Abstract
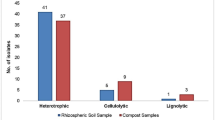
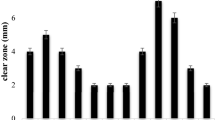
The aim of this study was to identify and investigate the diversity of culturable bacteria of leachate and screen potential cellulolytic bacteria. Some chemical characteristics of wheat straw based compost leachate was measured and the enumeration of bacteria in leachate performed. Cellulolytic bacteria were screened on plate containing carboxymethyl cellulose based medium through halo creation around the colonies which followed by assessing the isolates potential to produce enzyme in broth culture with cellulose powder and carboxymethyl cellulose. The obtained results showed that leachate was rich in nitrogen, potassium and iron with pH 7.76 and BOD5/COD ratio of 0.169. The enumeration of heterotrophic bacteria indicated the high population of bacteria (1.3 × 107 CFU mL−1) in the leachate. Isolation of the most prominent bacteria exhibited the variety of bacteria in compost leachate including both Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria which belonged to the phylum Actinobacteria, Gammaproteobacteria and Firmicutes consisted of genera Corynebacterium, Acinetobacter, Brevibacillus, Pseudomonas, Bacillus, Paenibacillus, Streptomyces, Cellulosimicrobium. About 7 isolates were screened on carboxymethyl cellulose containing plates which belonged to the genera Ochrobacterium, Acinetobacter, Psedoxanthomonas, Paenibacillus, Stenotrophomonas and Comamonas. The isolated bacteria Paenibacillus cellulosilyticus indicated higher enzyme activity of 0.27 and 0.17 IU mL−1 of CMCase and endoluoconase, respectively.
Graphic Abstract


Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
08 February 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01188-x
References
Acharya, S., Chaudhary, A.: Optimization of fermentation conditions for cellulases production by Bacillus licheniformis MVS21 and Bacillus sp. MVS3 isolated from Indian hot spring. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 55, 497–503 (2012)
APHA-AWWA-WEF: Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. American Public Health Association Press, Baltimore (2005)
Bhalla, B., Saini, M.S., Jha, M.K.: Characterization of leachate from municipal solid waste (MSW) landfilling sites of Ludhiana, India: a comparative study. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2(6), 732–745 (2013)
Bhat, M.K., Bhat, S.: Cellulose degrading enzymes and their potential industrial applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 15(3–4), 583–620 (1997)
Brown, K., Ghoshdastidar, A.J., Hanmore, J., Frazee, J., Tong, A.Z.: Membrane bioreactor technology: a novel approach to the treatment of compost leachate. Waste Manag. 33(11), 2188–2194 (2013)
Chandna, P., Nain, L., Singh, S., Kuhad, R.C.: Assessment of bacterial diversity during composting of agricultural byproducts. BMC Microbiol. 13(1), 1–11 (2013)
Chatterjee, N., Flury, M., Hinman, C., Cogger, C.G.: Chemical and physical characteristics of compost leachates. A Review Report prepared for the Washington State Department of Transportation. Washington State University (2013)
de Figueirecirc, V.R., Martos, E.T., Gonccedil, F., Maciel, W.P., da Silva, R., Rinker, D.L., Dias, E.S.: Microbial inoculation during composting improves productivity of sun mushroom (Agaricus subrufescens Peck). Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 7(35), 4430–4434 (2013)
De Guardia, A., Brunet, S., Rogeau, D., Matejka, G.: Fractionation and characterisation of dissolved organic matter from composting green wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 83(3), 181–187 (2002)
Dees, P.M., Ghiorse, W.C.: Microbial diversity in hot synthetic compost as revealed by PCR-amplified rRNA sequences from cultivated isolates and extracted DNA. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 35(2), 207–216 (2001)
Dias, E.S.: Mushroom cultivation in Brazil: challenges and potential for growth. Ciênc. Agrotecnol. 34(4), 795–803 (2010)
