi JS, Bambino K, et al. Bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells are a major determinant of nascent tumor neovascularization. Genes Dev. 2007;21:1546–58.
O’Hayre M, Vazquez-Prado J, Kufareva I, Stawiski EW, Handel TM, et al. The emerging mutational landscape of G proteins and G-protein-coupled receptors in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:412–24.
Phng LK, Potente M, Leslie JD, Babbage J, Nyqvist D, et al. Nrarp coordinates endothelial Notch and Wnt signaling to control vessel density in angiogenesis. Dev Cell. 2009;16:70–82.
Pierce KL, Premont RT, Lefkowitz RJ. Seven-transmembrane receptors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:639–50.
Ping YF, Yao XH, Jiang JY, Zhao LT, Yu SC, et al. The chemokine CXCL12 and its receptor CXCR4 promote glioma stem cell-mediated VEGF production and tumour angiogenesis via PI3K/AKT signalling. J Pathol. 2011;224:344–54.
Popenda M, Szachniuk M, Antczak M, Purzycka KJ, Lukasiak P, et al. Automated 3D structure composition for large RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:e112.
Popnikolov NK, Dalwadi BH, Thomas JD, Johannes GJ, Imagawa WT. Association of autotaxin and lysophosphatidic acid receptor 3 with aggressiveness of human breast carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2012;33:2237–43.
Proctor JR, Meyer IM. COFOLD: an RNA secondary structure prediction method that takes co-transcriptional folding into account. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:e102.
Qin C, Huang RY, Wang ZX. Potential role of miR-100 in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:1403–9.
Rasmussen SG, DeVree BT, Zou Y, Kruse AC, Chung KY, et al. Crystal structure of the beta2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex. Nature. 2011;477:549–55.
Rhodes DR, Ateeq B, Cao Q, Tomlins SA, Mehra R, et al. AGTR1 overexpression defines a subset of breast cancer and confers sensitivity to losartan, an AGTR1 antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:10284–9.
Richard DE, Vouret-Craviari V, Pouyssegur J. Angiogenesis and G-protein-coupled receptors: signals that bridge the gap. Oncogene. 2001;20:1556–62.
Rodriguez S, Huynh-Do U. The role of PTEN in tumor angiogenesis. J Oncol. 2012;2012:141236.
Roehr B. Fomivirsen approved for CMV retinitis. J Int Assoc Physicians AIDS Care. 1998;4:14–6.
Rosenbaum DM, Rasmussen SG, Kobilka BK. The structure and function of G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature. 2009;459:356–63.
Roskoski R Jr. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling in tumor progression. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2007;62:179–213.
Rupertus K, Sinistra J, Scheuer C, Nickels RM, Schilling MK, et al. Interaction of the chemokines I-TAC (CXCL11) and SDF-1 (CXCL12) in the regulation of tumor angiogenesis of colorectal cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2014;31:447–59.
Sardh E, Harper P, Balwani M, Stein P, Rees D, et al. Phase 1 trial of an RNA interference therapy for acute intermittent porphyria. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:549–58.
Sarramegna V, Talmont F, Demange P, Milon A. Heterologous expression of G-protein-coupled receptors: comparison of expression systems from the standpoint of large-scale production and purification. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003;60:1529–46.
Schratt GM, Tuebing F, Nigh EA, Kane CG, Sabatini ME, et al. A brain-specific microRNA regulates dendritic spine development. Nature. 2006;439:283–9.
Seitz H, Royo H, Bortolin ML, Lin SP, Ferguson-Smith AC, Cavaille J. A large imprinted microRNA gene cluster at the mouse Dlk1-Gtl2 domain. Genome Res. 2004;14:1741–8.
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, et al. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003;13:2498–504.
Shukla AK, Xiao K, Lefkowitz RJ. Emerging paradigms of beta-arrestin-dependent seven transmembrane receptor signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 2011;36:457–69.
Siekmann AF, Covassin L, Lawson ND. Modulation of VEGF signalling output by the Notch pathway. BioEssays. 2008;30:303–13.
Song Y, Wu J, Oyesanya RA, Lee Z, Mukherjee A, Fang X. Sp-1 and c-Myc mediate lysophosphatidic acid-induced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in ovarian cancer cells via a hypoxia-inducible factor-1-independent mechanism. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:492–501.
Strange PG. Signaling mechanisms of GPCR ligands. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2008;11:196–202.
Sun X, Cheng G, Hao M, Zheng J, Zhou X, et al. CXCL12 / CXCR4 / CXCR7 chemokine axis and cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010;29:709–22.
Tachezy M, Zander H, Gebauer F, von Loga K, Pantel K, et al. CXCR7 expression in esophageal cancer. J Transl Med. 2013;11:238.
Tahiri A, Leivonen SK, Luders T, Steinfeld I, Ragle Aure M, et al. Deregulation of cancer-related miRNAs is a common event in both benign and malignant human breast tumors. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35:76–85.
Takuwa Y, Du W, Qi X, Okamoto Y, Takuwa N, Yoshioka K. Roles of sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling in angiogenesis. World J Biol Chem. 2010;1:298–306.
Takuwa Y, Takuwa N, Sugimoto N. The Edg family G protein-coupled receptors for lysophospholipids: their signaling properties and biological activities. J Biochem. 2002;131:767–71.
