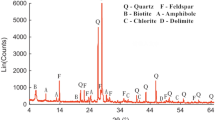
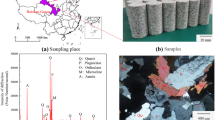
Abstract
The study of rock property deterioration law following subcritical water–rock interaction is of great importance for improving the efficiency of dry, hot rock development, reducing the usage of fossil energy, and achieving global energy conservation and emission reduction goals. This study examined granite's pore structure and mineral element dissolution properties after sub-critical water–rock interaction at different temperatures using NMR and ICP–MS. The damage evolution behavior of granite under sub-critical water–rock interaction was discussed and explained in conjunction with the microstructure images. The conclusions of the study are as follows. (1) The major pores of granite transition from mesopore to macropore after subcritical water–rock interaction. A few minerals on the surface of granite detach as the temperature rises, and the traces of dissolution and oxidation become more prevalent; (2) The dissolved mineral elements altered the properties of the solution, and Si element concentration was significantly higher than that of other elements; (3) The key temperature affecting the sub-critical water–rock interaction of granite is 300–350 °C. In general, the sub-critical water–rock interaction primarily influences the properties of granite in two ways: the oxidation and dissolution of minerals and the thermal stress resulting from thermal expansion.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Authors can confirm that all relevant data are included in the article.
References
Atkinson BK (1984) Subcritical crack growth in geological materials. J Geophys Res 89(B6):4077–4114. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB089iB06p04077
Axtmann RC (1975) Environmental impact of a geothermal power plant. Science 187(4179):795–803. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.187.4179.795
Bai S, Cheng D, Wan J, Yang L, Peng H, Guo X, Zeng J (2016) Quantitative characterization of sandstone NMR T2 spectrum. Aata Petrolei Sinica 37:98–107. https://doi.org/10.7623/syxb201603010
Cao P, Ning G, Fan X, Mei H, Huang X (2013) Influence of water-rock interaction on morphological characteristic of rock joint surface at different temperatures. J Cent South Univ Sci Technol 44:1510–1516
Caulk RA, Ghazanfari E, Perdrial JN, Perdrial N (2016) Experimental investigation of fracture aperture and permeability change within Enhanced Geothermal Systems. Geothermics 62:12–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2016.02.003
Chester FM, Chester JS, Kronenberg AK, Hajash A (2007) Subcritical creep compaction of quartz sand at diagenetic conditions: effects of water and grain size. 112(B6). https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JB004317.
Davis MC, Wesolowski DJ, Rosenqvist J, Brantley SL, Mueller KT (2011) Solubility and near-equilibrium dissolution rates of quartz in dilute NaCl solutions at 398–473K under alkaline conditions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 75(2):401–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2010.10.023
DeCuir MJ, Gupta RB, Sastri B (2020) Beneficiation of coal using supercritical water and carbon dioxide extraction: sulfur removal. Int J Coal Sci Technol 8(4):717–726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-020-00324-1
Ding Q, Hu X, Gao Q, Ye Y, Zhang P (2019) The hydrothermal alteration types and zoning features of Ordovician carbonate in Tarim Basin. J Zhejiang Univ (sci Ed) 46:600–609. https://doi.org/10.3785/j.issn.1008⁃9497.2019.05.013
Fournier RO, Berger BR, Bethke PM (1985) The behavior of silica in hydrothermal solutions. Geol Geochem Epitherm Syst. https://doi.org/10.5382/Rev.02.03
Gautier J-M, Oelkers EH, Schott J (2001) Are quartz dissolution rates proportional to BET surface areas? Geochim Cosmochim Acta 65(7):1059–1070. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00570-6
Hartlieb P, Toifl M, Kuchar F, Meisels R, Antretter T (2016) Thermo-physical properties of selected hard rocks and their relation to microwave-assisted comminution. Miner Eng 91:34–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2015.11.008
Hatheway AW (2009) The complete ISRM Suggested methods for rock characterization, testing and monitoring; 1974–2006. Environ Eng Geosci 15(1):47–48. https://doi.org/10.2113/gseegeosci.15.1.47
Hemlery JJ, Jones WR (1964) Chemical aspects of hydrothermal alteration with emphasis on hydrogen metasomatism. Econ Geol 59(04):538–569. https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.59.4.538
Hou X, Zhu Y, Wang Y, Liu Y (2019) Experimental study of the interplay between pore system and permeability using pore compressibility for high rank coal reservoirs. Fuel. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.115712
Hu X, Song X, Liu Y, Cheng Z, Ji J, Shen Z (2019) Experiment investigation of granite damage under the high-temperature and high-pressure supercritical water condition. J Petrol Sci Eng 180:289–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2019.05.031
Hu J, Xie H, Sun Q, Li C, Liu G (2021) Changes in the thermodynamic properties of alkaline granite after cyclic quenching following high temperature action. Int J Min Sci Technol 31(5):843–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2021.07.010
