Abstract
Neuroinflammation is associated with the pathophysiologies of neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders. Evaluating neuroinflammation using positron emission tomography (PET) plays an important role in the early diagnosis and determination of proper treatment of brain diseases. To quantify neuroinflammatory responses in vivo, many PET tracers have been developed using translocator proteins, imidazole-2 binding site, cyclooxygenase, monoamine oxidase-B, adenosine, cannabinoid, purinergic P2X7, and CSF-1 receptors as biomarkers. In this review, we introduce the latest developments in PET tracers that can image neuroinflammation, focusing on clinical trials, and further consider their current implications.





© SNMMI

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated in the current study.
References
Kempuraj D, Thangavel R, Natteru PA, Selvakumar GP, Saeed D, Zahoor H, et al. Neuroinflammation Induces Neurodegeneration. J Neurol Neurosurg Spine. 2016;1:1003.
Dong X. Current Strategies for Brain Drug Delivery. Theranostics. 2018;8:1481–93.
Sun YX, Minthon L, Wallmark A, Warkentin S, Blennow K, Janciauskiene S. Inflammatory markers in matched plasma and cerebrospinal fluid from patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2003;16:136–44.
Shastri A, Bonifati DM, Kishore U. Innate immunity and neuroinflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013: 342931.
Kwon HS, Koh SH. Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: the roles of microglia and astrocytes. Transl Neurodegener. 2020;9:42.
Jellinger KA. Basic mechanisms of neurodegeneration: a critical update. J Cell Mol Med. 2010;14:457–87.
de Araujo Boleti AP, de Oliveira Flores TM, Moreno SE, Anjos LD, Mortari MR, Migliolo L. Neuroinflammation: An overview of neurodegenerative and metabolic diseases and of biotechnological studies. Neurochem Int. 2020;136: 104714.
MacRitchie N, Frleta-Gilchrist M, Sugiyama A, Lawton T, McInnes IB, Maffia P. Molecular imaging of inflammation - Current and emerging technologies for diagnosis and treatment. Pharmacol Ther. 2020;211: 107550.
Brosseron F, Krauthausen M, Kummer M, Heneka MT. Body fluid cytokine levels in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: a comparative overview. Mol Neurobiol. 2014;50:534–44.
Morgan AR, Touchard S, Leckey C, O'Hagan C, Nevado-Holgado AJ, Consortium N et al. Inflammatory biomarkers in Alzheimer's disease plasma. Alzheimers Dement. 2019;15:776-87.
Nordengen K, Kirsebom BE, Henjum K, Selnes P, Gisladottir B, Wettergreen M, et al. Glial activation and inflammation along the Alzheimer’s disease continuum. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16:46.
Cagnin A, Brooks DJ, Kennedy AM, Gunn RN, Myers R, Turkheimer FE, et al. In-vivo measurement of activated microglia in dementia. Lancet. 2001;358:461–7.
Edison P, Archer HA, Gerhard A, Hinz R, Pavese N, Turkheimer FE, et al. Microglia, amyloid, and cognition in Alzheimer’s disease: An [11C](R)PK11195-PET and [11C]PIB-PET study. Neurobiol Dis. 2008;32:412–9.
Vivash L, O’Brien TJ. Imaging Microglial Activation with TSPO PET: Lighting Up Neurologic Diseases? J Nucl Med. 2016;57:165–8.
Zhang L, Hu K, Shao T, Hou L, Zhang S, Ye W, Josephson L, Meyer JH, Zhang MR, Vasdev N, Wang J, Xu H, Wang L, Liang SH. Recent developments on PET radiotracers for TSPO and their applications in neuroimaging. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021;11:373–93.
Venneti S, Wang G, Nguyen J, Wiley CA. The positron emission tomography ligand DAA1106 binds with high affinity to activated microglia in human neurological disorders. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2008;67:1001–10.
Doorduin J, Klein HC, de Jong JR, Dierckx RA, de Vries EF. Evaluation of [11C]DAA1106 for imaging and quantification of neuroinflammation in a rat model of herpes encephalitis. Nucl Med Biol. 2010;37:9–15.
Doorduin J, Klein HC, Dierckx RA, James M, Kassiou M, de Vries EF. [11C]DPA-713 and [18F]DPA-714 as new PET tracers for TSPO: a comparison with [11C](R)-PK11195 in a rat model of herpes encephalitis. Mol Imaging Biol. 2009;11:386–98.
Yokokura M, Terada T, Bunai T, Nakaizumi K, Takebayashi K, Iwata Y, et al. Depiction of microglial activation in aging and dementia: Positron emission tomography with [11C]DPA713 versus [11C](R)PK11195. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017;37:877–89.
Singhal T, Cicero S, Pan H, Carter K, Dubey S, Chu R, et al. Regional microglial activation in the substantia nigra is linked with fatigue in MS. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2020;7: e854.
Liu SY, Qiao HW, Song TB, Liu XL, Yao YX, Zhao CS, et al. Brain microglia activation and peripheral adaptive immunity in Parkinson’s disease: a multimodal PET study. J Neuroinflammation. 2022;19:209.
Kreisl WC, Lyoo CH, McGwier M, Snow J, Jenko KJ, Kimura N, et al. In vivo radioligand binding to translocator protein correlates with severity of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain. 2013;136:2228–38.
Alshikho MJ, Zurcher NR, Loggia ML, Cernasov P, Reynolds B, Pijanowski O, et al. Integrated magnetic resonance imaging and [11C]PBR28 positron emission tomographic imaging in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 2018;83:1186–97.
Felsky D, Roostaei T, Nho K, Risacher SL, Bradshaw EM, Petyuk V, et al. Neuropathological correlates and genetic architecture of microglial activation in elderly human brain. Nat Commun. 2019;10:409.
Hagens MHJ, Golla SV, Wijburg MT, Yaqub M, Heijtel D, Steenwijk MD, et al. In vivo assessment of neuroinflammation in progressive multiple sclerosis: a proof of concept study with [18F]DPA714 PET. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15:314.
Hamelin L, Lagarde J, Dorothee G, Potier MC, Corlier F, Kuhnast B, et al. Distinct dynamic profiles of microglial activation are associated with progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain. 2018;141:1855–70.
Kobayashi M, Jiang T, Telu S, Zoghbi SS, Gunn RN, Rabiner EA, et al. 11C-DPA-713 has much greater specific binding to translocator protein 18 kDa (TSPO) in human brain than 11C-(R)-PK11195. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018;38:393–403.
Owen DR, Yeo AJ, Gunn RN, Song K, Wadsworth G, Lewis A, et al. An 18-kDa translocator protein (TSPO) polymorphism explains differences in binding affinity of the PET radioligand PBR28. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2012;32:1–5.
Zanotti-Fregonara P, Pascual B, Veronese M, Yu M, Beers D, Appel SH, et al. Head-to-head comparison of 11C-PBR28 and 11C-ER176 for quantification of the translocator protein in the human brain. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019;46:1822–9.
Albert NL, Unterrainer M, Fleischmann DF, Lindner S, Vettermann F, Brunegraf A, et al. TSPO PET for glioma imaging using the novel ligand 18F-GE-180: first results in patients with glioblastoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017;44:2230–8.
Unterrainer M, Mahler C, Vomacka L, Lindner S, Havla J, Brendel M, et al. TSPO PET with [18F]GE-180 sensitively detects focal neuroinflammation in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018;45:1423–31.
Kim SJW, Lupo JM, Chen Y, Pampaloni MH, VanBrocklin HF, Narvid J, et al. A feasibility study for quantitative assessment of cerebrovascular malformations using flutriciclamide ([18F]GE-180) PET/MRI. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1091463.
Ikawa M, Lohith TG, Shrestha S, Telu S, Zoghbi SS, Castellano S, et al. 11C-ER176, a Radioligand for 18-kDa Translocator Protein, Has Adequate Sensitivity to Robustly Image All Three Affinity Genotypes in Human Brain. J Nucl Med. 2017;58:320–5.
Vettermann FJ, Harris S, Schmitt J, Unterrainer M, Lindner S, Rauchmann BS, et al. Impact of TSPO Receptor Polymorphism on [18F]GE-180 Binding in Healthy Brain and Pseudo-Reference Regions of Neurooncological and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Life (Basel). 2021;11:484.
Lee SH, Denora N, Laquintana V, Mangiatordi GF, Lopedota A, Lopalco A, et al. Radiosynthesis and characterization of [18F]BS224: a next-generation TSPO PET ligand insensitive to the rs6971 polymorphism. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021;49:110–24.
Rupprecht R, Papadopoulos V, Rammes G, Baghai TC, Fan J, Akula N, et al. Translocator protein (18 kDa) (TSPO) as a therapeutic target for neurological and psychiatric disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9:971–88.
Hasko G, Pacher P, Vizi ES, Illes P. Adenosine receptor signaling in the brain immune system. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2005;26:511–6.
Sheth S, Brito R, Mukherjea D, Rybak LP, Ramkumar V. Adenosine receptors: expression, function and regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15:2024–52.
Mishina M, Ishii K, Kimura Y, Suzuki M, Kitamura S, Ishibashi K et al. Adenosine A1 receptors measured with 11C-MPDX PET in early Parkinson's disease. Synapse. 2017;71.
Hayashi S, Inaji M, Nariai T, Oda K, Sakata M, Toyohara J, et al. Increased Binding Potential of Brain Adenosine A1 Receptor in Chronic Stages of Patients with Diffuse Axonal Injury Measured with [1-methyl-11C] 8-dicyclopropylmethyl-1-methyl-3-propylxanthine Positron Emission Tomography Imaging. J Neurotrauma. 2018;35:25–31.
Joya A, Ardaya M, Montilla A, Garbizu M, Plaza-Garcia S, Gomez-Vallejo V, et al. In vivo multimodal imaging of adenosine A1 receptors in neuroinflammation after experimental stroke. Theranostics. 2021;11:410–25.
Meyer PT, Elmenhorst D, Matusch A, Winz O, Zilles K, Bauer A. A1 adenosine receptor PET using [18F]CPFPX: displacement studies in humans. Neuroimage. 2006;32:1100–5.
Mishina M, Ishiwata K, Naganawa M, Kimura Y, Kitamura S, Suzuki M, et al. Adenosine A2A receptors measured with [11C]TMSX PET in the striata of Parkinson’s disease patients. PLoS One. 2011;6: e17338.
Rissanen E, Virta JR, Paavilainen T, Tuisku J, Helin S, Luoto P, et al. Adenosine A2A receptors in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis: a [11C]TMSX brain PET study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33:1394–401.
Ramlackhansingh AF, Bose SK, Ahmed I, Turkheimer FE, Pavese N, Brooks DJ. Adenosine 2A receptor availability in dyskinetic and nondyskinetic patients with Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2011;76:1811–6.
Barret O, Hannestad J, Vala C, Alagille D, Tavares A, Laruelle M, et al. Characterization in humans of 18F-MNI-444, a PET radiotracer for brain adenosine 2A receptors. J Nucl Med. 2015;56:586–91.
