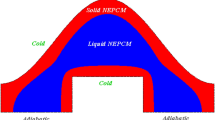
Abstract
New geometry with rectangular inner cylinder containing cold flow has been simulated in this article. Freezing phenomenon has been simulated and NEPCM was mixture of CuO and water. Time-dependent solid fraction term was added to energy equation. Software based on FEM with adaptive grid was implemented for modeling the problem. Diameter of nanomaterial and amplitude of outer wall were assumed as variable. To reach the reliability of assumption of neglecting buoyancy term, comparison with experimental data was illustrated. Providing greater value of A makes the freezing time to reduce about 5.82% which is associated with existence of more NEPCM near the rectangular cylinder when A = 0.3. Influence of A on Tave has no sensible impact for t < 70 s and t > 320 s. Increasing diameter of nano-powder can augment the conductivity but experimental observation shows that there is optimum value for this factor. As dp augments from 30 to 50 nm and 40 nm, the time of solidification alters from 186.57 s to 222.77 s and 149.37 s. With rise of dp, at first, the time declines about 19.98% then time augments about 49.16%. When A = 0.3 and dp = 40 nm, the quickest process takes place and it takes 149.37 s to reach full freezing.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Waeli AHA, Sopian K, Kazem HA, Yousif JH, Chaichan MT, Ibrahim A, Mat S, Ruslan MH (2018) Comparison of prediction methods of PV/T nanofluid and nano-PCM system using a measured dataset and artificial neural network. Sol Energy 162:378–396
Al-Waeli AHA, Kazem HA, Chaichan MT, Sopian K (2019) Experimental investigation of using nano-PCM/nanofluid on a photovoltaic thermal system (PVT): technical and economic study. Therm Sci Eng Prog 11:213–230
Chen X, Wang D, Wang T, Yang Z, Zou X, Wang P et al (2019) Enhanced photoresponsivity of a GaAs nanowire metal-semiconductor-metal photodetector by adjusting the Fermi level. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(36):33188–33193. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b07891
Chen C, Wang X, Wang Y, Yang D, Yao F, Zhang W, Wang B, Sewvandi GA, Yang D, Hu D (2020) Additive manufacturing of piezoelectric materials. Adv Funct Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202005141
Chu Y-M, Bach Q-V (2020) Application of TiO2 nanoparticle for solar photocatalytic oxidation system. Appl Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01614-5
Chu Y-M, Hajizadeh MR, Li Z, Bach Q-V (2020a) Investigation of nano powders influence on melting process within a storage unit. J Mol Liq 318:114321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114321
Chu Y-M, Salahshoor Z, Shahraki MS, Shafee A, Bach Q-V (2020b) Annulus shape tank with convective flow in a porous zone with impose of MHD. Int J Mod Phys C. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0129183120501685
Chu Y-M, Yadav D, Shafee A, Li Z, Bach Q-V (2020c) Influence of wavy enclosure and nanoparticles on heat release rate of PCM considering numerical study. J Mol Liq 319:114121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114121
Chu Y-M, Bilal S, Hajizadeh MR (2020d) Hybrid ferrofluid along with MWCNT for augmentation of thermal behavior of fluid during natural convection in a cavity. Math Methods Appl Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.6937
Chu Y-M, Abu-Hamdeh NH, Ben-Beya B, Hajizadeh MR, Li Z, Bach Q-V (2020e) Nanoparticle enhanced PCM exergy loss and thermal behavior by means of FVM. J Mol Liq 320(Part B):114457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114457
Chu Y-M, Abohamzeh E, Bach Q-V (2020f) Thermal two-phase analysis of nanomaterial in a pipe with turbulent flow. Appl Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01576-8
Chu Y-M, Salehi F, Jafaryar M, Bach Q-V (2020g) Simulation based on FVM for influence of nanoparticles on flow inside a pipe enhanced with helical tapes. Appl Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01583-9
Chu Y-M, Li Z, Bach Q-V (2020h) Application of nanomaterial for thermal unit including tube fitted with turbulator. Appl Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01587-5
Chu Y-M, Kumar R, Bach Q-V (2020i) Water-based nanofluid flow with various shapes of Al2O3 nanoparticles owing to MHD inside a permeable tank with heat transfer. Appl Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01609-2
Chu Y-M, Almusawi MB, Hajizadeh MR, Yao S-W, Bach Q-V (2020j) Hybrid nanomaterial treatment within a permeable tank considering irreversibility. Int J Mod Phys C. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0129183121500613
Deng R, Li M, Linghu S et al (2021a) Research on calculation method of steam absorption in steam injection thermal recovery technology. Fresenius Environ Bull 30(05):5362–5369
Deng R, Li M, Linghu S et al (2021b) Sensitivity analysis of steam injection parameters of steam injection thermal recovery technology. Fresenius Environ Bull 30(05):5385–5394
