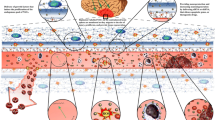
Abstract
The efficacy and safety of treating ischemic stroke is still a challenging problem at this stage. Ischemic stroke has a special stroke microenvironment. In recent years, improving stroke microenvironment has become a new idea for treating ischemic stroke. At the same time, nanoparticles have unique physical and chemical properties and significant advantages in studying ischemic stroke. Therefore, in recent years, researchers have designed various types of nanoparticles in response to stroke microenvironment to treat ischemic stroke. In this review, we summarized and analyzed the ischemic areas targeted by nanoparticles in response to reactive oxygen species, pH, high expression of receptors in the blood–brain barrier, enrichment of molecules in the stroke microenvironment, light, magnetic harmony, and other stimuli. We analyze its advantages and disadvantages and look forward to the development prospect of this field. Hope to provide strategies for better treatment of ischemic stroke.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable
References
Zhou, M., Wang, H., Zeng, X., Yin, P., Zhu, J., Chen, W., Li, X., Wang, L., Wang, L., Liu, Y., Liu, J., Zhang, M., Qi, J., Yu, S., Afshin, A., Gakidou, E., Glenn, S., Krish, V. S., Miller-Petrie, M. K., … Liang, X. (2019). Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet, 394(10204), 1145–1158.
Benjamin, E. J., Virani, S. S., Callaway, C. W., Chamberlain, A. M., Chang, A. R., Cheng, S., Chiuve, S. E., Cushman, M., Delling, F. N., Deo, R., de Ferranti, S. D., Ferguson, J. F., Fornage, M., Gillespie, C., Isasi, C. R., Jiménez, M. C., Jordan, L. C., Judd, S. E., Lackland, D., … Muntner, P. (2018). Heart Disease and stroke statistics-2018 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation, 137(12), e67–e492.
Benjamin, E. J., Blaha, M. J., Chiuve, S. E., Cushman, M., Das, S. R., Deo, R., de Ferranti, S. D., Floyd, J., Fornage, M., Gillespie, C., Isasi, C. R., Jiménez, M. C., Jordan, L. C., Judd, S. E., Lackland, D., Lichtman, J. H., Lisabeth, L., Liu, S., Longenecker, C. T., … Muntner, P. (2017). Heart disease and stroke statistics-2017 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation, 135(10), e146–e603.
Arumugam, T. V., Baik, S. H., Balaganapathy, P., Sobey, C. G., Mattson, M. P., & Jo, D. G. (2018). Notch signaling and neuronal death in stroke. Progress in Neurobiology, 165–167, 103–116.
Ham, P. B., 3rd, Raju, R., (2017). Mitochondrial function in hypoxic ischemic injury and influence of aging. Prog Neurobiol, 157, 92-116
He, Q., Ma, Y., Liu, J., Zhang, D., Ren, J., Zhao, R., Chang, J., Guo, Z. N., & Yang, Y. (2021). Biological functions and regulatory mechanisms of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in ischemic stroke. Frontiers in Immunology, 12, 801985.
Khaja, A. M., & Grotta, J. C. (2007). Established treatments for acute ischaemic stroke. Lancet, 369(9558), 319–330.
Sacco, R. L., Chong, J. Y., Prabhakaran, S., & Elkind, M. S. (2007). Experimental treatments for acute ischaemic stroke. Lancet, 369(9558), 331–341.
Mizuma, A., You, J. S., & Yenari, M. A. (2018). Targeting reperfusion injury in the age of mechanical thrombectomy. Stroke, 49(7), 1796–1802.
Jones, A. R., & Shusta, E. V. (2007). Blood-brain barrier transport of therapeutics via receptor-mediation. Pharmaceutical Research, 24(9), 1759–1771.
Patel, T., Zhou, J., Piepmeier, J. M., & Saltzman, W. M. (2012). Polymeric nanoparticles for drug delivery to the central nervous system. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 64(7), 701–705.
Lobatto, M. E., Fuster, V., Fayad, Z. A., & Mulder, W. J. (2011). Perspectives and opportunities for nanomedicine in the management of atherosclerosis. Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery, 10(11), 835–852.
Thomas, C. R., Ferris, D. P., Lee, J. H., Choi, E., Cho, M. H., Kim, E. S., Stoddart, J. F., Shin, J. S., Cheon, J., & Zink, J. I. (2010). Noninvasive remote-controlled release of drug molecules in vitro using magnetic actuation of mechanized nanoparticles. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 132(31), 10623–10625.
Zhang, N. N., Shen, X., Liu, K., Nie, Z., & Kumacheva, E. (2022). Polymer-tethered nanoparticles: From surface engineering to directional self-assembly. Accounts of Chemical Research, 55(11), 1503–1513.
Whitesides, G. M. (2003). The ‘right’ size in nanobiotechnology. Nature Biotechnology, 21(10), 1161–1165.
