Abstract
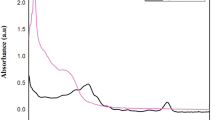
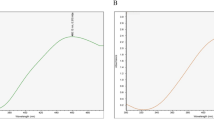
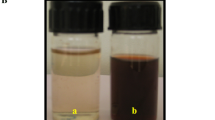
The present investigation was aimed to phytosynthesize silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) by utilizing aqueous extract of Mentha longifolia branches to reduce mass Ag into Ag° and evaluation of their potential to treat HCT116 colon cancer, Leishmanial, and bacterial cells. A characteristic Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) band to confirm synthesis was observed at ~ 450 nm of λ light by UV–Visible spectrophotometer. SEM and AFM micrographs unraveled that nanostructures are anisotropic, spherical and have a size under ~ 100 nm. Particle size analysis confirmed that the majority of the nanoparticles exist in ~ 6–20 nm of the size range. EDX investigation represented the highest peak of Ag with ~ 74% signal intensity. FTIR analysis confirmed the presence of the N–H (amine) group, C–N (cyanide) group and C≡C (alkynes) stretch as the surface capping agents. AgNPs were found biocompatible against human RBCs at a lower dose and LD100 was recorded as 117 μg/ml, which shows that a very high dose of AgNPs is required to cause toxicity to RBCs. The selective dose-dependent response of AgNPs was reported against Leishmania tropica and decreasing the dose of the nanoparticles resulted in increasing the survival rate of the pathogen (P < 0.05);10 μg/ml of AgNPs killed practically 67% of cells. Antibacterial action against plant bacterial pathogens was seen between 2 and 12 μg/ml. Annexin V apoptosis analysis and SRB examination showed that the plant aqueous extract and AgNPs are incapable to control the development of HCT116 colon cancer cells and only 3.77% cells indicated apoptosis. The results show the biocompatibility of phyto-functionalized nano-silver to selectively treat Leishmania and plant bacterial pathogens.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi BA, Iqbal J, Mahmood T et al (2019) Biofabrication of iron oxide nanoparticles by leaf extract of Rhamnus virgata: characterization and evaluation of cytotoxic, antimicrobial and antioxidant potentials. Appl Organomet Chem 33:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4947
Abdelhakim HK, El-Sayed ER, Rashidi FB (2020) Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles with antimicrobial, anticancer, antioxidant and photocatalytic activities by the endophytic Alternaria tenuissima. J Appl Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14581
Akhtar MS, Panwar J, Yun YS (2013) Biogenic synthesis of metallic nanoparticles by plant extracts. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 1:591–602. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc300118u
Al-Ansari M, Alkubaisi N, Gopinath K et al (2019) Facile and cost-effective Ag nanoparticles fabricated by Lilium lancifolium leaf extract: antibacterial and antibiofilm potential. J Clust Sci 30:1081–1089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-019-01569-w
Alsammarraie FK, Wang W, Zhou P et al (2018) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using turmeric extracts and investigation of their antibacterial activities. Coll Surf B Biointerfaces 171:398–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.07.059
Anandan M, Poorani G, Boomi P et al (2019) Green synthesis of anisotropic silver nanoparticles from the aqueous leaf extract of Dodonaea viscosa with their antibacterial and anticancer activities. Process Biochem 80:80–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2019.02.014
Ashokraja C, Sakar M, Balakumar S (2017) A perspective on the hemolytic activity of chemical and green-synthesized silver and silver oxide nanoparticles. Mater Res Express 4:12. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aa90f2
Bahadori MB, Zengin G, Bahadori S et al (2018) Phenolic composition and functional properties of wild mint (Mentha longifolia var. calliantha (Stapf) Briq.). Int J Food Prop 21:198–208. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2018.1440238
Bai J, Choi SH, Ponciano G et al (2000) Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae avirulence genes contribute differently and specifically to pathogen aggressiveness. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 13:1322–1329. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI.2000.13.12.1322
Behravan M, Hossein Panahi A, Naghizadeh A et al (2019) Facile green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Berberis vulgaris leaf and root aqueous extract and its antibacterial activity. Int J Biol Macromol 124:148–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.101
Champoiseau PG, Jones JB, Allen C (2009) Ralstonia solanacearum race 3 biovar 2 causes tropical losses and temperate anxieties. Plant Heal Prog 10:35. https://doi.org/10.1094/php-2009-0313-01-rv