Thurston G, Noguera-Troise I, Yancopoulos GD. The Delta paradox: DLL4 blockade leads to more tumour vessels but less tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:327–31.
Vanhaesebroeck B, Leevers SJ, Panayotou G, Waterfield MD. Phosphoinositide 3-kinases: a conserved family of signal transducers. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997;22:267–72.
Wacker D, Stevens RC, Roth BL. How ligands illuminate GPCR molecular pharmacology. Cell. 2017;170:414–27.
Wang J, Shiozawa Y, Wang J, Wang Y, Jung Y, et al. The role of CXCR7/RDC1 as a chemokine receptor for CXCL12/SDF-1 in prostate cancer. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:4283–94.
Wang Y, Cho SG, Wu X, Siwko S, Liu M. G-protein coupled receptor 124 (GPR124) in endothelial cells regulates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced tumor angiogenesis. Curr Mol Med. 2014;14:543–54.
Wang Z. Transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor by G protein-coupled receptors: recent progress, challenges and future research. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(1):95.
Xia H, Qi Y, Ng SS, Chen X, Chen S, et al. MicroRNA-15b regulates cell cycle progression by targeting cyclins in glioma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;380:205–10.
Xia J, Wang J, Chen N, Dai Y, Hong Y, et al. Expressions of CXCR7/ligands may be involved in oral carcinogenesis. J Mol Histol. 2011;42:175–80.
Xia L, Zhang D, Du R, Pan Y, Zhao L, et al. miR-15b and miR-16 modulate multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human gastric cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 2008;123:372–9.
Xie Y, Song J, Zong Q, Wang A, Yang Y, et al. Decreased expression of MIR-134 and its clinical significance in human colorectal cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2015;62:615–9.
Xu Y, Fang XJ, Casey G, Mills GB. Lysophospholipids activate ovarian and breast cancer cells. Biochem J. 1995;309(Pt 3):933–40.
Xue LJ, Mao XB, Ren LL, Chu XY. Inhibition of CXCL12/CXCR4 axis as a potential targeted therapy of advanced gastric carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2017;6:1424–36.
Yanagida K, Ishii S. Non-Edg family LPA receptors: the cutting edge of LPA research. J Biochem. 2011;150:223–32.
Yang S, Zhang L, Purohit V, Shukla SK, Chen X, et al. Active YAP promotes pancreatic cancer cell motility, invasion and tumorigenesis in a mitotic phosphorylation-dependent manner through LPAR3. Oncotarget. 2015;6:36019–31.
Yin W, Li Z, Jin M, Yin YL, de Waal PW, et al. A complex structure of arrestin-2 bound to a G protein-coupled receptor. Cell Res. 2019;29:971–83.
Young D, Waitches G, Birchmeier C, Fasano O, Wigler M. Isolation and characterization of a new cellular oncogene encoding a protein with multiple potential transmembrane domains. Cell. 1986;45:711–9.
Zhang C, Wang C, Chen X, Yang C, Li K, et al. Expression profile of microRNAs in serum: a fingerprint for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Chem. 2010;56:1871–9.
Zhang SL, Liu L. microRNA-148a inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion by targeting sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1. Exp Ther Med. 2015;9:579–84.
Zheng M, Jiang YP, Chen W, Li KD, Liu X, et al. Snail and Slug collaborate on EMT and tumor metastasis through miR-101-mediated EZH2 axis in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2015;6:6797–810.
Zhou SM, Zhang F, Chen XB, Jun CM, Jing X, et al. miR-100 suppresses the proliferation and tumor growth of esophageal squamous cancer cells via targeting CXCR7. Oncol Rep. 2016;35:3453–9.
Zhou XE, Melcher K, Xu HE. Understanding the GPCR biased signaling through G protein and arrestin complex structures. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2017;45:150–9.
Zhou Y, Nathans J. Gpr124 controls CNS angiogenesis and blood-brain barrier integrity by promoting ligand-specific canonical wnt signaling. Dev Cell. 2014;31:248–56.
Zuckerman V, Sokolov E, Swet JH, Ahrens WA, Showlater V, et al. Expression and function of lysophosphatidic acid receptors (LPARs) 1 and 3 in human hepatic cancer progenitor cells. Oncotarget. 2016;7:2951–67.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Department of Science and technology (DST)-SERB grant (File Number: SRG/2020/002215) awarded to KP and Seed Grant, Adamas University awarded to AB and SH (Ref No. AU/REG/2019-20/12/008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SM: Processed the experimental data, and performed the analysis under guidance of AB. DC: Performed the Literature survey. AB: Involved in planning, processed the experimental data performed the analysis. JP: Conceived of the presented idea, performed the Literature survey,and processed the experimental data, involved in planning. Drafted the manuscript and designed the figures. SH: Conceived of the presented idea, performed the Literature survey, processed the experimental data, involved in planning, drafted the manuscript and designed the figures, supervised this work. KP: Conceived of the presented idea, performed the Literature survey, processed the experimental data, involved in planning, drafted the manuscript and designed the figures, supervised this work.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Corresponding Editor: Somnath Paul; Reviewers: Kasturi Pal, Anisuzzaman Anisuzzaman.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandal, S., Chakrabarty, D., Bhattacharya, A. et al. miRNA regulation of G protein-coupled receptor mediated angiogenic pathways in cancer. Nucleus 64, 303–315 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-021-00365-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-021-00365-0