Abstract
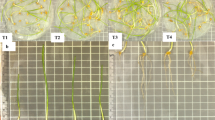
This study was carried out to evaluate the effect of Actinomycetes with Plant growoth promoting activity on the growth and yield of maize. This allowed the selection of three Actinomycetes: Actinomycetes sp. H7, O19 and AHB12 for their ability to solubilize phosphates, fix atmospheric nitrogen, and produce antimicrobial substances, enzymes, phytohormones and for their high vigour index. Five seeds, previously sanitized, inoculated and coated, were sown per pot. The best isolates selected in greenhouses were tested in station experiments. In pot, the inoculated seeds, with Actinomycete sp. H7 gave the best growth in plant size, 19.3% more compared to the uninoculated control (P ≤ 0.05). In station experiments, it was found that Actinomycete sp. H7 significantly increased the fresh and dry biomass of the aerial part with 919.7 g and 405.6 g, respectively, against 636.70 g and 297.36 g respectively for the control. The best yield of seeds was obtained with the combination O19-AHB12 with a yield of 311.5 g for 1000 seeds compared to 178.28 g for the uninoculated control. All corn seeds inoculated showed better growth than controls. These results confirm the value of the PGPRs and above all open a way for the formulation and the use of biofertilizers based on PGPRs in Mali.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adjanohoun A, Noumavo PA, Sikirou R, Allagbe M, Gotoechan-Hodonou H, Doss KK, Yehouenou B, Glele Kakaï R, Baba-Moussa L (2012) Effets des rhizobactéries PGPR sur le rendement et les teneurs en macroéléments du maïs sur sol ferralitique non dégradé au Sud-Bénin. Int. J. Biol. Chem Sci 6(1):279–288
Ahmad F, Ahmad I, Khan MS (2005) Indole acetic acid production by the indigenous isolates of azotobacter and fluorescent pseudomonas in the presence and absence of tryptophan. Turk J Biol 29:29–34
Alikhani HA, Saleh-Rhastin N, Antoun H (2006) Phosphate solubilisation activity of rhizobia native to Iranian soils. Plant Soil 287:35–41
Asghar H, Zahir Z, Arshadand M, Khaliq A (2002) Relationship between in VitroProduction of auxins by Rhizobacteria and their growth-promoting activities in bras- sica juncea L. Biol Fertil Soils 35(4):231–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-002-0462-8
Azcon R (2000) Papel de la simbiosis micorrizica y suinteraccionconotros microorganismos rizosfericos en el crecimiento vegetal y sostenibilidad Agricola; in: Ecologıa, fisiologıay biotecnologıa de la micorriza arbuscular. Edited by Alarcon, A. and Ferrera-Cerrato, R.; 1–35; Colegio de Postgraduados en Ciencias Agrıcolas. Montecillo, Estado de Mexico. Mundi Prensa, Mexico
Babana AH, Bathily H, Samaké F, Traoré D, Dicko AH (2011) Microbiological control of bacterial soft rot caused by Bacillus pumilus Od23 on potato in Mali. British Microbioly Res J 1(3):41–48
Babana AH, Dicko AH, Maiga K, Traoré D (2013) Characterization of rock phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms isolated from wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) rhizosphere in Mali. J Microbiol Microb Res 1(1):1–6
Burd GL, Dixon DG, Glick BR (2000) Plant growth promoting Rhizobacteria that decrease heavy metal toxicity in plants. Can J Microbiol 33(3):237–245. https://doi.org/10.1139/w99-143
Burr TJ (1978) Increased potato yields by treatment of seedpieces with specific strains of pseudomonas fluorescens and P. putida. Phytopathology 68(9):1377
Chakraborty BN, Chakraborty U, Saha A, Sunar K, Dey PL (2010) Evaluation of phosphate Solubilizers from soils of north Bengal and their diversity analysis. World J Agri Sci 6(2):195–200
Dicko A.H. 2012. Isolement et Caractérisation d’Actinomycètes à Activité Antibactérienne et Antifongique des Sols Rhizospheriques de Kabala. Mémoire de DEA, Université des Sciences, des Techniques et des Technologies de Bamako 50 pp.