Ciardi JA, Tieman DM, Lund ST et al (2000) Response to Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria in tomato involves regulation of ethylene receptor gene expression. Plant Physiol 123:81–92. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.123.1.81
de Oliveira AC, J, Araújo AR de, Quelemes PV, et al (2019) Solvent-free production of phthalated cashew gum for green synthesis of antimicrobial silver nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 213:176–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.02.033
Dong YH, Zhang XF, Xu JL, Zhang LH (2004) Insecticidal Bacillus thuringiensis silences Erwinia carotovora Virulence by a new form of microbial antagonism, signal interference. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:954–960. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.2.954-960.2004
Durán N, Durán M, de Jesus MB et al (2016) Silver nanoparticles: a new view on mechanistic aspects on antimicrobial activity. Nanomedicine nanotechnology. Biol Med 12:789–799
Fani S, Kamalidehghan B, Lo KM et al (2016) Anticancer activity of a monobenzyltin complex C1 against MDA-MB-231 cells through induction of Apoptosis and inhibition of breast cancer stem cells. Sci Rep 6:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38992
Fatih B, Madani K, Chibane M, Duez P (2017) Chemical composition and biological activities of mentha species. Aromat Med Plants Back Nat. https://doi.org/10.5772/67291
Francis S, Joseph S, Koshy EP, Mathew B (2018) Microwave assisted green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of elephantopus scaber and its environmental and biological applications artif cells. Nanomed Biotechnol 46:795–804. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2017.1345921
Iqbal G, Faisal S, Khan S et al (2019a) Photo-inactivation and efflux pump inhibition of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus using thiolated cobalt doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 192:141–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.01.021
Iqbal J, Abbasi BA, Mahmood T et al (2019b) Green synthesis and characterizations of Nickel oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Rhamnus virgata and their potential biological applications. Appl Organomet Chem 33:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4950
Javed B, Raja NI, Nadhman A, Mashwani ZUR (2020) Understanding the potential of bio - fabricated non—oxidative silver nanoparticles to eradicate Leishmania and plant bacterial pathogens. Appl Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01355-5
Jemilugba OT, Sakho EHM, Parani S et al (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Combretum erythrophyllum leaves and its antibacterial activities. Coll Interface Sci Commun 31:100191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2019.100191
Kalaiselvi D, Mohankumar A, Shanmugam G et al (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using latex extract of Euphorbia tirucalli: a novel approach for the management of root knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita. Crop Prot 117:108–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2018.11.020
Kędziora A, Speruda M, Krzyżewska E et al (2018) Similarities and differences between silver ions and silver in nanoforms as antibacterial agents. Int J Mol Sci 19:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020444
Khandel P, Shahi SK, Soni DK et al (2018) Alpinia calcarata: potential source for the fabrication of bioactive silver nanoparticles. Nano Converg 5:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40580-018-0167-9
Khatami M, Sharifi I, Nobre MAL et al (2018) Waste-grass-mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and evaluation of their anticancer, antifungal and antibacterial activity. Green Chem Lett Rev 11:125–134. https://doi.org/10.1080/17518253.2018.1444797
Ma P, Mumper RJ (2013) Anthracycline nano-delivery systems to overcome multiple drug resistance: a comprehensive review. Nano Today 8:313–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2013.04.006
Manosalva N, Tortella G, Cristina Diez M et al (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: effect of synthesis reaction parameters on antimicrobial activity. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2664-3
Mashwani Z ur R, Khan T, Khan MA, Nadhman A (2015) Synthesis in plants and plant extracts of silver nanoparticles with potent antimicrobial properties: current status and future prospects. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:9923–9934. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6987-1