Duan Z, Li C, Zhang Y, Dong L, Bai X, Yang M et al (2020) Milling surface roughness for 7050 aluminum alloy cavity influenced by nozzle position of nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication. Chin J Aeronaut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2020.04.029
Gao T, Li C, Zhang Y, Yang M, Jia D, Jin T et al (2019) Dispersing mechanism and tribological performance of vegetable oil-based CNT nanofluids with different surfactants. Tribol Int 131:51–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2018.10.025
Gao T, Li C, Jia D, Zhang Y, Yang M, Wang X et al (2020) Surface morphology assessment of CFRP transverse grinding using CNT nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication. J Clean Prod 277:123328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123328
Harikrishnan S, Kalaiselvam S (2012) Preparation and thermal characteristics of CuO–oleic acid nanofluids as a phase change material. Thermochim Acta 533:46–55
Huang W, Wang G, Li W, Li T, Ji G, Ren S et al (2020) Porous ligand creates new reaction route: bifunctional single-atom palladium catalyst for selective distannylation of terminal alkynes. Chem 6(9):2300–2313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chempr.2020.06.020
Ismail K, Alves C, Modesto M (2001) Numerical and experimental study on the solidification of PCM around a vertical axially finned isothermal cylinder. Appl Therm Eng 21:53–77
Jiang J, Peng ZY, Ye M, Wang YB, Wang X et al (2021) Thermal effect of welding on mechanical behavior of high-strength steel. J Mater Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0003837
Kant K, Shukla A, Sharma A, Biwole PH (2017) Heat transfer study of phase change materials with graphene nano particle for thermal energy storage. Sol Energy 146:453–463
Li H, Tang J, Kang Y, Zhao H, Fang D, Fang X et al (2018) Optical properties of quasi-type-II structure in GaAs/GaAsSb/GaAs coaxial single quantum-well nanowires. Appl Phys Lett 113(23):233104. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5053844
Li X, Feng Y, Liu B, Yi D, Yang X, Zhang W et al (2019) Influence of NbC particles on microstructure and mechanical properties of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy coatings prepared by laser cladding. J Alloy Compd 788:485–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.02.223
Li X, Yu P, Niu X, Yamaguchi H, Li D (2020) Non-contact manipulation of nonmagnetic materials by using a uniform magnetic field: experiment and simulation. J Magn Magn Mater 497:165957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.165957
Li F, Almarashi A, Jafaryar M, Hajizadeh MR, Chu Y-M (2021a) Melting process of nanoparticle enhanced PCM through storage cylinder incorporating fins. Powder Technol 381:551–560
Li J, Alawee WH, Rawa MJH, Dhahad HA, Chu Y-M, Issakhov A, Abu-Hamdeh NH, Hajizadeh MR (2021b) Heat recovery application of nanomaterial with existence of turbulator. J Mol Liq 326:115268
Liu J, Ren M, Lai X, Qiu G (2021a) Iron-catalyzed stereoselective haloamidation of amide-tethered alkynes. Chem Commun. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CC00870F
Liu Y, Wei Z, Zhong B, Wang H, Xia L, Zhang T et al (2021b) O-, N-coordinated single Mn atoms accelerating polysulfides transformation in lithium-sulfur batteries. Energy Storage Mater 35:12–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2020.11.011
Liu M, Xue Z, Zhang H, Li Y (2021c) Dual-channel membrane capacitive deionization based on asymmetric ion adsorption for continuous water desalination. Electrochem Commun 125:106974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2021.106974
Liu Y, Lv X, Tang Z (2021d) The impact of mortality salience on quantified self behavior during the COVID-19 pandemic. Pers Individ Differ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2021.110972
Lu H, Tian P, He L (2019) Evaluating the global potential of aquifer thermal energy storage and determining the potential worldwide hotspots driven by socio-economic, geo-hydrologic and climatic conditions. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 112:788–796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.06.013
Mahdi JM, Nsofor EC (2016) Solidification of a PCM with nanoparticles in triplex-tube thermal energy storage system. Appl Therm Eng 108:596–604
Nasef HA, Nada SA, Hassan H (2019) Integrative passive and active cooling system using PCM and nanofluid for thermal regulation of concentrated photovoltaic solar cells. Energy Convers Manag 199:112065
Qin Y, Luo J, Chen Z, Mei G, Yan L-E (2018a) Measuring the albedo of limited-extent targets without the aid of known-albedo masks. Sol Energy 171:971–976
Qin Y, He Y, Hiller JE, Mei G (2018b) A new water-retaining paver block for reducing runoff and cooling pavement. J Clean Prod 199:948–956
Qin Y, He H, Ou X, Bao T (2019) Experimental study on darkening water-rich mud tailings for accelerating desiccation. J Clean Prod 240:118235
Qin C et al (2020) A novel Chebyshev-wavelet-based approach for accurate and fast prediction of milling stability. Precis Eng 62:244–255
Qu S, Xu W, Zhao J, Zhang H (2021) Design and implementation of a fast sliding-mode speed controller with disturbance compensation for SPMSM syste. IEEE Trans Transp Electrif. https://doi.org/10.1109/TTE.2021.3060102