Dicko AH, Verma RK (2014) Effect of growth promoting microbes on initial growth of maize. Indian J Trop Biodiv 22(1):64–69
Dicko AH, Babana AH, Maïga K, Kassogué A, Traoré D, Faradji FA (2013) Isolation and characterization of crop rhizospheric actinomycetes with antimicrobial activity in Mali. African J Appl Microbiol Res 2(1):1–8
Döbereiner J, Baldani VLD, Baldani JI (1995) Como isolar e identificar bactérias diazotróficas de plantas não-leguminosas. Brasilia: EMBRAPA-SPI: Itaguí: EMBRAPA-CNPAB 19–25
Egamberdiyeva D (2007) The effect of plant growth promoting Bacteria on growth and nutrient uptake of maize in two different soils. Appl Soil Ecol 36(2–3):184–189
El-Kholy MA, El-Ashry S, Gomaa AM (2005) Biofertilization of maize crop and its impact on yield and grains nutrient content under low rates of mineral fertilizers. J Appl Sci Res 1(2):117–121
El-Tarabily KA (2008) Promotion of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) plant growth by rhizosphere competent 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid deaminase-producing streptomycete Actinomycetes. Plant Soil 308:161–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9616-2
Frommel MI, Nowak J, Lazarovits G (1993) Treatment of potato tubers with a growth promotingPseudomonas sp.: Plant growth responses and bacterium distribution in the rhizosphere. Plant Soil 150(1):51–60
Gholami A, Shahsavani S, Nezarat S (2009) The effect of plant growth promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) on germination, seedling growth and yield of maize. World Acad Sci Eng Technol 49:19–24
Gopalakrishnan S, Srinivas V, Alekhya G, Prakash B (2015) Effect of plant growth-promoting Streptomyces sp. on growth promotion and grain yield in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L). 3 Biotech 5:799–806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-015-0283-8
Glick BR, Liu C, Ghosh S, Dumbroff EB (1997) Early development of canola seedlings in the presence of the plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Pseudomonas putida GR12-2. Soil Biol Biochem 29(8):1233–1239
Govindappa M, Ravishankar RV, Lokesh S (2011) Screening of Pseudomonas fluorescens isolates for biological control of Macrophomina phaseolina root-rot of safflower. Afr J Agric Res 6(29):6256–6266
Hafsa Cherif (2014) Amélioration de la croissance du blé dur en milieu salin par inoculation avec Bacillus sp. et Pantoea agglomerans isolées de sols arides. These de doctorat, Université Ferhat Abbas Sétif 1. 177 pages
Hamdali H, Hafidi M, Virolle MJ, Ouhdouch Y (2008) Growth promotion and protection against damping-off of wheat by two rock phosphate solubilizing actinomycetes in a P-deficient soil under greenhouse conditions. Appl Soil Ecol 40:510–517
IITA (2011) 2006 Annual Report of the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture. IITA, Ibadan, p 77
Jog R, Pandya M, Nareshkumar G, Rajkumar S (2014) Mechanism of phosphate solubilization and antifungal activity of Streptomyces spp. isolated from wheat roots and rhizosphere and their application in improving plant growth. Microbiology 160:778–788. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.074146-0
Júnior FPI, Duarte Pereira GP, Perin L, Mesquita da Silva L, Baraúna AC, Alves FM, Passos SR, Zilli JE (2013) Diazotrophic bacteria isolated from wild rice Oryza glumaepatula (Poaceae) in the Brazilian Amazon. Rev Biol Trop. (Int. J. Trop. Biol. ISSN-0034-7744) 61(2):991–999
Merriman PR, Price RD, Kollmorgen JF, Piggott T, Ridge EH (1974) Effect of seed inoculation with Bacillus subtilis and Streptomyces griseus on the growth of cereals and carrots. Aust J Agric Res 25(2):219–226
Meunchang S, Thongraar P, Sanoh S, Kaewsuralikhit S, Ando S (2006) Development of rhizobacteria as a biofer tilizer for rice production. International Workshop on Sustained Management of the Soil-Rhizosphere System for Efficient Crop Production and Fertilizer Use, 16–20 October. P: 1–7
Noumavo PA, Eméric K, Yédéou OD, Adolphe A, Marcellin A, Rachidatou S, Emma WG, Simeon OK, Lamine BM (2013) Effect of different plant growth promoting Rhizobacteria on maize seed germination and seedling development. Am J Plant Sci 4:1013–1021
Pikovskaya RI (1948) Mobilization of phosphorus in soil inconnection with the vital activity of some microbial species. Mikrobiologiya 17:362–370
Ruget F, Bonhomme R, Chartier M (1996) Estimation Simple de la Surface Foliaire de Plantes de Maïs en Croissance. Agronomie 16(9):553–562. https://doi.org/10.1051/agro:19960903
Rupela OP, Gopalakrishnan S, Krajewski M, Sriveni M (2003) A novel method for the identification and enumeration of microorganisms with potential for suppressing fungal plant pathogens. Biol Fertil Soils 39:131–134
Saadoun I, Rawashdeh R, Dayeh T, Ababneh Q, Mahasneh A (2007) Isolation, characterization and screening for Fiber hydrolytic enzymes-producing Streptomyces of Jordanian Forest soils. Asian network for scientific information. Biotechnology 6(1):120–128
Salantur A, Ozturk A, Akten S (2006) Growth and yield response of spring wheat (Triticumaestivum L.) to inoculation with Rhizobacteria. Plant Soil Environ 52(3):111–118
Sompong M, Thongraar P, Sanoh S, Sirilak K and Shotaro A (2006) Development of Rhizobacteria as a biofertilizer for rice production. International Workshop on Sustained Management of the Soil-Rhizosphere System for Efficient Crop Production and Fertilizer Use 16–20 October, 12p
Steel RG, Torrie DJH (1980) Principles and procedures of statistics, a biometrical approach. MacGraw-Hill Book Co., New York
Venkatachalam P, Ronald J, Sambath K (2010) Effect of soil streptomyces on seed germination. Int J Pharm Bio Sci 1(4) 0975-6299
Wu SC, Cao ZH, Li ZG, Cheung KC, Wong MH (2005) Effects of biofertilizer containing N-fixer, P and K solubilizers and AM fungi on maize growth: a greenhouse trial. Geoderma 125:155–166
Zafar-Ul-Hye M, Zahir ZA, Shahzad SM, Naveed M, Arshad M, Khalid M (2007) Preliminary screening of rhizobacteria containing acc-deaminase for promoting growth of lentil seedlings under axenic condition. Pak J Bot 39(5):1725–1738
Zaki AEF, Samira RM, Yahia EZ, Samar I (2003) DNA-fingerprints and phylogenetic studies of some Chitinolytic Actinomycete isolates. Biotechnology 2(2):131–140
Acknowledgements
My thanks go to the International Foundation for Science (IFS), TWAS, Marketplace, Nam S/T center and World Bank through the West Africa Agricultural Productivity Program (WAAP/Mali) for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dicko, A.H., Babana, A.H., Kassogué, A. et al. A Malian native plant growth promoting Actinomycetes based biofertilizer improves maize growth and yield. Symbiosis 75, 267–275 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-018-0555-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-018-0555-2