Abstract
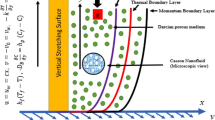
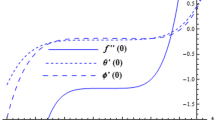
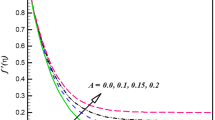
A mathematical framework for mixed convective non-Newtonian nanoliquid subjected to hydromagnetic characteristics is addressed in this attempt. The well-known Buongiorno nanoliquid model which elaborates thermophoretic and Brownian diffusions aspect is opted for formulation. In addition, heat generation, double stratification and convective conditions are retained. Apposite variables are introduced for dimensionless procedure. Homotopy scheme is employed to attain convergent expressions. Graphs are presented for description of sundry variables effect versus dimensionless quantities.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \({u,}\,{v}\) :
-
Velocity components
- \(\rho_{\text{f}}\) :
-
Density of base liquid
- \(x,\,\;y\) :
-
Space coordinates
- \(\nu\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity
- \(\mu\) :
-
Dynamic viscosity
- \(\alpha\) :
-
Thermal diffusivity
- \(k\) :
-
Thermal conductivity
- \((\rho c)_{\text{f}}\) :
-
Liquid heat capacity
- \(\tau\) :
-
Heat capacity ratio
- \(\pi_{\text{c}}\) :
-
Critical value of non-Newtonian model
- \(p_{\text{y}}\) :
-
Fluid yield stress
- \(u_{\text{w}} (x)\) :
-
Stretching velocity
- \(c\) :
-
Stretching rate
- \(\lambda\) :
-
Thermal buoyancy parameter
- \(D_{\text{B}}\) :
-
Brownian movement coefficient
- \(D_{\text{T}}\) :
-
Thermophoresis diffusion coefficient
- \(\sigma\) :
-
Electrical conductivity
- \(B_{0}\) :
-
Magnetic field strength
- T :
-
Temperature
- C :
-
Concentration
- \(a_{1} ,\;a_{2} ,\;d_{1} ,\;d_{2}\) :
-
Dimensional constants
- \(C_{{{\text{f}}_{x} }} \;Re_{x}^{{\tfrac{1}{2}}}\) :
-
Dimensionless drag force
- \(Nu\;Re_{x}^{{ - \tfrac{1}{2}}}\) :
-
Dimensionless heat transfer rate
- \(Sh\;Re_{x}^{{ - \tfrac{1}{2}}}\) :
-
Dimensionless mass transfer rate
- \(T_{\text{f}}\) :
-
Hot fluid temperature
- \(C_{\text{f}}\) :
-
Hot fluid concentration
- \(T_{\infty }\) :
-
Ambient fluid temperature
- \(C_{\infty }\) :
-
Ambient fluid concentration
- \(T_{0}\) :
-
Reference temperature
- \(C_{0}\) :
-
Reference concentration
- \(\pi\) :
-
Deformation rate
- \(\beta\) :
-
Material parameter of Casson fluid
- \(\gamma_{1}\) :
-
Thermal Biot number
- \(N_{\text{t}}\) :
-
Thermophoretic variable
- \(\gamma_{2}\) :
-
Solutal Biot number
- \(N_{\text{b}}\) :
-
Brownian motion variable
- \(Ha\) :
-
Hartman number
- \(N\) :
-
Buoyancy ratio parameter
- \(Sc\) :
-
Schmidt number
- \(S_{1}\) :
-
Thermal stratified variable
- \(S_{2}\) :
-
Solutal stratified variable
- \(Pr\) :
-
Prandtl number
- \(Re_{x}\) :
-
Reynolds numbers
- \(f(\eta )\) :
-
Dimensionless velocity
- \(\theta (\eta )\) :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- \(\phi (\eta )\) :
-
Dimensionless concentration
- \(\hbar_{f} ,\;\hbar_{\theta } ,\;\hbar_{\phi }\) :
-
Auxiliary variables
- \(\eta\) :
-
Dimensionless variable
References
Abbasi FM, Hayat T, Ahmad B (2015) Peristalsis of silver–water nanofluid in the presence of Hall and Ohmic heating effects: applications in drug delivery. J Mol Liq 207:248–255
Alshomrani AS, Irfan M, Salem A, Khan M (2018) Chemically reactive flow and heat transfer of magnetite Oldroyd-B nanofluid subject to stratifications. Appl Nanosci 8:1743–1754
Animasaun IL, Adebile EA, Fagbade AI (2016) Casson fluid flow with variable thermo-physical property along exponentially stretching sheet with suction and exponentially decaying internal heat generation using the homotopy analysis method. J Niger Math Soc 35:1–17
Buongiorno J (2006) Convective transport in nanofluids. ASME J Heat Transf 128:240–250
Chen C (2010) On the analytic solution of MHD flow and heat transfer for two types of viscoelastic fluid over a stretching sheet with energy dissipation, internal heat source and thermal radiation. Int J Heat Mass Transf 53:4264–4273
Choi SUS, Eastman JA (1995) Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. In: ASME international mechanical engineering congress expo, pp 99–105
Eastman JA, Choi SUS, Li S, Yu W, Thompson LJ (2001) Anomalously increased effective thermal conductivities of ethylene glycol-based nanofluids containing copper nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett 78:718
Fotukian SM, Esfahany MN (2010) Experimental investigation of turbulent convective heat transfer of dilute γ-Al2O3/water nanofluid inside a circular tube. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 31:606–612
Godson L, Raja B, Lal DM, Wongwises S (2010) Enhancement of heat transfer using nanofluids-an overview. Renew Sust Energy Rev 14:629–641
Hamid A, Hashim Y, Khan M (2018) Impacts of binary chemical reaction with activation energy on unsteady flow of magneto-Williamson nanofluid. J Mol Liq 262:435–442