Sciacovelli A, Colella F, Verda V (2013) Melting of PCM in a thermal energy storage unit: numerical investigation and effect of nanoparticle enhancement. Int J Energy Res 37(13):1610–1623
Sheikholeslami M (2018) Numerical simulation for solidification in a LHTESS by means of nano-enhanced PCM. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 86:25–41
Sheikholeslami M, Farshad SA (2021) Investigation of solar collector system with turbulator considering hybrid nanoparticles. Renew Energy 171:1128–1158
Sheikholeslami M, Ghasemi A (2018) Solidification heat transfer of nanofluid in existence of thermal radiation by means of FEM. Int J Heat Mass Transf 123:418–431
Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M (2020) Nanoparticles for improving the efficiency of heat recovery unit involving entropy generation analysis. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 115:96–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2020.09.033
Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Shafee A, Babazadeh H (2020) Acceleration of discharge process of clean energy storage unit with insertion of porous foam considering nanoparticle enhanced paraffin. J Clean Prod 261:121206
Sheikholeslami M, Farshad SA, Ebrahimpour Z, Said Z (2021) Recent progress on flat plate solar collectors and photovoltaic systems in the presence of nanofluid: a review. J Clean Prod 293:126119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126119
Shi M, Wang B, Shen Y, Jiang J, Zhu W, Su Y et al (2020) 3D assembly of MXene-stabilized spinel ZnMn2O4 for highly durable aqueous zinc-ion batteries. Chem Eng J 399:125627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125627
Singh RP, Kaushik SC, Rakshit D (2018) Melting phenomenon in a finned thermal storage system with graphene nano-plates for medium temperature applications. Energy Convers Manag 163:86–99
Sui M, Li C, Wu W, Yang M, Ali HM, Zhang Y et al (2021) Temperature of grinding carbide with castor oil-based MoS2 nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication. J Therm Sci Eng Appl 13(5):51001. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4049982
Sun M, Yan L, Zhang L, Song L, Guo J, Zhang H (2019) New insights into the rapid formation of initial membrane fouling after in-situ cleaning in a membrane bioreactor. Process Biochem 1991(78):108–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2019.01.004
Sun M, Hou B, Wang S, Zhao Q, Zhang L, Song L et al (2021) Effects of NaClO shock on MBR performance under continuous operating conditions. Environ Sci: Water Res Technol 7(2):344–396. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ew00760a
Venkitaraj KP, Suresh S, Praveen B, Nair SC (2018) Experimental heat transfer analysis of macro packed neopentylglycol with CuO nano additives for building cooling applications. J Energy Storage 17:1–10
Wang X, Li C, Zhang Y, Ding W, Yang M, Gao T et al (2020a) Vegetable oil-based nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication turning: academic review and perspectives. J Manuf Processes 59:76–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.09.044
Wang T, Almarashi A, Al-Turki YA, Abu-Hamdeh NH, Hajizadeh MR, Chu Y-M (2020b) Approaches for expedition of discharging of PCM involving nanoparticles and radial fins. J Mol Liq. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.115052
Xiong P-Y, Almarashi A, Dhahad HA, Alawee WH, Abusorrah AM, Issakhov A, Abu-Hamdeh NH, Shafee A, Chu Y-M (2021a) Nanomaterial transportation and exergy loss modeling incorporating CVFEM. J Mol Liq. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.115591
Xiong P-Y, Almarashi A, Dhahad HA, Alawee WH, Issakhov A, Chu Y-M (2021b) Nanoparticles for phase change process of water utilizing FEM. J Mol Liq. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.116096
Yadav D, Chu Y-M, Li Z (2021) Examination of the nanofluid convective instability of vertical constant throughflow in a porous medium layer with variable gravity. Appl Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01700-2
Yan X, Huang X, Chen Y, Liu Y, Xia L, Zhang T et al (2021) A theoretical strategy of pure carbon materials for lightweight and excellent absorption performance. Carbon (new York) 174:662–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.11.044
Yang X, Li Q, Lu E, Wang Z, Gong X, Yu Z et al (2019) Taming the stability of Pd active phases through a compartmentalizing strategy toward nanostructured catalyst supports. Nat Commun 10(1):1611. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09662-4
Yang Y, Chen H, Zou X, Shi X, Liu W, Feng L et al (2020) Flexible carbon-fiber/semimetal Bi nanosheet arrays as separable and recyclable plasmonic photocatalysts and photoelectrocatalysts. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(22):24845–24854. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c05695
Yang M, Li C, Luo L, Li R, Long Y (2021) Predictive model of convective heat transfer coefficient in bone micro-grinding using nanofluid aerosol cooling. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer 125:105317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2021.105317