Ishibashi K, Miura Y, Wagatsuma K, Toyohara J, Ishiwata K, Ishii K. Occupancy of adenosine A2A receptors by istradefylline in patients with Parkinson’s disease using 11C-preladenant PET. Neuropharmacology. 2018;143:106–12.
Pacher P, Mechoulam R. Is lipid signaling through cannabinoid 2 receptors part of a protective system? Prog Lipid Res. 2011;50:193–211.
Schmole AC, Lundt R, Gennequin B, Schrage H, Beins E, Kramer A, et al. Expression Analysis of CB2-GFP BAC Transgenic Mice. PLoS One. 2015;10: e0138986.
Benito C, Tolon RM, Pazos MR, Nunez E, Castillo AI, Romero J. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors in human brain inflammation. Br J Pharmacol. 2008;153:277–85.
Evens N, Bosier B, Lavey BJ, Kozlowski JA, Vermaelen P, Baudemprez L, et al. Labelling and biological evaluation of [11C]methoxy-Sch225336: a radioligand for the cannabinoid-type 2 receptor. Nucl Med Biol. 2008;35:793–800.
Evens N, Vandeputte C, Coolen C, Janssen P, Sciot R, Baekelandt V, et al. Preclinical evaluation of [11C]NE40, a type 2 cannabinoid receptor PET tracer. Nucl Med Biol. 2012;39:389–99.
Ahmad R, Postnov A, Bormans G, Versijpt J, Vandenbulcke M, Van Laere K. Decreased in vivo availability of the cannabinoid type 2 receptor in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;43:2219–27.
Horti AG, Gao Y, Ravert HT, Finley P, Valentine H, Wong DF, et al. Synthesis and biodistribution of [11C]A-836339, a new potential radioligand for PET imaging of cannabinoid type 2 receptors (CB2). Bioorg Med Chem. 2010;18:5202–7.
Pottier G, Gomez-Vallejo V, Padro D, Boisgard R, Dolle F, Llop J, et al. PET imaging of cannabinoid type 2 receptors with [11C]A-836339 did not evidence changes following neuroinflammation in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017;37:1163–78.
Vandeputte C, Casteels C, Struys T, Koole M, van Veghel D, Evens N, et al. Small-animal PET imaging of the type 1 and type 2 cannabinoid receptors in a photothrombotic stroke model. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012;39:1796–806.
Valenzano KJ, Tafesse L, Lee G, Harrison JE, Boulet JM, Gottshall SL, et al. Pharmacological and pharmacokinetic characterization of the cannabinoid receptor 2 agonist, GW405833, utilizing rodent models of acute and chronic pain, anxiety, ataxia and catalepsy. Neuropharmacology. 2005;48:658–72.
Vandeputte C, Evens N, Toelen J, Deroose CM, Bosier B, Ibrahimi A, et al. A PET brain reporter gene system based on type 2 cannabinoid receptors. J Nucl Med. 2011;52:1102–9.
Ahamed M, van Veghel D, Ullmer C, Van Laere K, Verbruggen A, Bormans GM. Synthesis, Biodistribution and In vitro Evaluation of Brain Permeable High Affinity Type 2 Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists [11C]MA2 and [18F]MA3. Front Neurosci. 2016;10:431.
Attili B, Celen S, Ahamed M, Koole M, Haute CVD, Vanduffel W, et al. Preclinical evaluation of [18F]MA3: a CB(2) receptor agonist radiotracer for PET. Br J Pharmacol. 2019;176:1481–91.
Dubois RN, Abramson SB, Crofford L, Gupta RA, Simon LS, Van De Putte LB, et al. Cyclooxygenase in biology and disease. FASEB J. 1998;12:1063–73.
Choi SH, Aid S, Bosetti F. The distinct roles of cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 in neuroinflammation: implications for translational research. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009;30:174–81.
Shukuri M, Takashima-Hirano M, Tokuda K, Takashima T, Matsumura K, Inoue O, et al. In vivo expression of cyclooxygenase-1 in activated microglia and macrophages during neuroinflammation visualized by PET with 11C-ketoprofen methyl ester. J Nucl Med. 2011;52:1094–101.
Ohnishi A, Senda M, Yamane T, Mikami T, Nishida H, Nishio T, et al. Exploratory human PET study of the effectiveness of 11C-ketoprofen methyl ester, a potential biomarker of neuroinflammatory processes in Alzheimer’s disease. Nucl Med Biol. 2016;43:438–44.
Kim MJ, Shrestha SS, Cortes M, Singh P, Morse C, Liow JS, et al. Evaluation of Two Potent and Selective PET Radioligands to Image COX-1 and COX-2 in Rhesus Monkeys. J Nucl Med. 2018;59:1907–12.
Kim MJ, Anaya FJ, Manly LS, Lee JH, Hong J, Shrestha S, et al. Whole-Body PET Imaging in Humans Shows That 11C-PS13 Is Selective for Cyclooxygenase-1 and Can Measure the In Vivo Potency of Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs. J Nucl Med. 2023;64:159–64.
Zhao YF, Tang Y, Illes P. Astrocytic and Oligodendrocytic P2X7 Receptors Determine Neuronal Functions in the CNS. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021;14: 641570.
Ory D, Celen S, Gijsbers R, Van Den Haute C, Postnov A, Koole M, et al. Preclinical Evaluation of a P2X7 Receptor-Selective Radiotracer: PET Studies in a Rat Model with Local Overexpression of the Human P2X7 Receptor and in Nonhuman Primates. J Nucl Med. 2016;57:1436–41.