Morachis, J. M., Mahmoud, E. A., & Almutairi, A. (2012). Physical and chemical strategies for therapeutic delivery by using polymeric nanoparticles. Pharmacological Reviews, 64(3), 505–519.
Algar, W. R., Massey, M., Rees, K., Higgins, R., Krause, K. D., Darwish, G. H., Peveler, W. J., Xiao, Z., Tsai, H. Y., Gupta, R., Lix, K., Tran, M. V., & Kim, H. (2021). Photoluminescent nanoparticles for chemical and biological analysis and imaging. Chemical Reviews, 121(15), 9243–9358.
Kim, K. S., Suzuki, K., Cho, H., Youn, Y. S., & Bae, Y. H. (2018). Oral nanoparticles exhibit specific high-efficiency intestinal uptake and lymphatic transport. ACS Nano, 12(9), 8893–8900.
Hutter, E., & Maysinger, D. (2011). Gold nanoparticles and quantum dots for bioimaging. Microscopy Research and Technique, 74(7), 592–604.
Bhumkar, D. R., Joshi, H. M., Sastry, M., & Pokharkar, V. B. (2007). Chitosan reduced gold nanoparticles as novel carriers for transmucosal delivery of insulin. Pharmaceutical Research, 24(8), 1415–1426.
Phillips, R. L., Miranda, O. R., You, C. C., Rotello, V. M., & Bunz, U. H. (2008). Rapid and efficient identification of bacteria using gold-nanoparticle-poly(para-phenyleneethynylene) constructs. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English), 47(14), 2590–2594.
Kairdolf, B. A., Qian, X., & Nie, S. (2017). Bioconjugated nanoparticles for biosensing, in vivo imaging, and medical diagnostics. Analytical Chemistry, 89(2), 1015–1031.
Saha, K., Agasti, S. S., Kim, C., Li, X., & Rotello, V. M. (2012). Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chemical Reviews, 112(5), 2739–2779.
Kaviarasi, S., Yuba, E., Harada, A., & Krishnan, U. M. (2019). Emerging paradigms in nanotechnology for imaging and treatment of cerebral ischemia. Journal of Controlled Release, 300, 22–45.
Nozohouri, S., Sifat, A. E., Vaidya, B., & Abbruscato, T. J. (2020). Novel approaches for the delivery of therapeutics in ischemic stroke. Drug Discovery Today, 25(3), 535–551.
Bharadwaj, V. N.; Nguyen, D. T.; Kodibagkar, V. D.; Stabenfeldt, S. E., Nanoparticle-based therapeutics for brain injury. Adv Healthc Mater 2018, 7 (1).
Sahay, G., Alakhova, D. Y., & Kabanov, A. V. (2010). Endocytosis of nanomedicines. Journal of Controlled Release, 145(3), 182–195.
Terstappen, G. C., Meyer, A. H., Bell, R. D., & Zhang, W. (2021). Strategies for delivering therapeutics across the blood-brain barrier. Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery, 20(5), 362–383.
Sandoval, K. E., & Witt, K. A. (2008). Blood-brain barrier tight junction permeability and ischemic stroke. Neurobiology of Diseases, 32(2), 200–219.
Jin, L., Zhu, Z., Hong, L., Qian, Z., Wang, F., & Mao, Z. (2023). ROS-responsive 18β-glycyrrhetic acid-conjugated polymeric nanoparticles mediate neuroprotection in ischemic stroke through HMGB1 inhibition and microglia polarization regulation. Bioact Mater, 19, 38–49.
Zhang, S., Peng, B., Chen, Z., Yu, J., Deng, G., Bao, Y., Ma, C., Du, F., Sheu, W. C., Kimberly, W. T., Simard, J. M., Coman, D., Chen, Q., Hyder, F., Zhou, J., & Sheth, K. N. (2022). Brain-targeting, acid-responsive antioxidant nanoparticles for stroke treatment and drug delivery. Bioact Mater, 16, 57–65.
Shen, Z., Liu, T., Li, Y., Lau, J., Yang, Z., Fan, W., Zhou, Z., Shi, C., Ke, C., Bregadze, V. I., Mandal, S. K., Liu, Y., Li, Z., Xue, T., Zhu, G., Munasinghe, J., Niu, G., Wu, A., & Chen, X. (2018). Fenton-reaction-acceleratable magnetic nanoparticles for ferroptosis therapy of orthotopic brain tumors. ACS Nano, 12(11), 11355–11365.
Bao, Q., Hu, P., Xu, Y., Cheng, T., Wei, C., Pan, L., & Shi, J. (2018). Simultaneous blood-brain barrier crossing and protection for stroke treatment based on edaravone-loaded ceria nanoparticles. ACS Nano, 12(7), 6794–6805.