Yin F, Xue X, Zhang C, Zhang K, Han J, Liu B et al (2021) Multifidelity genetic transfer: an efficient framework for production optimization. SPE J. https://doi.org/10.2118/205013-PA
Zhang Y, Li C, Jia D, Zhang D, Zhang X (2015) Experimental evaluation of the lubrication performance of MoS2/CNT nanofluid for minimal quantity lubrication in Ni-based alloy grinding. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 99:19–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2015.09.003
Zhang H, Sun M, Song L, Guo J, Zhang L (2019a) Fate of NaClO and membrane foulants during in-situ cleaning of membrane bioreactors: combined effect on thermodynamic properties of sludge. Biochem Eng J 147:146–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2019.04.016
Zhang T, Wu X, Fan X, Tsang DCW, Li G, Shen Y (2019b) Corn waste valorization to generate activated hydrochar to recover ammonium nitrogen from compost leachate by hydrothermal assisted pretreatment. J Environ Manag 236:108–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.01.018
Zhang K, Huo Q, Zhou Y, Wang H, Li G, Wang Y, Wang Y (2019c) Textiles/metal–organic frameworks composites as flexible air filters for efficient particulate matter removal. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(19):17368–17374. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b01734
Zhang W, Hu Y, Liu J, Wang H, Wei J, Sun P et al (2020a) Progress of ethylene action mechanism and its application on plant type formation in crops. Saudi J Biol Sci 27(6):1667–1673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.12.038
Zhang H, Guan W, Zhang L, Guan X, Wang S (2020b) Degradation of an organic dye by bisulfite catalytically activated with iron manganese oxides: the role of superoxide radicals. ACS Omega 5(29):18007–18012. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c01257
Zhang J, Wu W, Li C, Yang M, Zhang Y, Jia D et al (2020c) Convective heat transfer coefficient model under nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication coupled with cryogenic air grinding Ti–6Al–4V. Int J Precis Eng Manuf-Green Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-020-00268-6
Zhang K, Yang Z, Mao X, Chen X, Li H, Wang Y (2020d) Multifunctional textiles/metal−organic frameworks composites for efficient ultraviolet radiation blocking and noise reduction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(49):55316–55323. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c18147
Zhang J, Wang M, Tang Y, Ding Q, Wanga C, Huang X et al (2021a) Angular velocity measurement with improved scale factor based on a wideband-tunable optoelectronic oscillator. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2021.3067183
Zhang L, Zheng H, Wan T, Shi D, Lyu L, Cai G (2021b) An integrated control algorithm of power distribution for islanded microgrid based on improved virtual synchronous generator. IET Renew Power Gener. https://doi.org/10.1049/rpg2.12191
Zhao CY, Tao YB, Yu YS (2020a) Molecular dynamics simulation of nanoparticle effect on melting enthalpy of paraffin phase change material. Int J Heat Mass Transfer 150:119382
Zhao X, Gu B, Gao F, Chen S (2020b) Matching model of energy supply and demand of the integrated energy system in coastal areas. J Coastal Res 103(sp1):983. https://doi.org/10.2112/SI103-205.1
Zhenjing D, Qingan Y, Changhe L, Lan D, Xiufang B, Yanbin Z et al (2020) Milling force and surface morphology of 45 steel under different Al2O3 nanofluid concentrations. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 107(3–4):1277–1296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-04969-9
Zhu D, Wang B, Ma H, Wang H (2020) Evaluating the vulnerability of integrated electricity-heat-gas systems based on the high-dimensional random matrix theory. CSEE J Power Energy Syst 6(4):878–889. https://doi.org/10.17775/CSEEJPES.2019.00440
Zuo C, Chen Q, Tian L, Waller L, Asundi A (2015) Transport of intensity phase retrieval and computational imaging for partially coherent fields: the phase space perspective. Opt Lasers Eng 71:20–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2015.03.006
Zuo C, Sun J, Li J, Zhang J, Asundi A et al (2017) High-resolution transport-of-intensity quantitative phase microscopy with annular illumination. Sci Rep 7(1):7622–7654. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06837-1
Zuo X, Dong M, Gao F, Tian S (2020) The modeling of the electric heating and cooling system of the integrated energy system in the coastal area. J Coastal Res 103(sp1):1022. https://doi.org/10.2112/SI103-213.1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest
Ethical stardard
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by the author.
Informed constent
In this article, no patient care was involved.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, Y. Effect of inclusion of nanoparticles on unsteady heat transfer. Appl Nanosci 13, 957–970 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01960-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01960-y