Huang Y, Yang S, Li W, Hall MR (2019) Influence of super-critical CO2 on the strength and fracture behavior of brine-saturated sandstone specimens. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(02):653–670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01933-2
Jia Y, Fang Y, Elsworth D, Wu W (2020) Slip velocity dependence of friction-permeability response of shale fractures. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(5):2109–2121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-02036-8
Jing Z, Watanabe K, Willis-Richards J, Hashida T (2002) A 3-D water/rock chemical interaction model for prediction of HDR/HWR geothermal reservoir performance. Geothermics 31(1):1–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0375-6505(00)00059-6
Jing Y, Jing Z, Willis-Richards J, Hashida T (2014) A simple 3-D thermoelastic model for assessment of the long-term performance of the Hijiori deep geothermal reservoir. J Volcanol Geoth Res 269:14–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2013.10.012
Kamila Z, Kaya E, Zarrouk SJ (2021) Reinjection in geothermal fields: an updated worldwide review 2020. Geothermics 89:101970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2020.101970
Kenyon WE, Howard JJ, Sezginer A, Straley C, Matteson A, Horkowitz K, Ehrlich R (1989) Pore-size distribution and NMR in microporous cherty sandstones. In: SPWLA 30th annual logging symposium
Kogbara RB, Iyengar SR, Grasley ZC, Masad EA, Zollinger DG (2015) Non-destructive evaluation of concrete mixtures for direct LNG containment. Mater Des 82:260–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.05.084
Kritzer P, Dinjus E (2001) An assessment of supercritical water oxidation (SCWO) existing problems, possible solutions and new reactor concepts. Chem Eng J 83(3):207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1385-8947(00)00255-2
Lai J, Wang G, Wang Z, Chen J, Pang X, Wang S, Zhou Z, He Z, Qin Z, Fan X (2017) A review on pore structure characterization in tight sandstones. Earth Sci Rev 177:436–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.12.003
Laubach SE, Lander RH, Criscenti LJ, Anovitz LM, Urai JL, Pollyea RM, Hooker JN, Narr W, Evans MA, Kerisit SN, Olson JE, Dewers T, Fisher D, Bodnar R, Evans B, Dove P, Bonnell LM, Marder MP, Pyrak-Nolte L (2019) The role of chemistry in fracture pattern development and opportunities to advance interpretations of geological materials. 57(3):1065–1111. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019RG000671
Lebedev EB, Zharikov AV (2000) Study of intergranular films and interstitial phases in geomaterials using high temperature centrifuge and ultrasonic method at high pressure. Phys Chem Earth Part A 25(2):209–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1464-1895(00)00033-8
Liaw H-K, Kulkarni R, Chen S, Watson AT (1996) Characterization of fluid distributions in porous media by NMR techniques. AIChE J 42(02):538–546. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.690420223
Liu S, Xu J (2015) An experimental study on the physico-mechanical properties of two post-high-temperature rocks. Eng Geol 185:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.11.013
Mookherjee M, Stixrude L, Karki B (2008) Hydrous silicate melt at high pressure. Nature 452(7190):983–986. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06918
Morriss C, Rossini D, Straley C, Tutunjian P, Vinegar H (1997) Core analysis by low-field NMR. Log Anal 38(02):84–93
Nangia S, Garrison BJ (2008) Reaction rates and dissolution mechanisms of quartz as a function of pH. J Phys Chem A 112(10):2027–2033. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp076243w
Nara Y, Yamanaka H, Oe Y, Kaneko K (2013) Influence of temperature and water on subcritical crack growth parameters and long-term strength for igneous rocks. Geophys J Int 193:47–60. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggs116
Nara Y, Tanaka M, Harui T (2017) Evaluating long-term strength of rock under changing environments from air to water. Eng Fract Mech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2017.04.015
Rathnaweera TD, Wu W, Ji Y, Gamage RP (2020) Understanding injection-induced seismicity in enhanced geothermal systems: from the coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical process to anthropogenic earthquake prediction. Earth-Sci Rev 205:103182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103182
Sano O, Kudo Y (1992) Relation of fracture resistance to fabric for granitic rocks. Pure Appl Geophys 138(4):657–677. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00876343
Simmons S, Christenson B (1994) Origin of calcite in a boiling geothermal system. Am J Sci 294(03):361–400. https://doi.org/10.2475/ajs.294.3.361
Sirdesai NN, Singh TN, Ranjith PG, Singh R (2016) Effect of varied durations of thermal treatment on the tensile strength of red sandstone. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50(1):205–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-1047-4
Somerton WH (1961) Additional thermal data for porous rocks-thermal expansion and heat of reaction. Soc Petrol Eng J 1(04):249–253. https://doi.org/10.2118/1613-G
Steiger M, Charola AE, Sterflinger K (2011) Weathering and deterioration. In: Siegesmund S, Snethlage R (eds) Stone in architecture. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-14475-2_4.
Sumi K (1966) Hydrothermal rock alteration of matsukawa geothermal area, iwate prefecture. Min Geol. https://doi.org/10.11456/shigenchishitsu1951.16.79_261
Tenthorey E, Cox SF, Todd HF (2003) Evolution of strength recovery and permeability during fluid–rock reaction in experimental fault zones. Earth Planet Sci Lett 206(1):161–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0012-821X(02)01082-8
Viswanathan HS, Ajo-Franklin JB, Birkholzer JT, Carey JW, Guglielmi Y, Hyman JDH, Karra S, Pyrak-Nolte L, Rajaram H, Srinivasan G et al (2022) From fluid flow to coupled processes in fractured rock: recent advances and new frontiers. J Earth Space Sci Open Arch. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021RG000744
Wu G, Wang Y, Swift G, Chen J (2013) Laboratory investigation of the effects of temperature on the mechanical properties of sandstone. Geotech Geol Eng 31(2):809–816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-013-9614-x
Xu C, Lin C, Kang Y, You L (2018) An experimental study on porosity and permeability stress-sensitive behavior of sandstone under hydrostatic compression: characteristics, mechanisms and controlling factors. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51(08):2321–2338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1481-6
Yasuhara H, Polak A, Mitani Y, Grader AS, Halleck PM, Elsworth D (2006) Evolution of fracture permeability through fluid–rock reaction under hydrothermal conditions. Earth Planet Sci Lett 244(1):186–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2006.01.046
Yin TB, Li XB, Cao WZ, Xia KW (2015) Effects of thermal treatment on tensile strength of laurentian granite using brazilian test. Rock Mech Rock Eng 48(06):2213–2223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0712-3
Zhang R, Hu S, Zhang X (2006) Geochemical kinetics and ore genesis in Middle Crust. Acta Geoscientica Sinica. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2006.05.008
Zhang R, Zhang X, Hu S, Su Y (2007) Kinetic experiments of water rock interactions at high temperatures and high pressures corresponding to the middle crust conditions. Acta Petrologica Sinica 23:2933–2942. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.11.024
Zhang R, Zhang X, Hu S (2015) Dissolution kinetics of quartz in water at high temperatures across the critical state of water. J Supercrit Fluids 100:58–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2015.02.010
Zhang R, Hu S, Zhang X (2016) From equilibrium-static-close system to non-equilibrium-kinetics-open study: new conception outline of hydrothermal ore deposition. Acta Geoscientica Sinica. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.09.022
Zhang H, Sun Q, Jia H, Dong Z, Luo T (2021) Effects of high-temperature thermal treatment on the porosity of red sandstone: an NMR analysis. Acta Geophys 69(01):113–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-020-00526-w
Zhang H, Sun Q, Dong Z, Ge Z, Dai J, Wang Z, Cao Y (2022) Metamorphic response characteristics of yellow sandstone after heat treatment under 800–1250 °C. J Therm Anal Calorim. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11336-1
Zhou Z, Cai X, Ma D, Cao W, Chen L, Zhou J (2018) Effects of water content on fracture and mechanical behavior of sandstone with a low clay mineral content. Eng Fract Mech 193:47–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.02.028
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 41972288).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QS and HZ wrote the main manuscript text, JG and SZ offered valuable advices, and JH prepared figures 2–4 and 7–8. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Q., Zhang, H., Hu, J. et al. Damage mechanism of granite under subcritical water–rock interaction. Environ Earth Sci 82, 124 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-10827-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-10827-0