Hayat T, Shafiq A, Alsaedi A (2016) Hydromagnetic boundary layer flow of Williamson fluid in the presence of thermal radiation and Ohmic dissipation. Alex Eng J 55:2229–2240
Hayat T, Khalid H, Waqas M, Alsaedi A, Ayub M (2017) Homotopic solutions for stagnation point flow of third-grade nanoliquid subject to magnetohydrodynamics. Results Phys 7:4310–4317
Hussain T, Shehzad SA, Alsaedi A, Hayat T, Ramzan M (2015) Flow of Casson nanofluid with viscous dissipation and convective conditions: a mathematical model. J Cent South Univ 22:1132–1140
Liao S (2004) On the homotopy analysis method for nonlinear problems. Appl Math Comput 147:499–513
Mabood F, Das K (2019) Outlining the impact of melting on MHD Casson fluid flow past a stretching sheet in a porous medium with radiation. Heliyon 5:e01216
Mahanthesh B, Gireesh BJ, Shehzad SA, Rauf A, Kumar PBS (2018) Nonlinear radiated MHD flow of nanoliquids due to a rotating disk with irregular heat source and heat flux condition. Phys B 537:98–104
Mohammed L, Gomaa HG, Ragab D, Zhu J (2017) Magnetic nanoparticles for environmental and biomedical applications: a review. Particuology 30:1–14
Pal D, Mandal G (2015) Hydromagnetic convective-radiative boundary layer flow of nanofluids induced by a non-linear vertical stretching/shrinking sheet with viscous-Ohmic dissipation. Powder Technol 279:61–74
Patterson C, Syed M, Takemura Y (2018) Harmonic decomposition of magneto-optical signal from suspensions of superparamagnetic nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 451:248–253
Qayyum S, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2018) Thermal radiation and heat generation/absorption aspects in third grade magneto-nanofluid over a slendering stretching sheet with Newtonian conditions. Phys B 537:139–149
Sadiq MA, Waqas M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2019) Modeling and analysis of Maxwell nanofluid considering mixed convection and Darcy–Forchheimer relation. Appl Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-00968-9
Sezer N, Atieh MA, Koc M (2019) A comprehensive review on synthesis, stability, thermophysical properties, and characterization of nanofluids. Powder Technol 344:404–431
Shahsavani E, Afrand M, Kalbasi R (2018) Experimental study on rheological behavior of water–ethylene glycol mixture in the presence of functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J Therm Anal Calorim 131:1177–1185
Sithole H, Mondal H, Goqo S, Sibanda P, Motsa S (2018) Numerical simulation of couple stress nanofluid flow in magneto-porous medium with thermal radiation and a chemical reaction. Appl Math Comput 339:820–836
Waqas M (2019) A mathematical and computational framework for heat transfer analysis of ferromagnetic non-Newtonian liquid subjected to heterogeneous and homogeneous reactions. J Magn Magn Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.165646
Waqas M, Farooq M, Khan MI, Alsaedi A, Hayat T, Yasmeen T (2016) Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) mixed convection flow of micropolar liquid due to nonlinear stretched sheet with convective condition. Int J Heat Mass Transf 102:766–772
Waqas M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2018a) A theoretical analysis of SWCNT–MWCNT and H2O nanofluids considering Darcy–Forchheimer relation. Appl Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-0833-6
Waqas M, Hayat T, Shehzad SA, Alsaedi A (2018b) Transport of magnetohydrodynamic nanomaterial in a stratified medium considering gyrotactic microorganisms. Phys B 529:33–40
Waqas M, Shehzad SA, Hayat T, Khan MI, Alsaedi A (2019a) Simulation of magnetohydrodynamics and radiative heat transport in convectively heated stratified flow of Jeffrey nanofluid. J Phys Chem Solids 133:45–51
Waqas M, Jabeen S, Hayat T, Khan MI, Alsaedi A (2019b) Modeling and analysis for magnetic dipole impact in nonlinear thermally radiating Carreau nanofluid flow subject to heat generation. J Magn Magn Mater 485:197–204
Waqas M, Khan MI, Hayat T, Farooq S, Alsaedi A (2019c) Interaction of thermal radiation in hydromagnetic viscoelastic nanomaterial subject to gyrotactic microorganisms. Appl Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-00938-7
Xing M, Yu J, Wang R (2015) Thermo-physical properties of water-based single-walled carbon nanotube nanofluid as advanced coolant. Appl Therm Eng 87:344–351
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gulzar, M.M., Waqas, M., Asghar, Z. et al. Rheology of mixed convective Casson nanofluid in a convectively heated stratified medium. Appl Nanosci 10, 3227–3233 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01166-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01166-3