Du, R., Yan, J.B., Li, S.Z., Zhang, L., Zhang, S.R., Li, J.H., Zhao, G., Qi, P.L.: Cellulosic ethanol production by natural bacterial consortia is enhanced by Pseudoxanthomonas taiwanensis. Biotechnol. Biofuels 8(1), 1–10 (2015)
Eiland, F., Klamer, M., Lind, A.M., Leth, M., Bth, E.: Influence of initial C/N ratio on chemical and microbial composition during long term composting of straw. Microb. Ecol. 41(3), 272–280 (2001)
Ekperigin, M.M.: Preliminary studies of cellulase production by Acinetobacter anitratus and Branhamella sp. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 6(1), 28–33 (2007)
Elouaqoudi, F.Z., Fels, L., Amir, S., Merlina, G., Meddich, A., Lemee, L., Ambles, A., Hafidi, M.: Lipid signature of the microbial community structure during composting of date palm waste alone or mixed with couch grass clippings. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 97, 75–84 (2015)
Gaur, R., Tiwari, S.: Isolation, production, purification and characterization of an organic-solvent-thermostable alkalophilic cellulase from Bacillus vallismortis RG-07. BMC Biotechnol. 15(1), 1–12 (2015)
Gautam, S.P., Bundela, P.S., Pandey, A.K., Awasthi, M.K., Sarsaiya, S.: Diversity of cellulolytic microbes and the biodegradation of municipal solid waste by a potential strain. Int. J. Microbiol. 1, 1–12 (2012)
Gyalai-Korpos, M., Nagy, G., Mareczky, Z., Schuster, A., Réczey, K., Schmoll, M.: Relevance of the light signaling machinery for cellulase expression in Trichoderma reesei (Hypocrea jecorina). BMC. Res. notes. 3(1), 1–10 (2010)
Hou, L., Jiang, J., Xu, Z., Zhou, Y., Leung, F.C.C.: Complete genome sequence of Pseudoxanthomonas suwonensis strain J1, a cellulose-degrading bacterium isolated from leaf-and wood-enriched soil. Genome Announc 3(3), 614–615 (2015)
Insam, H., De Bertoldi, M.: Microbiology of the composting process. In: L.F. Diaz, M. de Bertoldi, W. Bidlingmaier, E. Stentinford (Eds.), Compost Science and Technology Waste Management Series, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 25–48(2007)
Ishii, K., Fukui, M., Takii, S.: Microbial succession during a composting process as evaluated by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 89(5), 768–777 (2012)
Jalak, J., Kurašin, M., Teugjas, H., Väljamäe, P.: Endo-exo synergism in cellulose hydrolysis revisited. J. Biol. Chem. 287(34), 28802–28815 (2012)
Kasana, R.C., Salwan, R., Dhar, H., Dutt, S., Gulati, A.: A rapid and easy method for the detection of microbial cellulases on agar plates using Gram’s iodine. Curr. Microbiol. 57(5), 503–507 (2008)
Kertesz, M., Safianowicz, K., Bell, T.: New insights into the microbial communities and biological activities that define mushroom compost. Sci. Cultiv. Edib. Fungi 19, 161–165 (2016)
Kertesz, M.A., Thai, M.: Compost bacteria and fungi that influence growth and development of Agaricus bisporus and other commercial mushrooms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 102(4), 1639–1650 (2018)
Khianngam, S., Pootaengon, Y., Techakriengkrai, T., Tanasupawat, S.: Screening and identification of cellulase producing bacteria isolated from oil palm meal. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 4(4), 90–96 (2014)
Kim, J.Y., Hur, S.H., Hong, J.H.: Purification and characterization of an alkaline cellulase from a newly isolated alkalophilic Bacillus sp. HSH-810. Biotechnol. Lett. 27(5), 313–316 (2005)
Kumar, M., Revathi, K., Khanna, S.: Biodegradation of cellulosic and lignocellulosic waste by Pseudoxanthomonas sp R-28. Carbohydr. Polym. 134, 761–766 (2015)
Kutu, F.R., Mokase, T.J., Dada, O.A., Rhode, O.H.J.: Assessing microbial population dynamics, enzyme activities and phosphorus availability indices during phospho-compost production. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 8(1), 87–97 (2019)
Ladeira, S.A., Cruz, E., Delatorre, A.B., Barbosa, J.B., Martins, L.: M.L.: Cellulase production by thermophilic Bacillus sp: SMIA-2 and its detergent compatibility. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 18(2), 110–115 (2015)
Liang, Y.L., Zhang, Z., Wu, M., Wu, Y., Feng, J.X.: Isolation, screening, and identification of cellulolytic bacteria from natural reserves in the subtropical region of China and optimization of cellulase production by Paenibacillus terrae ME27-1. BioMed. Res. Int. 10, 1–13 (2014)
Lu, Y., Wu, X., Guo, J.: Characteristics of municipal solid waste and sewage sludge co-composting. Waste Manag. 29(3), 1152–1157 (2009)
Lynd, L.R., Weimer, P.J., Van Zyl, W.H., Pretorius, I.S.: Pretorius IS. Microbial cellulose utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 66(3), 506–577 (2002)
Mandels, M., Reese, E.T.: Induction of cellulase in Trichoderma viride as influenced by carbon sources and metals. J. Bacteriol. 73(2), 269–278 (1975)
Marco, ÉG., Heck, K., Martos, E.T., Van Der Sand, S.T.: Purification and characterization of a thermostable alkaline cellulase produced by Bacillus licheniformis 380 isolated from compost. An. Acad. Bras. Ciên. 89(3), 2359–2370 (2017)
Marjamaa, K., Toth, K., Bromann, P.A., Szakacs, G., Kruus, K.: Novel Penicillium cellulases for total hydrolysis of lignocellulosics. Enzyme Microbl. Technol. 52(6–7), 358–369 (2013)
Martins, L.F., Kolling, D., Camassola, M., Dillon, A.J.P., Ramos, L.P.: Comparison of Penicillium echinulatum and Trichoderma reesei cellulases in relation to their activity against various cellulosic substrates. Bioresour. Technol. 99(5), 1417–1424 (2008)
Mass, E.V.: Crop salt tolerance. Agricultural salinity assessment and management manual. Tanji, K.K. (ed.). ASCE, New York. pp. 262–304(1990)
Meng, Q., Yang, W., Men, M., Bello, A., Xu, X., Xu, B., Deng, L., Jiang, X., Sheng, S., Wu, X., Han, Y.: Microbial community succession and response to environmental variables during cow manure and corn straw composting. Front. Microbial. 10, 1–13 (2019)
Ming, L., Xuya, P., Youcai, Z., Wenchuan, D., Huashuai, C., Guotao, L., Zhengsong, W.: Microbial inoculum with leachate recirculated cultivation for the enhancement of OFMSW composting. J. Hazard. Mater. 153(1–2), 885–891 (2008)
Nakazawa, K., Kitamura, K.: Purification and some properties of a cellulase active on crystalline cellulose from Cellulomonas uda. J. Ferment. Technol. 61, 379–382 (1983)
Partanen, P., Hultman, J., Paulin, L., Auvinen, P., Romantschuk, M.: Bacterial diversity at different stages of the composting process. BMC Microbiol. 10(1), 1–11 (2010)
Pavan Kumar, A., Devendra kumar, C., Prakash, A., Johri, B.N.: Bacterial diversity in a bagasse-based compost prepared for the cultivation of edible mushrooms Agaricus bisporus. J. Agr. Technol. 7(5), 1303–1311 (2011)
Pérez-Avalo, O., Sánchez-Herrera, L.M., Salgado, T.A.: Ponce-Noyola: bifunctional endoglucanase/endoxylanase from Cellulomonas flavigena with potential use in industrial processes at different pH. Curr. Microbiol. 57(1), 39–44 (2008)
Pierre, G., Maache-Rezzoug, Z., Sannier, F., Rezzoug, S.A., Maugard, T.: High-performance hydrolysis of wheat straw using cellulase and thermomechanical pretreatment. Process Biochem. 46(11), 2194–2200 (2011)
Queipo-Ortuño, M.I., Colmenero, J.D.D., Macias, M., Bravo, M.J., Morata, P.: Preparation of bacterial DNA template by boiling and effect of immunoglobulin G as an inhibitor in real-time PCR for serum samples from patients with brucellosis. Clin. Vaccine. Immunol. 15(2), 293–296 (2008)
Rastogi, G., Muppidi, G.L., Gurram, R.N., Adhikari, A., Bischoff, K.M., Hughes, S.R., Apel, W.A., Bang, S.S., Dixon, D.J., Sani, R.K.: Isolation and characterization of cellulose-degrading bacteria from the deep subsurface of the Homestake gold mine, Lead, South Dakota, USA. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 36(4), 585–598 (2009)
Romero, C., Ramos, P., Costa, C., Márquez, M.C.: Raw and digested municipal waste compost leachate as potential fertilizer: comparison with a commercial fertilizer. J. Clean Prod. 59, 73–78 (2013)
Roy, D., Azaïs, A., Benkaraache, S., Drogui, P., Tyagi, R.D.: Composting leachate: characterization, treatment, and future perspectives. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 17(2), 323–349 (2018)
Ryckeboer, J., Mergaert, J., Vaes, K., Klammer, S., De Clercq, D., Coosemans, J., Insam, H., Swings, J.: A survey of bacteria and fungi occurring during composting and self-heating processes. Ann. Microbiol. 53(4), 349–410 (2003)
Sadana, C., Lachke, A.H., Patil, R.V.: Endo-(1→ 4)-β-d-glucanases from Sclerotium rolfsii. Purification, substrate specificity, and mode of action. Carbohydr. Res. 133(2), 297–312 (1984)
Sadana, J.C., Patil, R.V.: 1, 4-β-d-Glucan cellobiohydrolase from Sclerotium rolfsii. In Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 160, pp. 307–314. Academic Press, New York (1988)
Safianowicz, K., Bell, T.L., Kertesz, M.A.: Bacterial population dynamics in recycled mushroom compost leachate. Appl. Microbial. Biotechnol. 102(12), 5335–5342 (2018)
Saini, A., Aggarwal, N.K., Yadav, A.: Isolation and screening of cellulose hydrolyzing bacteria from different ecological niches. Bioeng. Biosci. 5(1), 7–13 (2017)
Schwarz, W.: The cellulosome and cellulose degradation by anaerobic bacteria. Appl. Microbial. Biotechnol. 56(5–6), 634–649 (2001)
Song, B.C., Kim, K.Y., Yoon, J.J., Sim, S.H., Lee, K., Kim, Y.S., Kim, Y.K., Cha, C.J.: Functional analysis of a gene encoding endoglucanase that belongs to glycosyl hydrolase family 12 from the brown-rot basidiomycete Fomitopsis palustris. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 18(3), 404–409 (2008)
Székely, A.J., Sipos, R., Berta, B., Vajna, B., Haj dú, C., Márialigeti, K.: DGGE and T-RFLP analysis of bacterial succession during mushroom compost production and sequence-aided T-RFLP profile of mature compost. Microb. Ecol. 57(3), 522–533 (2009)
Vajna, B., Szili, D., Nagy, A., Marialigeti, K.: An improved sequenceaided T-RFLP analysis of bacterial succession during oyster mushroom substrate preparation. Microb. Ecol. 64(3), 702–713 (2012)
Velázquez-Cedeño, M., Farnet, A.M., Mata, G., Savoie, J.M.: Role of Bacillus spp. in antagonism between Pleurotus ostreatus and Trichoderma harzianum in heat-treated wheat-straw substrates. Bioresour. Technol. 99(15), 6966–6973 (2008)
Villar, I., Alves, D., Garrido, J., Mato, S.: Evolution of microbial dynamics during the maturation phase of the composting of different types of waste. Waste Manag. 54, 83–92 (2016)
Vishan, I., Sivaprakasam, S., Kalamdhad, A.: Isolation and identification of bacteria from rotary drum compost of water hyacinth. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric 6(3), 245–253 (2017)
Yoon, M.H., Choi, W.Y.: Characterization and action patterns of two beta-1,4-glucanases purified from cellulomonas uda CS1-1. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 17(8), 1291–1299 (2007)
Zainudin, M.H.M., Hassan, M.A., Tokura, M., Shirai, Y.: Indigenous cellulolytic and hemicellulolytic bacteria enhanced rapid co-composting of lignocellulose oil palm empty fruit bunch with palm oil mill effluent anaerobic sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 147, 632–635 (2013)
Zhang, X., Zhong, Y.H., Yang, S.D., Zhang, W.X., Xu, M.Q., Ma, A.Z., Zhuang, G.Q., Chen, G.J., Liu, W.F.: Diversity and dynamics of the microbial community on decomposing wheat straw during mushroom compost production. Bioresour. Technol. 170, 183–195 (2014)
Zhang, Y.H.P., Hong, J., Ye, X.: Cellulase assays. Methods Mol. Biol. 581, 213–231 (2009)
Zhang, Y.H.P., Lynd, L.R.: Toward an aggregated understanding of enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose: noncomplexed cellulase systems. Biotechnol. Bioengin. 88(7), 797–824 (2004)
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to Thank Deputy of Research and Technology of Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz (GN. SCU.AS98.248) and Jolgeh-y-Sabz Company for the support of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadipour, Z., Enayatizamir, N., Ghezelbash, G. et al. Bacterial Diversity and Chemical Properties of Wheat Straw-Based Compost Leachate and Screening of Cellulase Producing Bacteria. Waste Biomass Valor 12, 1293–1302 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01119-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01119-w