Van Weehaeghe D, Koole M, Schmidt ME, Deman S, Jacobs AH, Souche E, et al. [11C]JNJ54173717, a novel P2X7 receptor radioligand as marker for neuroinflammation: human biodistribution, dosimetry, brain kinetic modelling and quantification of brain P2X7 receptors in patients with Parkinson’s disease and healthy volunteers. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019;46:2051–64.
Berdyyeva T, Xia C, Taylor N, He Y, Chen G, Huang C, et al. PET Imaging of the P2X7 Ion Channel with a Novel Tracer [18F]JNJ-64413739 in a Rat Model of Neuroinflammation. Mol Imaging Biol. 2019;21:871–8.
Koole M, Schmidt ME, Hijzen A, Ravenstijn P, Vandermeulen C, Van Weehaeghe D, et al. 18F-JNJ-64413739, a Novel PET Ligand for the P2X7 Ion Channel: Radiation Dosimetry, Kinetic Modeling, Test-Retest Variability, and Occupancy of the P2X7 Antagonist JNJ-54175446. J Nucl Med. 2019;60:683–90.
Ginhoux F, Greter M, Leboeuf M, Nandi S, See P, Gokhan S, et al. Fate mapping analysis reveals that adult microglia derive from primitive macrophages. Science. 2010;330:841–5.
Tanzey SS, Shao X, Stauff J, Arteaga J, Sherman P, Scott PJH, et al. Synthesis and Initial In Vivo Evaluation of [11C]AZ683-A Novel PET Radiotracer for Colony Stimulating Factor 1 Receptor (CSF1R). Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2018;11:136.
Horti AG, Naik R, Foss CA, Minn I, Misheneva V, Du Y, et al. PET imaging of microglia by targeting macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116:1686–91.
Knight AC, Varlow C, Zi T, Liang SH, Josephson L, Schmidt K, et al. In Vitro Evaluation of [3H]CPPC as a Tool Radioligand for CSF-1R. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021;12:998–1006.
Kawamura K, Maeda J, Hatori A, Okauchi T, Nagai Y, Higuchi M, et al. In vivo and in vitro imaging of I2 imidazoline receptors in the monkey brain. Synapse. 2011;65:452–5.
Kawamura K, Naganawa M, Konno F, Yui J, Wakizaka H, Yamasaki T, et al. Imaging of I2-imidazoline receptors by small-animal PET using 2-(3-fluoro-[4-11C]tolyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole ([11C]FTIMD). Nucl Med Biol. 2010;37:625–35.
Kawamura K, Kimura Y, Yui J, Wakizaka H, Yamasaki T, Hatori A, et al. PET study using [11C]FTIMD with ultra-high specific activity to evaluate I2-imidazoline receptors binding in rat brains. Nucl Med Biol. 2012;39:199–206.
Kawamura K, Shimoda Y, Kumata K, Fujinaga M, Yui J, Yamasaki T, et al. In vivo evaluation of a new 18F-labeled PET ligand, [18F]FEBU, for the imaging of I2-imidazoline receptors. Nucl Med Biol. 2015;42:406–12.
Kawamura K, Yui J, Konno F, Yamasaki T, Hatori A, Wakizaka H, et al. Synthesis and evaluation of PET probes for the imaging of I2 imidazoline receptors in peripheral tissues. Nucl Med Biol. 2012;39:89–99.
Tyacke RJ, Myers JFM, Venkataraman A, Mick I, Turton S, Passchier J, et al. Evaluation of 11C-BU99008, a PET Ligand for the Imidazoline2 Binding Site in Human Brain. J Nucl Med. 2018;59:1597–602.
Wilson H, Dervenoulas G, Pagano G, Tyacke RJ, Polychronis S, Myers J, et al. Imidazoline 2 binding sites reflecting astroglia pathology in Parkinson’s disease: an in vivo 11C-BU99008 PET study. Brain. 2019;142:3116–28.
Mohamed MA, Zeng Z, Gennaro M, Lao-Kaim NP, Myers JFM, Calsolaro V et al. Astrogliosis in aging and Parkinson's disease dementia: a new clinical study with 11C-BU99008 PET. Brain Commun. 2022;4:fcac199.
Calsolaro V, Matthews PM, Donat CK, Livingston NR, Femminella GD, Guedes SS, et al. Astrocyte reactivity with late-onset cognitive impairment assessed in vivo using 11C-BU99008 PET and its relationship with amyloid load. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26:5848–55.
Livingston NR, Calsolaro V, Hinz R, Nowell J, Raza S, Gentleman S, et al. Relationship between astrocyte reactivity, using novel 11C-BU99008 PET, and glucose metabolism, grey matter volume and amyloid load in cognitively impaired individuals. Mol Psychiatry. 2022;27:2019–29.
Levitt P, Pintar JE, Breakefield XO. Immunocytochemical demonstration of monoamine oxidase B in brain astrocytes and serotonergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982;79:6385–9.
Fowler JS, MacGregor RR, Wolf AP, Arnett CD, Dewey SL, Schlyer D, et al. Mapping human brain monoamine oxidase A and B with 11C-labeled suicide inactivators and PET. Science. 1987;235:481–5.
Fowler JS, Wolf AP, MacGregor RR, Dewey SL, Logan J, Schlyer DJ, et al. Mechanistic positron emission tomography studies: demonstration of a deuterium isotope effect in the monoamine oxidase-catalyzed binding of [11C]L-deprenyl in living baboon brain. J Neurochem. 1988;51:1524–34.
Rusjan PM, Wilson AA, Miler L, Fan I, Mizrahi R, Houle S et al. Kinetic modeling of the monoamine oxidase B radioligand [11C]SL25.1188 in human brain with high-resolution positron emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2014;34:883-9.
