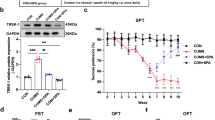
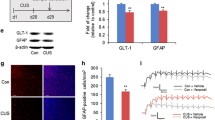
Abstract
Although monoaminergic-based antidepressant drugs are largely used to treat major depressive disorder (MDD), their mechanisms are still incompletely understood. Intracellular Ca2+ (iCa2+) and Calmodulin 1(CaM-1) homeostasis have been proposed to participate in the therapeutic effects of these compounds. We investigated whether intra-hippocampal inhibition of CaM-1 would modulate the behavioral responses to chronic treatment with imipramine (IMI) or 7-nitroindazole (7-NI), a selective inhibitor of the neuronal nitric oxide synthase 1 (NOS1) enzyme that shows antidepressant-like effects. We also investigated the interactions of IMI and CaM-1 on transient astrocyte iCa2+ evoked by glutamate stimuli. Intra-hippocampal microinjection of the lentiviral delivered (LV) short hairpin iRNA-driven against the CaM-1 mRNA (LV-shRNA-CaM-1) or the CaM-1 inhibitor N-(6-aminohexyl)-5-chloro-1-naphthalene sulphonamide (W-7) blocked the antidepressant-like effect of chronic treatment with IMI or 7-NI. The shRNA also inhibited the mRNA expression of the tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB) in the microinjection region. The iCa2+ in ex vivo hippocampus slices stained with fluorescent Ca2+indicator Oregon Green 488 BAPTA-1 revealed that IMI increased the intensity and duration of iCa2+ oscillation and reduced the number of events evoked by glutamate stimuli, evaluated by using CCD imaging and the % ΔF/Fo parameters. The pre-treatment with W-7 fully antagonized this effect. The present results indicate that the behavioral benefits of chronic antidepressant treatment might be associated with astrocyte intracellular Ca2+dynamics and TrkB mRNA expression in the hippocampus.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data and materials are available.
References
Axelrod J, Whitby LG, Hertting G (1961) Effect of psychotropic drugs on the uptake of H3-norepinephrine by tissues. Science 133:383–384
Ban TA (2001) Pharmacotherapy of depression: a historical analysis. J Neural Transm 108(6):707–716
Bjorkholm C, Monteggia LM (2016) BDNF - a key transducer of antidepressant effects. Neuropharmacology 102:72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.10.034
Bogdanova OV, Kanekar S, D’Anci KE, Renshaw PF (2013) Factors influencing behavior in the forced swim test. Physiol Behav 118(2):27–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2013.05.012
Byrne MJ, Putkey JA, Waxham MN, Kubota Y (2009) Dissecting cooperative calmodulin binding to CaM kinase II: a detailed stochastic model. J Comput Neurosci 27(3):621–638
Campbell S, Marriott M, Nahmias C, MacQueen GM (2004) Lower hippocampal volume in patients suffering from depression: a meta-analysis. Am J Psychiatry 161(4):598–607
Cao X, Li LP, Wang Q, Wu Q, Hu HH, Zhang M, Gao TM (2013) Astrocyte-derived ATP modulates depressive-like behaviors. Nat Med 19(6):773–777. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3162
Carlezon WA Jr, Duman RS, Nestler EJ (2005) The many faces of CREB. Trends Neurosci 28(8):436–445
Castren E, Voikar V, Rantamaki T (2007) Role of neurotrophic factors in depression. Curr Opin Pharmacol 7(1):18–21
Caulfield MP, Robbins J, Sim JA, Brown DA, Mac Neil S, Blackburn GM (1991) The naphthalenesulphonamide calmodulin antagonist W7 and its 5-iodo-1-C8 analogue inhibit potassium and calcium currents in NG108-15 neuroblastoma x glioma cells in a manner possibly unrelated to their antagonism of calmodulin. Neurosci Lett 125(1):57–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3940(91)90130-l
Chen F, Madsen TM, Wegener G, Nyengaard JR (2010) Imipramine treatment increases the number of hippocampal synapses and neurons in a genetic animal model of depression. Hippocampus 20(12):1376–1384. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.20718
Cheng A, Wang S, Yang D, Xiao R, Mattson MP (2003) Calmodulin mediates brain-derived neurotrophic factor cell survival signaling upstream of Akt kinase in embryonic neocortical neurons. J Biol Chem 278(9):7591–7599
de Morais H, de Souza CP, da Silva LM, Ferreira DM, Werner MF, Andreatini R, Zanoveli JM (2013) Increased oxidative stress in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus is related to depressive-like behavior in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Behav Brain Res 258C:52–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2013.10.011
Duman RS, Deyama S, Fogaca MV (2019) Role of BDNF in the pathophysiology and treatment of depression: Activity-dependent effects distinguish rapid-acting antidepressants. Eur J Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.14630
Emamghoreishi M, Li PP, Schlichter L, Parikh SV, Cooke R, Warsh JJ (2000) Associated disturbances in calcium homeostasis and G protein-mediated cAMP signaling in bipolar I disorder. Biol Psychiatry 48(7):665–673
Emamghoreishi M, Schlichter L, Li PP, Parikh S, Sen J, Kamble A, Warsh JJ (1997) High intracellular calcium concentrations in transformed lymphoblasts from subjects with bipolar I disorder. Am J Psychiatry 154(7):976–982
Ferreira FR, Oliveira AM, Dinarte AR, Pinheiro DG, Greene LJ, Silva WA Jr, Guimaraes FS (2012) Changes in hippocampal gene expression by 7-nitroindazole in rats submitted to forced swimming stress. Genes Brain Behav 11(3):303–313. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-183X.2011.00757.x
Fiori MG (1977) Tricyclic antidepressants: a review of their toxicology. Curr Dev Psychopharmacol 4:71–110
Gass P, Riva MA (2007) CREB, neurogenesis and depression. BioEssays 29(10):957–961
Gaynes BN, Warden D, Trivedi MH, Wisniewski SR, Fava M, Rush AJ (2009) What did STAR*D teach us? Results from a large-scale, practical, clinical trial for patients with depression. Psychiatr Serv 60(11):1439–1445. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ps.60.11.1439
Guo L, Wang L, Yang R, Feng R, Li Z, Zhou X, Xu X (2017) Optimizing conditions for calcium phosphate mediated transient transfection. Saudi J Biol Sci 24(3):622–629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.01.034
Hasbi A, Fan T, Alijaniaram M, Nguyen T, Perreault ML, O’Dowd BF, George SR (2009) Calcium signaling cascade links dopamine D1–D2 receptor heteromer to striatal BDNF production and neuronal growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(50):21377–21382
Hesslinger B, Riedel H, Hellwig B, Walden J, Berger M (1996) Phase prevention in bipolar affective disorder with nimodipine. A case report. Nervenarzt 67(5):394–396
Hroudova J, Fisar Z (2011) Connectivity between mitochondrial functions and psychiatric disorders. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 65(2):130–141
Iwata M, Shirayama Y, Ishida H, