Abstract
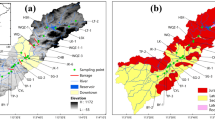
The aim of the present work was to investigate links between the low-field magnetic susceptibility (MS) and chemical and mineral composition of sediments from several Croatian and Slovenian rivers, as well as to determine possible anthropogenic influence on these sediments. MS measurements are a fast and simple method, which serves as a proxy for the estimation of pollution in different environmental systems. The investigated rivers are predominantly unpolluted rivers from Croatian and Slovenian karstic and flysch areas, which belong to the Adriatic or the Black Sea watersheds: the Dragonja, the Mirna, the Raša, the Rižana, the Reka, the Rak, the Cerknišnica, the Unec and the Ljubljanica rivers. It was assumed that, due to their mostly unpolluted status, they could serve as a database for natural MS background values for this region. For comparison, several rivers and a lake from the Celje old metallurgic industrial area (Slovenia) were also investigated: the Savinja, the Hudinja, the Voglajna rivers and Slivniško Lake. They form a sub-basin of the Sava River drainage basin. Sediments of the clean karstic and flysch rivers showed extremely low MS values, with mass susceptibility values ranging from 0.58 × 10−7 to 5.11 × 10−7 m3/kg, and isothermal remanent magnetism (IRM) values ranging from 0.71 to 7.88 A/m. In the Celje industrial area, river sediments showed much higher MS values, with mass susceptibility values ranging from 1.31 × 10−7 to 38.3 × 10−7 m3/kg, and IRM values ranging from 0.91 to 100.42 A/m. The highest MS value was found in the Voglajna River at Teharje-Štore, a point which showed a significant number of anomalies of toxic metals in earlier investigations. Semiquantitative determination of relations between grain size and concentration of magnetite was performed using the Thompson-Oldfield method. X-ray diffraction (XRD) mineralogical analysis showed that sediments of the Celje area have mostly quartz as major mineral, with relatively small amount of carbonate minerals, while in sediments of karstic rivers carbonate minerals prevail. Statistically significant correlations were obtained between MS and Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd and Ba in the Slovenian karstic region and between MS and Cr, Fe, Co, Ni and Zn in flysch drainage basins. On the contrary, no correlation of MS and Hg content was obtained.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babić LJ, Ćorić S, Hernitz-Kučenjak M, Zupanič J (2007) The Middle Eocene age of the supposed late Oligocene sediments in the flysch of the Pazin Basin (Istria, outer Dinarides). Nat Croatica Periodicum Musei historiae naturalis Croatici 16(2):83–103
Barišić D, Marović G, Senčar J, Lulić S (2001) Natural radionuclides in slag/ash pile from coal-fired power plant Plomin. In: Obelić, Bogomil; Ranogajec-Komor, Maria; Miljanić, Saveta; Krajcar Bronić, Ines (eds) Proceedings of the IRPA Regional Congress on Radiation Protection in Central Europe “Radiation Protection and Health”—Zagreb: HDZZ/CRPA
Botsou F, Karageorgis AP, Dassenakis E, Scoullos M (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination and mineral magnetic characterization of the Asopos River sediments (Central Greece). Mar Pollut Bull 62(3):547–563
Boyko T, Scholger R, Stanjek H (2004) Topsoil magnetic susceptibility mapping as a tool for pollution monitoring: repeatability of in situ measurements. J Appl Geophys 55(3–4):249–259
Chen M, Ma QL (2001) Comparison of three aqua regia digestion methods for twenty Florida soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65:491–499
Dlouha Š, Petrovsky E, Kapička A, Borüvka L, Ash C, Drábek O (2013) Investigation of polluted alluvial soils by magnetic susceptibility methods: a case study of the Litavka River. Soil Water Res 8(4):151–157
FGI (1970) Geological map of SFR Yugoslavia 1:500 000. Federal Geological Institute, Beograd
Fialová H, Maier G, Petrovsky E, Kapička A, Boyko T, Scholger R (2006) MAGPROX Team. Magnetic properties of soils from sites with different geological and environmental settings. Appl Geophys 59:273–283