Momin B, Rahman S, Jha N, Annapure US (2019) Valorization of mutant Bacillus licheniformis M09 supernatant for green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: photocatalytic dye degradation, antibacterial activity, and cytotoxicity. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 42:541–553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-018-2057-2
Nadhman A, Nazir S, Ihsanullah Khan M et al (2014) PEGylated silver doped zinc oxide nanoparticles as novel photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy against Leishmania. Free Radic Biol Med 77:230–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.09.005
Nadhman A, Nazir S, Khan MI et al (2015) Visible-light-responsive ZnCuO nanoparticles: Benign photodynamic killers of infectious protozoans. Int J Nanomedicine 10:6891–6903. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S91666
Naz S, Sirajuddin M, Hussain I et al (2020) 2-Phenylbutyric acid based organotin(IV) carboxylates; synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, antibacterial action against plant pathogens and in vitro hemolysis. J Mol Struct 1203:127378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.127378
Ng CM, Chen PC, Manickam S (2012) Green high-gravitational synthesis of silver nanoparticles using a rotating packed bed reactor (RPBR). Ind Eng Chem Res 51:5375–5381. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie201795u
Nindawat S, Agrawal V (2019) Fabrication of silver nanoparticles using Arnebia hispidissima (Lehm.) A. DC. root extract and unravelling their potential biomedical applications artif cells. Nanomedicine Biotechnol 47:166–180. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2018.1548469
Pareek V, Gupta R, Panwar J (2018) Do physico-chemical properties of silver nanoparticles decide their interaction with biological media and bactericidal action? A review. Mater Sci Eng C 90:739–749
Parthiban E, Manivannan N, Ramanibai R, Mathivanan N (2019) Green synthesis of silver-nanoparticles from Annona reticulata leaves aqueous extract and its mosquito larvicidal and anti-microbial activity on human pathogens. Biotechnol Rep 21:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2018.e00297
Prabhu D, Arulvasu C, Babu G et al (2013) Biologically synthesized green silver nanoparticles from leaf extract of Vitex negundo L. induce growth-inhibitory effect on human colon cancer cell line HCT15. Process Biochem 48:317–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2012.12.013
Rajeshkumar S, Bharath LV, Geetha R (2019) Broad spectrum antibacterial silver nanoparticle green synthesis: characterization, and mechanism of action. In: Green synthesis, characterization and applications of nanoparticles. Elsevier, pp 429–444
Rolim WR, Pelegrino MT, de Araújo LB et al (2019) Green tea extract mediated biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles: characterization, cytotoxicity evaluation and antibacterial activity. Appl Surf Sci 463:66–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.08.203
Sunayana N, Uzma M, Dhanwini RP et al (2019) Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles from Vitex negundo leaf extract to inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation through in vitro and in vivo. J Clust Sci 31:463–477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-019-01661-1
Thirumagal N, Jeyakumari AP (2019) Structural, optical and antibacterial properties of green synthesized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using Justicia adhatoda L. Leaf Extract J Clust Sci 31:487–497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-019-01663-z
Ulaeto SB, Mathew GM, Pancrecious JK, et al (2019) Biogenic Ag nanoparticles from neem extract: their structural evaluation and antimicrobial effects against pseudomonas nitroreducens and Aspergillus unguis (NII 08123)
Vichai V, Kirtikara K (2006) Sulforhodamine B colorimetric assay for cytotoxicity screening. Nat Protoc 1:1112–1116. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.179
Wei L, Lu J, Xu H et al (2015) Silver nanoparticles: synthesis, properties, and therapeutic applications. Drug Discov Today 20:595–601
Zhang Z, Li S, Gu X et al (2019) Biosynthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles by the Arctic anti-oxidative bacterium Paracoccus sp. Arc7-R13 artif cells. Nanomedicine Biotechnol 47:1488–1495. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1601631
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Javed, B., Nadhman, A. & Mashwani, ZuR. Phytosynthesis of Ag nanoparticles from Mentha longifolia: their structural evaluation and therapeutic potential against HCT116 colon cancer, Leishmanial and bacterial cells. Appl Nanosci 10, 3503–3515 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01428-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01428-5