Kim, H. Y., Kim, T. J., Kang, L., Kim, Y. J., Kang, M. K., Kim, J., Ryu, J. H., Hyeon, T., Yoon, B. W., Ko, S. B., & Kim, B. S. (2020). Mesenchymal stem cell-derived magnetic extracellular nanovesicles for targeting and treatment of ischemic stroke. Biomaterials, 243, 119942.
Correa-Paz, C., Navarro Poupard, M. F., Polo, E., Rodríguez-Pérez, M., Migliavacca, M., Iglesias-Rey, R., Ouro, A., Maqueda, E., Hervella, P., Sobrino, T., Castillo, J., Del Pino, P., Pelaz, B., & Campos, F. (2022). Sonosensitive capsules for brain thrombolysis increase ischemic damage in a stroke model. J Nanobiotechnology, 20(1), 46.
Yu, W., Yin, N., Yang, Y., Xuan, C., Liu, X., Liu, W., Zhang, Z., Zhang, K., Liu, J., & Shi, J. (2022). Rescuing ischemic stroke by biomimetic nanovesicles through accelerated thrombolysis and sequential ischemia-reperfusion protection. Acta Biomaterialia, 140, 625–640.
Chamorro, Á., Dirnagl, U., Urra, X., & Planas, A. M. (2016). Neuroprotection in acute stroke: Targeting excitotoxicity, oxidative and nitrosative stress, and inflammation. Lancet Neurology, 15(8), 869–881.
Minnerup, J., Sutherland, B. A., Buchan, A. M., & Kleinschnitz, C. (2012). Neuroprotection for stroke: Current status and future perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(9), 11753–11772.
de Los Ríos la Rosa, F.; Khoury, J.; Kissela, B. M.; Flaherty, M. L.; Alwell, K.; Moomaw, C. J.; Khatri, P.; Adeoye, O.; Woo, D.; Ferioli, S.; Kleindorfer, D. O., (2012). Eligibility for intravenous recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator within a population: The effect of the European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (ECASS) III Trial. Stroke, 43 (6), 1591–5.
Fu, Y., Liu, Q., Anrather, J., & Shi, F. D. (2015). Immune interventions in stroke. Nature Reviews. Neurology, 11(9), 524–535.
Mracsko, E., Javidi, E., Na, S. Y., Kahn, A., Liesz, A., & Veltkamp, R. (2014). Leukocyte invasion of the brain after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Stroke, 45(7), 2107–2114.
Kleinschnitz, C., Kraft, P., Dreykluft, A., Hagedorn, I., Göbel, K., Schuhmann, M. K., Langhauser, F., Helluy, X., Schwarz, T., Bittner, S., Mayer, C. T., Brede, M., Varallyay, C., Pham, M., Bendszus, M., Jakob, P., Magnus, T., Meuth, S. G., Iwakura, Y., … Wiendl, H. (2013). Regulatory T cells are strong promoters of acute ischemic stroke in mice by inducing dysfunction of the cerebral microvasculature. Blood, 121(4), 679–691.
Kanazawa, M., Ninomiya, I., Hatakeyama, M., Takahashi, T., Shimohata, T., (2017). Microglia and monocytes/macrophages polarization reveal novel therapeutic mechanism against stroke. Int J Mol Sci, 18 (10).
Ma, Y., Wang, J., Wang, Y., & Yang, G. Y. (2017). The biphasic function of microglia in ischemic stroke. Progress in Neurobiology, 157, 247–272.
Tang, C., Wang, C., Zhang, Y., Xue, L., Li, Y., Ju, C., & Zhang, C. (2019). Recognition, intervention, and monitoring of neutrophils in acute ischemic stroke. Nano Letters, 19(7), 4470–4477.
Mai, C. L., Tan, Z., Xu, Y. N., Zhang, J. J., Huang, Z. H., Wang, D., Zhang, H., Gui, W. S., Zhang, J., Lin, Z. J., Meng, Y. T., Wei, X., Jie, Y. T., Grace, P. M., Wu, L. J., Zhou, L. J., & Liu, X. G. (2021). CXCL12-mediated monocyte transmigration into brain perivascular space leads to neuroinflammation and memory deficit in neuropathic pain. Theranostics, 11(3), 1059–1078.
Hubert, V., Hristovska, I., Karpati, S., Benkeder, S., Dey, A., Dumot, C., Amaz, C., Chounlamountri, N., Watrin, C., Comte, J. C., Chauveau, F., Brun, E., Marche, P., Lerouge, F., Parola, S., Berthezène, Y., Vorup-Jensen, T., Pascual, O., & Wiart, M. (2021). Multimodal imaging with nanogd reveals spatiotemporal features of neuroinflammation after experimental stroke. Adv Sci (Weinh), 8(17), e2101433.
Wang, J., Su, Q., Lv, Q., Cai, B., Xiaohalati, X., Wang, G., Wang, Z., & Wang, L. (2021). Oxygen-generating cyanobacteria powered by upconversion-nanoparticles-converted near-infrared light for ischemic stroke treatment. Nano Letters, 21(11), 4654–4665.