Frančišković-Bilinski S (2008a) Detection of coal combustion products in stream sediments by chemical analysis and magnetic susceptibility measurements. Mineral Mag 72:43–48
Frančišković-Bilinski S (2008b) Detection of geochemical anomalies in stream sediments of the upper Sava River drainage basin (Slovenia, Croatia). Fresenius Environ Bull 17(2):188–196
Frančišković-Bilinski S, Bilinski H, Tibljaš D, Hanžel D (2003) Characterization of sediments from Dragonja, river at the border line between Croatia and Slovenia (In Croatian-with an English summary). In: 3rd Croatian Conference on Waters, Osijek, Croatia, pp 1147–1154
Frančišković-Bilinski S, Bilinski H, Darko Tibljaš, Rantitsch G (2005) Effects of mercury mining regions from NW Dinarides on quality of stream sediments. Fresenius Environ Bull 14(10):913–927
Frančišković-Bilinski S, Bilinski H, Tibljaš D, Hanžel D (2006) Sediments from Savinja, Voglajna and Hudinja rivers (Slovenia), reflecting anomalies in an old metallurgic area. Fresenius Environ Bull 15(3):220–228
Frančišković-Bilinski S, Bilinski H, Tibljaš D (2007) Contamination status of flysch-draining rivers of Croatia and Slovenia, flowing to the north Adriatic Sea. In: Briand F, Sakellariou D, Font J, Fisher N (eds) Abstracts of the 38th CIESM congress, Commission internationale pour l’exploration scientifique de la mer Méditerranée. CIESM, Monaco, pp 90–90
Frančišković-Bilinski S, Bilinski H, Scholger R, Tomašić N, Maldini K (2014) Magnetic spherules in sediments of the karstic Dobra River (Croatia). J Soils Sediments. doi:10.1007/s11368-013-0808-x
Gams I (2004) Kras v Sloveniji. Založba ZRC pp 515
Halamić J, Miko S (2009) Geochemical atlas of the Republic of Croatia. Croatian Geological Survey, Zagreb, p 87
Hanesch M, Scholger R (2002) Monitoring of heavy metal loadings in soils by means of magnetic susceptibility measurements. Environ Geol 42:857–870
Hanesch M, Scholger R, Rey D (2003) Mapping dust distribution around an industrial site by measuring magnetic parameters of tree leaves. Atmos Environ 37:5125–5133
Hay KL, Dearing JA, Baban SMJ, Loveland P (1997) A preliminary attempt to identify atmospherically derived pollution particles in English topsoils from magnetic susceptibility measurements. Phys Chem Earth 22(1–2):207–210
Heller F, Strzyszcz Z, Magiera T (1998) Magnetic record of industrial pollution in forest soils of Upper Silesia, Poland. J Geophys Res 103(B8):17767–17774
Kapička A, Petrovský E, Ustjak S, Macháčková K (1999) Proxy mapping of fly ash pollution of soils around a coal-burning power plant. J Geochem Explor 66:291–297
Kogovšek J (2001) Observations of the Reka flood pulse in May 1999. Acta Carsologica 30/1, 4:55–68
Magdalenić Z (1972) Sedimentology of central Istria flysch deposits (in Croatian with English summary). Acta Geologica 7/2:1–34, 71–101
Mikes T, Dunkl I, Frisch W, von Eynatten H (2006) Geochemistry of Eocene flysch sandstones in the NW External Dinarides. Acta Geol Hung 49(2):103–124
Novakova T, Grygar TM, Babek O, Famera M, Mihaljević M, Strnad L (2012) Distinguishing regional and local sources of pollution by trace metals and magnetic particles in fluvial sediments of the Morava River, Czech Republic. J Soils Sediments. 14 December 2012, p 14. doi:10.1007/s11368-012-0632-8
Oldfield F, Hunt A, Jones MDH, Chester R, Dearing JA, Olsson L, Prospero JM (1985) Magnetic differentiation of atmospheric dusts. Nature 317:516–518
Petrovský E, Ellwood BB (1999) Magnetic monitoring of air-, land-, and water-pollution. In: Maher BA, Thompson R (eds) Quaternary Climates, Environments and Magnetism. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 279–322
Petrovsky E, Kapička A, Jordanova N, Knab M, Hoffmann V (2000) Low-field magnetic susceptibility: a proxy method of estimating increased pollution of different environmental systems. Environ Geol 39(3–4):312–318
Philips Analytical B.V. (2001) High Score ver. 1.0. Almelo
Plater AJ, Ridgeway J, Appleby PG, Berry A, Wright MR (1998) Historical contaminant fluxes in the Tees estuary, UK. Mar Pollut Bull 37:343–360
Poje M (2008) Kakovost površinskih virov pitne vode v Sloveniji. Agencija Republike Slovenije za okolje, Ljubljana, pp 39. http://www.arso.gov.si/vode/reke/publikacije%20in%20poro%C4%8Dila/PVOPV_publikacija-01.pdf
Powder Diffraction File (1997) International Centre for Diffraction Data, Newtown Square, Pennsylvania, USA
Reimann C, Filzmoser P, Garrett RG (2005) Background and threshold: critical comparison of methods of determination. Sci Total Environ 346:1–16
Salminen R, Tarvainen T (1997) The problem of defining geochemical baselines. A case study of selected elements and geological materials in Finland. J Geochem Explor 60:91–98
Scholger R (1998) Heavy metal pollution monitoring by magnetic susceptibility measurements applied to sediments of the river Mur (Styria, Austria). Eur J Environ Eng Geophys 3:25–37
Shoumkova A (2006) Physico-chemical characterization and magnetic separation of coal fly ashes from “Varna”, “Bobov Dol” and “Maritza-Istok I” power plants, Bulgaria. II—magnetic separation. J Univ Chem Technol Metall 41(2):181–186
SMSP and Falconbridge NC SAS (2005) Koniambo project, Environmental and social impact assessment, Chapter 4 Mine, 4.2-7 Quality criteria for freshwater sediment. Available at: http://www.koniambo-nickel.com/en/pdf/02_Appendices/ESIA_Volume%20II_TOC_Rev_1_2.pdf
Šoltes I (2010) Sanacija starih bremen industrijskih odpadkov in nedovoljenih odlagališč gradbenih odpadkov. The Court of Audit of Republic of Slovenia. p 61. http://www.rs-rs.si/rsrs/rsrs.nsf/I/KABD7677C5FCE2EFFC125774B0029896C/$file/MOPIndOdpad.SP04-08.pdf
Sondi I, Juračić M, Prohić E, Pravdić V (1994) Particulate sand the environmental capacity for trace metals—a small river as a model for a land-sea transfer system—the Raša River estuary. Sci Total Environ 155(2):173–185
Sondi I, Juračić M, Pravdić V (1995) Sedimentation in a disequilibrium river-dominated estuary—the Raša River estuary (Adriatic Sea, Croatia). Sedimentology 42(5):769–782
StatSoft Inc. (2007) STATISTICA (data analysis software system), version 8. www.statsoft.com
Štern J, Förstner U (1976) Heavy metals distribution in the sediment of the Sava Basin in Slovenia. Geologija 19:259–274
Strzyszcz Z (1993) Magnetic susceptibility of soils in the areas influenced by industrial emissions. In: Schulin R (ed) soil monitoring, Monte Verita, Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, pp 255–269
Strzyszcz Z, Magiera T, Heller F (1996) The influence of industrial emissions on the magnetic susceptibility of soils in Upper Silesia. Studia geophisica et geodetica 40:276–286
Thompson R, Oldfield F (1986) Environmental magnetism. Allen & Unwin, London
Tukey JW (1977) Exploratory data analysis. Addison-Wesley, Menlo Park ISBN0-201-07616-0
Zhang C, Qiao Q, Piper JDA, Huang B (2011) Assessment of heavy metal pollution from a Fe-smelting plant in urban river sediments using environmental magnetic and geochemical methods. Environ Pollut 159:3057–3070
Acknowledgments
Field work was organized within the Croatian–Slovenian bilateral project (2001–2003), principal investigators H. Bilinski and D. Hanžel. Magnetic measurements were performed at the Montanuniversität Leoben and at its Paleomagnetic Laboratory in Gams. A short stay of S. F–B. in Austria was covered from the Croatian–Austrian bilateral project (2010-2011), principal investigators S. Frančišković-Bilinski and T. Hofmann. Additional expenses were covered from projects of Croatian Ministry of Science Education and Sport No. 098-0982934-2720 (Principal investigator I. Pižeta) and No. 119-1191155-1156 (Principal investigator D. Balen). Authors are grateful to R. Košćal for preparing graphics. We also thank three anonymous reviewers, whose suggestions helped a lot to improve the overall quality of manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frančišković-Bilinski, S., Scholger, R., Bilinski, H. et al. Magnetic, geochemical and mineralogical properties of sediments from karstic and flysch rivers of Croatia and Slovenia. Environ Earth Sci 72, 3939–3953 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3282-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3282-x