Moriguchi S, Wilson AA, Miler L, Rusjan PM, Vasdev N, Kish SJ et al. Monoamine Oxidase B Total Distribution Volume in the Prefrontal Cortex of Major Depressive Disorder: An [11C]SL25.1188 Positron Emission Tomography Study. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76:634-41.
Gill T, Watling SE, Richardson JD, McCluskey T, Tong J, Meyer JH et al. Imaging of astrocytes in posttraumatic stress disorder: A PET study with the monoamine oxidase B radioligand [11C]SL25.1188. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022;54:54-61.
Koshimori Y, Cusimano MD, Vieira EL, Rusjan PM, Kish SJ, Vasdev N et al. Astrogliosis marker 11C-SL2511.88 PET in traumatic brain injury with persistent symptoms. Brain. 2023:awad279.
Ballweg A, Klaus C, Vogler L, Katzdobler S, Wind K, Zatcepin A, et al. [18F]F-DED PET imaging of reactive astrogliosis in neurodegenerative diseases: preclinical proof of concept and first-in-human data. J Neuroinflammation. 2023;20:68.
Dahl K, Bernard-Gauthier V, Nag S, Varnas K, Narayanaswami V, Mahdi Moein M et al. Synthesis and preclinical evaluation of [18F]FSL25.1188, a reversible PET radioligand for monoamine oxidase-B. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019;29:1624-7.
Harada R, Hayakawa Y, Ezura M, Lerdsirisuk P, Du Y, Ishikawa Y, et al. 18F-SMBT-1: A Selective and Reversible PET Tracer for Monoamine Oxidase-B Imaging. J Nucl Med. 2021;62:253–8.
Villemagne VL, Harada R, Dore V, Furumoto S, Mulligan R, Kudo Y, et al. Assessing Reactive Astrogliosis with 18F-SMBT-1 Across the Alzheimer Disease Spectrum. J Nucl Med. 2022;63:1560–9.
Chatterjee P, Dore V, Pedrini S, Krishnadas N, Thota R, Bourgeat P, et al. Plasma Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Is Associated with 18F-SMBT-1 PET: Two Putative Astrocyte Reactivity Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;92:615–28.
Galatro TF, Holtman IR, Lerario AM, Vainchtein ID, Brouwer N, Sola PR, et al. Transcriptomic analysis of purified human cortical microglia reveals age-associated changes. Nat Neurosci. 2017;20:1162–71.
Gosselin D, Skola D, Coufal NG, Holtman IR, Schlachetzki JCM, Sajti E et al. An environment-dependent transcriptional network specifies human microglia identity. Science. 2017;356:eaal3222.
Oberheim NA, Goldman SA, Nedergaard M. Heterogeneity of astrocytic form and function. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;814:23–45.
Tarassishin L, Suh HS, Lee SC. LPS and IL-1 differentially activate mouse and human astrocytes: role of CD14. Glia. 2014;62:999–1013.
Zhang Y, Sloan SA, Clarke LE, Caneda C, Plaza CA, Blumenthal PD, et al. Purification and Characterization of Progenitor and Mature Human Astrocytes Reveals Transcriptional and Functional Differences with Mouse. Neuron. 2016;89:37–53.
Camsonne R, Crouzel C, Comar D, Mazi6re M, Prenant C, Sastre J et al. Synthesis of N-(11C) methyl, N-(methyl-1 propyl), (chloro-2 phenyl)-1 isoquinoleine carboxamide-3 (PK 11195): A new ligand for peripheral benzodiazepine receptors. J Label Compd Radiopharm. 1984;21:985-91.
Schroeter M, Dennin MA, Walberer M, Backes H, Neumaier B, Fink GR, et al. Neuroinflammation extends brain tissue at risk to vital peri-infarct tissue: a double tracer [11C]PK11195- and [18F]FDG-PET study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2009;29:1216–25.
Becker G, Debatisse J, Riviere M, Crola Da Silva C, Beaudoin-Gobert M, Eker O et al. Spatio-Temporal Characterization of Brain Inflammation in a Non-human Primate Stroke Model Mimicking Endovascular Thrombectomy. Neurotherapeutics. 2023;20:789-802.
Debruyne JC, Versijpt J, Van Laere KJ, De Vos F, Keppens J, Strijckmans K, et al. PET visualization of microglia in multiple sclerosis patients using [11C]PK11195. Eur J Neurol. 2003;10:257–64.
Zhang MR, Kida T, Noguchi J, Furutsuka K, Maeda J, Suhara T, et al. [11C]DAA1106: radiosynthesis and in vivo binding to peripheral benzodiazepine receptors in mouse brain. Nucl Med Biol. 2003;30:513–9.
Maeda J, Suhara T, Zhang MR, Okauchi T, Yasuno F, Ikoma Y, et al. Novel peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligand [11C]DAA1106 for PET: an imaging tool for glial cells in the brain. Synapse. 2004;52:283–91.
Yasuno F, Ota M, Kosaka J, Ito H, Higuchi M, Doronbekov TK, et al. Increased binding of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor in Alzheimer’s disease measured by positron emission tomography with [11C]DAA1106. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;64:835–41.
James ML, Fulton RR, Henderson DJ, Eberl S, Meikle SR, Thomson S, et al. Synthesis and in vivo evaluation of a novel peripheral benzodiazepine receptor PET radioligand. Bioorg Med Chem. 2005;13:6188–94.
Chauveau F, Van Camp N, Dolle F, Kuhnast B, Hinnen F, Damont A, et al. Comparative evaluation of the translocator protein radioligands [11C]DPA-713, [18F]DPA-714, and [11C]PK11195 in a rat model of acute neuroinflammation. J Nucl Med. 2009;50:468–76.
Tsukada H, Nishiyama S, Ohba H, Kanazawa M, Kakiuchi T, Harada N. Comparing amyloid-beta deposition, neuroinflammation, glucose metabolism, and mitochondrial complex I activity in brain: a PET study in aged monkeys. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41:2127–36.
Endres CJ, Pomper MG, James M, Uzuner O, Hammoud DA, Watkins CC, et al. Initial evaluation of 11C-DPA-713, a novel TSPO PET ligand, in humans. J Nucl Med. 2009;50:1276–82.
Imaizumi M, Briard E, Zoghbi SS, Gourley JP, Hong J, Musachio JL, et al. Kinetic evaluation in nonhuman primates of two new PET ligands for peripheral benzodiazepine receptors in brain. Synapse. 2007;61:595–605.
Lartey FM, Ahn GO, Shen B, Cord KT, Smith T, Chua JY, et al. PET imaging of stroke-induced neuroinflammation in mice using [18F]PBR06. Mol Imaging Biol. 2014;16:109–17.
Fujimura Y, Zoghbi SS, Simeon FG, Taku A, Pike VW, Innis RB, et al. Quantification of translocator protein (18 kDa) in the human brain with PET and a novel radioligand, [18F]PBR06. J Nucl Med. 2009;50:1047–53.
Briard E, Zoghbi SS, Imaizumi M, Gourley JP, Shetty HU, Hong J, et al. Synthesis and evaluation in monkey of two sensitive 11C-labeled aryloxyanilide ligands for imaging brain peripheral benzodiazepine receptors in vivo. J Med Chem. 2008;51:17–30.
Imaizumi M, Kim HJ, Zoghbi SS, Briard E, Hong J, Musachio JL, et al. PET imaging with [11C]PBR28 can localize and quantify upregulated peripheral benzodiazepine receptors associated with cerebral ischemia in rat. Neurosci Lett. 2007;411:200–5.
Imaizumi M, Briard E, Zoghbi SS, Gourley JP, Hong J, Fujimura Y, et al. Brain and whole-body imaging in nonhuman primates of [11C]PBR28, a promising PET radioligand for peripheral benzodiazepine receptors. Neuroimage. 2008;39:1289–98.
Zanotti-Fregonara P, Pascual B, Rizzo G, Yu M, Pal N, Beers D, et al. Head-to-Head Comparison of [11C]PBR28 and [18F]GE180 for Quantification of the Translocator Protein in the Human Brain. J Nucl Med. 2018;59:1260–6.
James ML, Fulton RR, Vercoullie J, Henderson DJ, Garreau L, Chalon S, et al. DPA-714, a new translocator protein-specific ligand: synthesis, radiofluorination, and pharmacologic characterization. J Nucl Med. 2008;49:814–22.
Arlicot N, Vercouillie J, Ribeiro MJ, Tauber C, Venel Y, Baulieu JL, et al. Initial evaluation in healthy humans of [18F]DPA-714, a potential PET biomarker for neuroinflammation. Nucl Med Biol. 2012;39:570–8.
Wadsworth H, Jones PA, Chau WF, Durrant C, Fouladi N, Passmore J, et al. [18F]GE-180: a novel fluorine-18 labelled PET tracer for imaging Translocator protein 18 kDa (TSPO). Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012;22:1308–13.
Liu B, Le KX, Park MA, Wang S, Belanger AP, Dubey S, et al. In Vivo Detection of Age- and Disease-Related Increases in Neuroinflammation by [18F]GE180 TSPO MicroPET Imaging in Wild-Type and Alzheimer’s Transgenic Mice. J Neurosci. 2015;35:15716–30.
Lee JH, Simeon FG, Liow JS, Morse CL, Gladding RL, Santamaria JAM, et al. In Vivo Evaluation of 6 Analogs of 11C-ER176 as Candidate 18F-Labeled Radioligands for 18-kDa Translocator Protein. J Nucl Med. 2022;63:1252–8.
Simeon FG, Lee JH, Morse CL, Stukes I, Zoghbi SS, Manly LS, et al. Synthesis and Screening in Mice of Fluorine-Containing PET Radioligands for TSPO: Discovery of a Promising 18F-Labeled Ligand. J Med Chem. 2021;64:16731–45.
Zanotti-Fregonara P, Zhang Y, Jenko KJ, Gladding RL, Zoghbi SS, Fujita M, et al. Synthesis and evaluation of translocator 18 kDa protein (TSPO) positron emission tomography (PET) radioligands with low binding sensitivity to human single nucleotide polymorphism rs6971. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014;5:963–71.
Ishiwata K, Noguchi J, Wakabayashi S, Shimada J, Ogi N, Nariai T, et al. 11C-labeled KF18446: a potential central nervous system adenosine A2A receptor ligand. J Nucl Med. 2000;41:345–54.
Mishina M, Ishiwata K, Kimura Y, Naganawa M, Oda K, Kobayashi S, et al. Evaluation of distribution of adenosine A2A receptors in normal human brain measured with [11C]TMSX PET. Synapse. 2007;61:778–84.
Todde S, Moresco RM, Simonelli P, Baraldi PG, Cacciari B, Spalluto G, et al. Design, radiosynthesis, and biodistribution of a new potent and selective ligand for in vivo imaging of the adenosine A2A receptor system using positron emission tomography. J Med Chem. 2000;43:4359–62.
Moresco RM, Todde S, Belloli S, Simonelli P, Panzacchi A, Rigamonti M, et al. In vivo imaging of adenosine A2A receptors in rat and primate brain using [11C]SCH442416. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005;32:405–13.
Marques TR, Natesan S, Rabiner EA, Searle GE, Gunn R, Howes OD, et al. Adenosine A2A receptor in schizophrenia: an in vivo brain PET imaging study. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022;239:3439–45.
Ishiwata K, Nariai T, Kimura Y, Oda K, Kawamura K, Ishii K, et al. Preclinical studies on [11C]MPDX for mapping adenosine A1 receptors by positron emission tomography. Ann Nucl Med. 2002;16:377–82.
Fukumitsu N, Ishii K, Kimura Y, Oda K, Sasaki T, Mori Y, et al. Imaging of adenosine A1 receptors in the human brain by positron emission tomography with [11C]MPDX. Ann Nucl Med. 2003;17:511–5.
Holschbach MH, Olsson RA, Bier D, Wutz W, Sihver W, Schuller M, et al. Synthesis and evaluation of no-carrier-added 8-cyclopentyl-3-(3-[18F]fluoropropyl)-1-propylxanthine ([18F]CPFPX): a potent and selective A1-adenosine receptor antagonist for in vivo imaging. J Med Chem. 2002;45:5150–6.
Bauer A, Holschbach MH, Cremer M, Weber S, Boy C, Shah NJ, et al. Evaluation of 18F-CPFPX, a novel adenosine A1 receptor ligand: in vitro autoradiography and high-resolution small animal PET. J Nucl Med. 2003;44:1682–9.
Bauer A, Holschbach MH, Meyer PT, Boy C, Herzog H, Olsson RA, et al. In vivo imaging of adenosine A1 receptors in the human brain with [18F]CPFPX and positron emission tomography. Neuroimage. 2003;19:1760–9.
Zhou X, Khanapur S, Huizing AP, Zijlma R, Schepers M, Dierckx RA, et al. Synthesis and preclinical evaluation of 2-(2-furanyl)-7-[2-[4-[4-(2-[11C]methoxyethoxy)phenyl]-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]7H-pyrazolo[4,3-e][1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidine-5-amine ([11C]Preladenant) as a PET tracer for the imaging of cerebral adenosine A2A receptors. J Med Chem. 2014;57:9204–10.
Zhou X, Boellaard R, Ishiwata K, Sakata M, Dierckx R, de Jong JR, et al. In Vivo Evaluation of 11C-Preladenant for PET Imaging of Adenosine A2A Receptors in the Conscious Monkey. J Nucl Med. 2017;58:762–7.
Ishibashi K, Miura Y, Wagatsuma K, Toyohara J, Ishiwata K, Ishii K. Adenosine A2A Receptor Occupancy by Caffeine After Coffee Intake in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov Disord. 2022;37:853–7.
Barret O, Hannestad J, Alagille D, Vala C, Tavares A, Papin C, et al. Adenosine 2A receptor occupancy by tozadenant and preladenant in rhesus monkeys. J Nucl Med. 2014;55:1712–8.
Vala C, Morley TJ, Zhang X, Papin C, Tavares AA, Lee HS, et al. Synthesis and in vivo Evaluation of Fluorine-18 and Iodine-123 Pyrazolo[4,3-e]-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidine Derivatives as PET and SPECT Radiotracers for Mapping A2A Receptors. ChemMedChem. 2016;11:1936–43.
Evens N, Muccioli GG, Houbrechts N, Lambert DM, Verbruggen AM, Van Laere K, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of carbon-11- and fluorine-18-labeled 2-oxoquinoline derivatives for type 2 cannabinoid receptor positron emission tomography imaging. Nucl Med Biol. 2009;36:455–65.
Takashima-Hirano M, Shukuri M, Takashima T, Goto M, Wada Y, Watanabe Y, et al. General method for the 11C-labeling of 2-arylpropionic acids and their esters: construction of a PET tracer library for a study of biological events involved in COXs expression. Chemistry. 2010;16:4250–8.
Ohnishi A, Senda M, Yamane T, Sasaki M, Mikami T, Nishio T, et al. Human whole-body biodistribution and dosimetry of a new PET tracer, [11C]ketoprofen methyl ester, for imagings of neuroinflammation. Nucl Med Biol. 2014;41:594–9.
Singh P, Shrestha S, Cortes-Salva MY, Jenko KJ, Zoghbi SS, Morse CL et al. 3-Substituted 1,5-Diaryl-1 H-1,2,4-triazoles as Prospective PET Radioligands for Imaging Brain COX-1 in Monkey. Part 1: Synthesis and Pharmacology. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018;9:2610-9.
Kim MJ, Lee JH, Juarez Anaya F, Hong J, Miller W, Telu S, et al. First-in-human evaluation of [11C]PS13, a novel PET radioligand, to quantify cyclooxygenase-1 in the brain. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020;47:3143–51.
Shrestha S, Kim MJ, Eldridge M, Lehmann ML, Frankland M, Liow JS, et al. PET measurement of cyclooxygenase-2 using a novel radioligand: upregulation in primate neuroinflammation and first-in-human study. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17:140.
Kolb HC, Barret O, Bhattacharya A, Chen G, Constantinescu C, Huang C, et al. Preclinical Evaluation and Nonhuman Primate Receptor Occupancy Study of 18F-JNJ-64413739, a PET Radioligand for P2X7 Receptors. J Nucl Med. 2019;60:1154–9.
Coughlin JM, Du Y, Lesniak WG, Harrington CK, Brosnan MK, O’Toole R, et al. First-in-human use of 11C-CPPC with positron emission tomography for imaging the macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor. EJNMMI Res. 2022;12:64.
Kealey S, Turner EM, Husbands SM, Salinas CA, Jakobsen S, Tyacke RJ, et al. Imaging imidazoline-I2 binding sites in porcine brain using 11C-BU99008. J Nucl Med. 2013;54:139–44.
Kawamura K, Yamasaki T, Zhang Y, Wakizaka H, Hatori A, Xie L, et al. Change in the Binding of [11C]BU99008 to Imidazoline I2 Receptor Using Brain PET in Zucker Rats. Mol Imaging Biol. 2019;21:105–12.
Parker CA, Nabulsi N, Holden D, Lin SF, Cass T, Labaree D, et al. Evaluation of 11C-BU99008, a PET ligand for the imidazoline2 binding sites in rhesus brain. J Nucl Med. 2014;55:838–44.
Venkataraman AV, Keat N, Myers JF, Turton S, Mick I, Gunn RN, et al. First evaluation of PET-based human biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of 11C-BU99008, a tracer for imaging the imidazoline2 binding site. EJNMMI Res. 2018;8:71.
Bench CJ, Price GW, Lammertsma AA, Cremer JC, Luthra SK, Turton D, et al. Measurement of human cerebral monoamine oxidase type B (MAO-B) activity with positron emission tomography (PET): a dose ranging study with the reversible inhibitor Ro 19–6327. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1991;40:169–73.
Rodriguez-Vieitez E, Ni R, Gulyas B, Toth M, Haggkvist J, Halldin C, et al. Astrocytosis precedes amyloid plaque deposition in Alzheimer APPswe transgenic mouse brain: a correlative positron emission tomography and in vitro imaging study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;42:1119–32.
Arakawa R, Stenkrona P, Takano A, Nag S, Maior RS, Halldin C. Test-retest reproducibility of [11C]-L-deprenyl-D2 binding to MAO-B in the human brain. EJNMMI Res. 2017;7:54.
Bramoullé Y, Puech F, Saba W, Valette H, Bottlaender M, George P et al. Radiosynthesis of (S)-5-methoxymethyl-3-[6-(4,4,4-trifluorobutoxy)benzo[d]isoxazol-3-yl] oxazolidin-2-[11C]one ([11C]SL25.1188), a novel radioligand for imaging monoamine oxidase-B with PET. Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals. 2008;51:153-8.
Saba W, Valette H, Peyronneau MA, Bramoulle Y, Coulon C, Curet O et al. [11C]SL25.1188, a new reversible radioligand to study the monoamine oxidase type B with PET: preclinical characterisation in nonhuman primate. Synapse. 2010;64:61-9.
Nag S, Fazio P, Lehmann L, Kettschau G, Heinrich T, Thiele A, et al. In Vivo and In Vitro Characterization of a Novel MAO-B Inhibitor Radioligand, 18F-Labeled Deuterated Fluorodeprenyl. J Nucl Med. 2016;57:315–20.
Villemagne VL, Harada R, Dore V, Furumoto S, Mulligan R, Kudo Y, et al. First-in-Humans Evaluation of 18F-SMBT-1, a Novel 18F-Labeled Monoamine Oxidase-B PET Tracer for Imaging Reactive Astrogliosis. J Nucl Med. 2022;63:1551–9.
Fan Z, Calsolaro V, Atkinson RA, Femminella GD, Waldman A, Buckley C, et al. Flutriciclamide (18F-GE180) PET: First-in-Human PET Study of Novel Third-Generation In Vivo Marker of Human Translocator Protein. J Nucl Med. 2016;57:1753–9.
Feeney C, Scott G, Raffel J, Roberts S, Coello C, Jolly A, et al. Kinetic analysis of the translocator protein positron emission tomography ligand [18F]GE-180 in the human brain. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;43:2201–10.
Sakata M, Ishibashi K, Imai M, Wagatsuma K, Ishii K, Zhou X, et al. Initial Evaluation of an Adenosine A2A Receptor Ligand, 11C-Preladenant, in Healthy Human Subjects. J Nucl Med. 2017;58:1464–70.
Acknowledgements
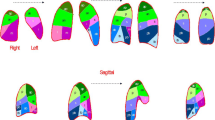
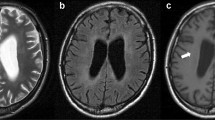
In this paper, we used figures from the previously published papers to help readers understand. Fig. 2. was published in “Exploratory human PET study of the effectiveness of 11C-ketoprofen methyl ester, a potential biomarker of neuroinflammatory processes in Alzheimer's disease.” Nucl Med Biol 2016;43:438 and reprint permission was obtained from Elsevier. The articles containing Fig. 3 and Fig. 4. were licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction. Fig. 3. was published in “Relationship between astrocyte reactivity, using novel 11C-BU99008 PET, and glucose metabolism, grey matter volume and amyloid load in cognitively impaired individuals.” Mol Psychiatry 2022;27:2019. Fig. 4. was published in “[18F]F-DED PET imaging of reactive astrogliosis in neurodegenerative diseases: preclinical proof of concept and first-in-human data.” J Neuroinflammation 2023;20:68. Fig 5. was originally published in “Assessing Reactive Astrogliosis with 18F-SMBT-1 Across the Alzheimer Disease Spectrum” J Nucl Med 2022;63:1560.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from the Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences (KIRAMS), the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), Republic of Korea (No. 50461–2023), and the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (NRF-2020R1A2C2008618).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Namhun Lee, Jae Yong Choi, and Young Hoon Ryu declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required and informed consent is not applicable.
Consent for publication
The participants signed consent regarding publishing their data.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, N., Choi, J.Y. & Ryu, Y.H. The development status of PET radiotracers for evaluating neuroinflammation. Nucl Med Mol Imaging (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-023-00831-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-023-00831-4