Powers, W. J., Rabinstein, A. A., Ackerson, T., Adeoye, O. M., Bambakidis, N. C., Becker, K., Biller, J., Brown, M., Demaerschalk, B. M., Hoh, B., Jauch, E. C., Kidwell, C. S., Leslie-Mazwi, T. M., Ovbiagele, B., Scott, P. A., Sheth, K. N., Southerland, A. M., Summers, D. V., & Tirschwell, D. L. (2019). Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke, 50(12), e344–e418.
Li, J., Dirisala, A., Ge, Z., Wang, Y., Yin, W., Ke, W., Toh, K., Xie, J., Matsumoto, Y., Anraku, Y., Osada, K., & Kataoka, K. (2017). Therapeutic vesicular nanoreactors with tumor-specific activation and self-destruction for synergistic tumor ablation. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English), 56(45), 14025–14030.
Li, J., Anraku, Y., & Kataoka, K. (2020). Self-boosting catalytic nanoreactors integrated with triggerable crosslinking membrane networks for initiation of immunogenic cell death by pyroptosis. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English), 59(32), 13526–13530.
Yang, G., Song, J., & Zhang, J. (2020). Biomimetic and bioresponsive nanotherapies for inflammatory vascular diseases. Nanomedicine (London, England), 15(20), 1917–1921.
Dou, Y., Li, C., Li, L., Guo, J., & Zhang, J. (2020). Bioresponsive drug delivery systems for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Journal of Controlled Release, 327, 641–666.
Cheng, J., Zhang, R., Li, C., Tao, H., Dou, Y., Wang, Y., Hu, H., & Zhang, J. (2018). A targeting nanotherapy for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 72(21), 2591–2605.
Yuan, J., Li, L., Yang, Q., Ran, H., Wang, J., Hu, K., Pu, W., Huang, J., Wen, L., Zhou, L., Jiang, Y., Xiong, X., Zhang, J., & Zhou, Z. (2021). Targeted treatment of ischemic stroke by bioactive nanoparticle-derived reactive oxygen species responsive and inflammation-resolving nanotherapies. ACS Nano, 15(10), 16076–16094.
Lv, W., Xu, J., Wang, X., Li, X., Xu, Q., & Xin, H. (2018). Bioengineered boronic ester modified dextran polymer nanoparticles as reactive oxygen species responsive nanocarrier for ischemic stroke treatment. ACS Nano, 12(6), 5417–5426.
Hong, H. Y., Choi, J. S., Kim, Y. J., Lee, H. Y., Kwak, W., Yoo, J., Lee, J. T., Kwon, T. H., Kim, I. S., Han, H. S., & Lee, B. H. (2008). Detection of apoptosis in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia using a homing peptide selected from in vivo phage display. Journal of Controlled Release, 131(3), 167–172.
Zhao, Y., Jiang, Y., Lv, W., Wang, Z., Lv, L., Wang, B., Liu, X., Liu, Y., Hu, Q., Sun, W., Xu, Q., Xin, H., & Gu, Z. (2016). Dual targeted nanocarrier for brain ischemic stroke treatment. Journal of Controlled Release, 233, 64–71.
Chen, Y., Brennan-Minnella, A. M., Sheth, S., El-Benna, J., & Swanson, R. A. (2015). Tat-NR2B9c prevents excitotoxic neuronal superoxide production. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 35(5), 739–742.
Srejic, L. R., Hutchison, W. D., & Aarts, M. M. (2013). Uncoupling PSD-95 interactions leads to rapid recovery of cortical function after focal stroke. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 33(12), 1937–1943.
Hacke, W., Kaste, M., Bluhmki, E., Brozman, M., Dávalos, A., Guidetti, D., Larrue, V., Lees, K. R., Medeghri, Z., Machnig, T., Schneider, D., von Kummer, R., Wahlgren, N., & Toni, D. (2008). Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med, 359(13), 1317–29.
Larrue, V., von Kummer, R. R., Müller, A., & Bluhmki, E. (2001). Risk factors for severe hemorrhagic transformation in ischemic stroke patients treated with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator: A secondary analysis of the European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study (ECASS II). Stroke, 32(2), 438–441.
Kanazawa, M., Takahashi, T., Nishizawa, M., & Shimohata, T. (2017). Therapeutic strategies to attenuate hemorrhagic transformation after tissue plasminogen activator treatment for acute ischemic stroke. Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis, 24(3), 240–253.
Granger, D. N., & Kvietys, P. R. (2015). Reperfusion injury and reactive oxygen species: The evolution of a concept. Redox Biology, 6, 524–551.
Faraci, F. M. (2006). Reactive oxygen species: Influence on cerebral vascular tone. J Appl Physiol (1985), 100(2), 739–43.
Mei, T., Kim, A., Vong, L. B., Marushima, A., Puentes, S., Matsumaru, Y., Matsumura, A., & Nagasaki, Y. (2019). Encapsulation of tissue plasminogen activator in pH-sensitive self-assembled antioxidant nanoparticles for ischemic stroke treatment-Synergistic effect of thrombolysis and antioxidant. Biomaterials, 215, 119209.
Palma-Tortosa, S., Tornero, D., Grønning Hansen, M., Monni, E., Hajy, M., Kartsivadze, S., Aktay, S., Tsupykov, O., Parmar, M., Deisseroth, K., Skibo, G., Lindvall, O., & Kokaia, Z. (2020). Activity in grafted human iPS cell-derived cortical neurons integrated in stroke-injured rat brain regulates motor behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 117(16), 9094–9100.
Rossi, F., & Cattaneo, E. (2002). Opinion: Neural stem cell therapy for neurological diseases: Dreams and reality. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 3(5), 401–409.
Lin, B., Lu, L., Wang, Y., Zhang, Q., Wang, Z., Cheng, G., Duan, X., Zhang, F., Xie, M., Le, H., Shuai, X., & Shen, J. (2021). Nanomedicine directs neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells via silencing long noncoding RNA for stroke therapy. Nano Letters, 21(1), 806–815.
Yoo, A. S., Staahl, B. T., Chen, L., & Crabtree, G. R. (2009). MicroRNA-mediated switching of chromatin-remodelling complexes in neural development. Nature, 460(7255), 642–646.
Makeyev, E. V., Zhang, J., Carrasco, M. A., & Maniatis, T. (2007). The MicroRNA miR-124 promotes neuronal differentiation by triggering brain-specific alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Molecular Cell, 27(3), 435–448.
Saraiva, C., Paiva, J., Santos, T., Ferreira, L., & Bernardino, L. (2016). MicroRNA-124 loaded nanoparticles enhance brain repair in Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Controlled Release, 235, 291–305.
Farh, K. K., Grimson, A., Jan, C., Lewis, B. P., Johnston, W. K., Lim, L. P., Burge, C. B., & Bartel, D. P. (2005). The widespread impact of mammalian MicroRNAs on mRNA repression and evolution. Science, 310(5755), 1817–1821.
Xu, X. H., Yuan, T. J., Dad, H. A., Shi, M. Y., Huang, Y. Y., Jiang, Z. H., & Peng, L. H. (2021). Plant exosomes as novel nanoplatforms for MicroRNA transfer stimulate neural differentiation of stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Nano Letters, 21(19), 8151–8159.
Zhang, J., Chen, C., Fu, H., Yu, J., Sun, Y., Huang, H., Tang, Y., Shen, N., & Duan, Y. (2020). MicroRNA-125a-loaded polymeric nanoparticles alleviate systemic lupus erythematosus by restoring effector/regulatory t cells balance. ACS Nano, 14(4), 4414–4429.
Saraiva, C., Talhada, D., Rai, A., Ferreira, R., Ferreira, L., Bernardino, L., & Ruscher, K. (2018). MicroRNA-124-loaded nanoparticles increase survival and neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells in vitro but do not contribute to stroke outcome in vivo. PLoS ONE, 13(3), e0193609.
Yang, H., Han, M., Li, J., Ke, H., Kong, Y., Wang, W., Wang, L., Ma, W., Qiu, J., Wang, X., Xin, T., & Liu, H. (2022). Delivery of miRNAs through metal-organic framework nanoparticles for assisting neural stem cell therapy for ischemic stroke. ACS Nano, 16(9), 14503–14516.
Lo, E. H., Dalkara, T., & Moskowitz, M. A. (2003). Mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in stroke. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 4(5), 399–415.
Becher, B., Spath, S., & Goverman, J. (2017). Cytokine networks in neuroinflammation. Nature Reviews Immunology, 17(1), 49–59.
Iadecola, C., & Anrather, J. (2011). The immunology of stroke: From mechanisms to translation. Nature Medicine, 17(7), 796–808.
Shichita, T., Sakaguchi, R., Suzuki, M., & Yoshimura, A. (2012). Post-ischemic inflammation in the brain. Frontiers in Immunology, 3, 132.
Pan, J., Konstas, A. A., Bateman, B., Ortolano, G. A., & Pile-Spellman, J. (2007). Reperfusion injury following cerebral ischemia: Pathophysiology, MR imaging, and potential therapies. Neuroradiology, 49(2), 93–102.
Kalogeris, T., Baines, C. P., Krenz, M., & Korthuis, R. J. (2012). Cell biology of ischemia/reperfusion injury. International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology, 298, 229–317.
Lakhan, S. E., Kirchgessner, A., & Hofer, M. (2009). Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: Therapeutic approaches. Journal of Translational Medicine, 7, 97.
Gautier, S., Ouk, T., Petrault, O., Caron, J., & Bordet, R. (2009). Neutrophils contribute to intracerebral haemorrhages after treatment with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator following cerebral ischaemia. British Journal of Pharmacology, 156(4), 673–679.
Khan, M. M., Motto, D. G., Lentz, S. R., & Chauhan, A. K. (2012). ADAMTS13 reduces VWF-mediated acute inflammation following focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 10(8), 1665–1671.
Vinten-Johansen, J. (2004). Involvement of neutrophils in the pathogenesis of lethal myocardial reperfusion injury. Cardiovascular Research, 61(3), 481–497.
Fulurija, A., Ashman, R. B., & Papadimitriou, J. M. (1996). Neutrophil depletion increases susceptibility to systemic and vaginal candidiasis in mice, and reveals differences between brain and kidney in mechanisms of host resistance. Microbiology (Reading), 142(Pt 12), 3487–3496.
Jaeger, B. N., Donadieu, J., Cognet, C., Bernat, C., Ordoñez-Rueda, D., Barlogis, V., Mahlaoui, N., Fenis, A., Narni-Mancinelli, E., Beaupain, B., Bellanné-Chantelot, C., Bajénoff, M., Malissen, B., Malissen, M., Vivier, E., & Ugolini, S. (2012). Neutrophil depletion impairs natural killer cell maturation, function, and homeostasis. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 209(3), 565–580.
Kolaczkowska, E., & Kubes, P. (2013). Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nature Reviews Immunology, 13(3), 159–175.
Spite, M., Norling, L. V., Summers, L., Yang, R., Cooper, D., Petasis, N. A., Flower, R. J., Perretti, M., & Serhan, C. N. (2009). Resolvin D2 is a potent regulator of leukocytes and controls microbial sepsis. Nature, 461(7268), 1287–1291.
Chiang, N., Dalli, J., Colas, R. A., & Serhan, C. N. (2015). Identification of resolvin D2 receptor mediating resolution of infections and organ protection. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 212(8), 1203–1217.
Dong, X., Gao, J., Zhang, C. Y., Hayworth, C., Frank, M., & Wang, Z. (2019). Neutrophil membrane-derived nanovesicles alleviate inflammation to protect mouse brain injury from ischemic stroke. ACS Nano, 13(2), 1272–1283.
Liu, S., Shi, H., Liu, W., Furuichi, T., Timmins, G. S., & Liu, K. J. (2004). Interstitial pO2 in ischemic penumbra and core are differentially affected following transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 24(3), 343–349.
Saxena, R., Wijnhoud, A. D., Carton, H., Hacke, W., Kaste, M., Przybelski, R. J., Stern, K. N., & Koudstaal, P. J. (1999). Controlled safety study of a hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier, DCLHb, in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke, 30(5), 993–996.
Deuchar, G. A., Brennan, D., Holmes, W. M., Shaw, M., Macrae, I. M., & Santosh, C. (2018). Perfluorocarbon enhanced glasgow oxygen level dependent (GOLD) magnetic resonance metabolic imaging identifies the penumbra following acute ischemic stroke. Theranostics, 8(6), 1706–1722.
Kakehata, J., Yamaguchi, T., Togashi, H., Sakuma, I., Otani, H., Morimoto, Y., & Yoshioka, M. (2010). Therapeutic potentials of an artificial oxygen-carrier, liposome-encapsulated hemoglobin, for ischemia/reperfusion-induced cerebral dysfunction in rats. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences, 114(2), 189–197.
Atsumi, S., Higashide, W., & Liao, J. C. (2009). Direct photosynthetic recycling of carbon dioxide to isobutyraldehyde. Nature Biotechnology, 27(12), 1177–1180.
Cohen, J. E., Goldstone, A. B., Paulsen, M. J., Shudo, Y., Steele, A. N., Edwards, B. B., Patel, J. B., MacArthur, J. W., Jr., Hopkins, M. S., Burnett, C. E., Jaatinen, K. J., Thakore, A. D., Farry, J. M., Truong, V. N., Bourdillon, A. T., Stapleton, L. M., Eskandari, A., Fairman, A. S., Hiesinger, W., … Woo, Y. J. (2017). An innovative biologic system for photon-powered myocardium in the ischemic heart. Sci Adv, 3(6), e1603078.
Qiao, Y.; Yang, F.; Xie, T.; Du, Z.; Zhong, D.; Qi, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Lu, Z.; Rao, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, M., Engineered algae: A novel oxygen-generating system for effective treatment of hypoxic cancer. Sci Adv 2020, 6 (21), eaba5996.
Wang, F., Deng, R., Wang, J., Wang, Q., Han, Y., Zhu, H., Chen, X., & Liu, X. (2011). Tuning upconversion through energy migration in core-shell nanoparticles. Nature Materials, 10(12), 968–973.
Wang, J., Wang, F., Wang, C., Liu, Z., & Liu, X. (2011). Single-band upconversion emission in lanthanide-doped KMnF3 nanocrystals. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English), 50(44), 10369–10372.
Jin, R., Yang, G., & Li, G. (2010). Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: Role of inflammatory cells. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 87(5), 779–789.
Zhang, T., Lee, Y. W., Rui, Y. F., Cheng, T. Y., Jiang, X. H., & Li, G. (2013). Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote growth and angiogenesis of breast and prostate tumors. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 4(3), 70.
Gu, Y., Zhang, Y., Bi, Y., Liu, J., Tan, B., Gong, M., Li, T., & Chen, J. (2015). Mesenchymal stem cells suppress neuronal apoptosis and decrease IL-10 release via the TLR2/NFκB pathway in rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Molecular Brain, 8(1), 65.
Bhang, S. H., Lee, Y. E., Cho, S. W., Shim, J. W., Lee, S. H., Choi, C. Y., Chang, J. W., & Kim, B. S. (2007). Basic fibroblast growth factor promotes bone marrow stromal cell transplantation-mediated neural regeneration in traumatic brain injury. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 359(1), 40–45.
Zhang, R., Liu, Y., Yan, K., Chen, L., Chen, X. R., Li, P., Chen, F. F., & Jiang, X. D. (2013). Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in experimental traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 10, 106.
Eggenhofer, E., Luk, F., Dahlke, M. H., & Hoogduijn, M. J. (2014). The life and fate of mesenchymal stem cells. Frontiers in Immunology, 5, 148.
Smyth, T., Kullberg, M., Malik, N., Smith-Jones, P., Graner, M. W., & Anchordoquy, T. J. (2015). Biodistribution and delivery efficiency of unmodified tumor-derived exosomes. Journal of Controlled Release, 199, 145–155.
Zhu, X., Badawi, M., Pomeroy, S., Sutaria, D. S., Xie, Z., Baek, A., Jiang, J., Elgamal, O. A., Mo, X., Perle, K., Chalmers, J., Schmittgen, T. D., & Phelps, M. A. (2017). Comprehensive toxicity and immunogenicity studies reveal minimal effects in mice following sustained dosing of extracellular vesicles derived from HEK293T cells. J Extracell Vesicles, 6(1), 1324730.
Zhang, B., Yeo, R. W. Y., Lai, R. C., Sim, E. W. K., Chin, K. C., & Lim, S. K. (2018). Mesenchymal stromal cell exosome-enhanced regulatory T-cell production through an antigen-presenting cell-mediated pathway. Cytotherapy, 20(5), 687–696.
Jo, W., Kim, J., Yoon, J., Jeong, D., Cho, S., Jeong, H., Yoon, Y. J., Kim, S. C., Gho, Y. S., & Park, J. (2014). Large-scale generation of cell-derived nanovesicles. Nanoscale, 6(20), 12056–12064.
Eckert, M. A., Vu, Q., Xie, K., Yu, J., Liao, W., Cramer, S. C., & Zhao, W. (2013). Evidence for high translational potential of mesenchymal stromal cell therapy to improve recovery from ischemic stroke. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 33(9), 1322–1334.
Fan, Y., Shen, F., Frenzel, T., Zhu, W., Ye, J., Liu, J., Chen, Y., Su, H., Young, W. L., & Yang, G. Y. (2010). Endothelial progenitor cell transplantation improves long-term stroke outcome in mice. Annals of Neurology, 67(4), 488–497.
Zhang, Z. G., Zhang, L., Jiang, Q., & Chopp, M. (2002). Bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells participate in cerebral neovascularization after focal cerebral ischemia in the adult mouse. Circulation Research, 90(3), 284–288.
Taguchi, A., Soma, T., Tanaka, H., Kanda, T., Nishimura, H., Yoshikawa, H., Tsukamoto, Y., Iso, H., Fujimori, Y., Stern, D. M., Naritomi, H., & Matsuyama, T. (2004). Administration of CD34+ cells after stroke enhances neurogenesis via angiogenesis in a mouse model. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 114(3), 330–338.
Chen, J., Sanberg, P. R., Li, Y., Wang, L., Lu, M., Willing, A. E., Sanchez-Ramos, J., & Chopp, M. (2001). Intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood reduces behavioral deficits after stroke in rats. Stroke, 32(11), 2682–2688.
Roche, E. T., Hastings, C. L., Lewin, S. A., Shvartsman, D., Brudno, Y., Vasilyev, N. V., O’Brien, F. J., Walsh, C. J., Duffy, G. P., & Mooney, D. J. (2014). Comparison of biomaterial delivery vehicles for improving acute retention of stem cells in the infarcted heart. Biomaterials, 35(25), 6850–6858.
Berra, E., Benizri, E., Ginouvès, A., Volmat, V., Roux, D., & Pouysségur, J. (2003). HIF prolyl-hydroxylase 2 is the key oxygen sensor setting low steady-state levels of HIF-1alpha in normoxia. EMBO Journal, 22(16), 4082–4090.
Jaakkola, P., Mole, D. R., Tian, Y. M., Wilson, M. I., Gielbert, J., Gaskell, S. J., von Kriegsheim, A., Hebestreit, H. F., Mukherji, M., Schofield, C. J., Maxwell, P. H., Pugh, C. W., & Ratcliffe, P. J. (2001). Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science, 292(5516), 468–472.
Wu, S., Nishiyama, N., Kano, M. R., Morishita, Y., Miyazono, K., Itaka, K., Chung, U. I., & Kataoka, K. (2008). Enhancement of angiogenesis through stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 by silencing prolyl hydroxylase domain-2 gene. Molecular Therapy, 16(7), 1227–1234.
Wang, C., Lin, G., Luan, Y., Ding, J., Li, P. C., Zhao, Z., Qian, C., Liu, G., Ju, S., & Teng, G. J. (2019). HIF-prolyl hydroxylase 2 silencing using siRNA delivered by MRI-visible nanoparticles improves therapy efficacy of transplanted EPCs for ischemic stroke. Biomaterials, 197, 229–243.
He, L.; Huang, G.; Liu, H.; Sang, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, T., Highly bioactive zeolitic imidazolate framework-8-capped nanotherapeutics for efficient reversal of reperfusion-induced injury in ischemic stroke. Sci Adv 2020, 6 (12), eaay9751.
Li, C., Zhao, Z., Luo, Y., Ning, T., Liu, P., Chen, Q., Chu, Y., Guo, Q., Zhang, Y., Zhou, W., Chen, H., Zhou, Z., Wang, Y., Su, B., You, H., Zhang, T., Li, X., Song, H., Li, C., … Jiang, C. (2021). Macrophage-disguised manganese dioxide nanoparticles for neuroprotection by reducing oxidative stress and modulating inflammatory microenvironment in acute ischemic stroke. Adv Sci (Weinh), 8(20), e2101526.
Liu, Y., Ai, K., Ji, X., Askhatova, D., Du, R., Lu, L., & Shi, J. (2017). Comprehensive insights into the multi-antioxidative mechanisms of melanin nanoparticles and their application to protect brain from injury in ischemic stroke. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 139(2), 856–862.
Li, X., Han, Z., Wang, T., Ma, C., Li, H., Lei, H., Yang, Y., Wang, Y., Pei, Z., Liu, Z., Cheng, L., & Chen, G. (2022). Cerium oxide nanoparticles with antioxidative neurorestoration for ischemic stroke. Biomaterials, 291, 121904.
Shi, J., Yang, Y., Yin, N., Liu, C., Zhao, Y., Cheng, H., Zhou, T., Zhang, Z., & Zhang, K. (2022). Engineering CXCL12 biomimetic decoy-integrated versatile immunosuppressive nanoparticle for ischemic stroke therapy with management of overactivated brain immune microenvironment. Small Methods, 6(1), e2101158.
Tian, T., Cao, L., He, C., Ye, Q., Liang, R., You, W., Zhang, H., Wu, J., Ye, J., Tannous, B. A., & Gao, J. (2021). Targeted delivery of neural progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles for anti-inflammation after cerebral ischemia. Theranostics, 11(13), 6507–6521.
Yang, H., Luo, Y., Hu, H., Yang, S., Li, Y., Jin, H., Chen, S., He, Q., Hong, C., Wu, J., Wan, Y., Li, M., Li, Z., Yang, X., Su, Y., Zhou, Y., & Hu, B. (2021). pH-Sensitive, Cerebral vasculature-targeting hydroxyethyl starch functionalized nanoparticles for improved angiogenesis and neurological function recovery in ischemic stroke. Adv Healthc Mater, 10(12), e2100028.
Deng, G., Ma, C., Zhao, H., Zhang, S., Liu, J., Liu, F., Chen, Z., Chen, A. T., Yang, X., Avery, J., Zou, P., Du, F., Lim, K. P., Holden, D., Li, S., Carson, R. E., Huang, Y., Chen, Q., Kimberly, W. T., … Zhou, J. (2019). Anti-edema and antioxidant combination therapy for ischemic stroke via glyburide-loaded betulinic acid nanoparticles. Theranostics, 9(23), 6991–7002.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BW is the corresponding author who contributed to the review conception, design, and revision. DC prepared the manuscript and wrote the major part of the manuscript. WC, AM, and M collected and discussed the literature. BW helped to revise the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Research involving humans and animals statement
None.
Informed consent
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, D., Chen, W., Ma, A. et al. Nanoparticles Treat Ischemic Stroke by Responding to Stroke Microenvironment. BioNanoSci. 14, 380–394 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-023-01247-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-023-01247-2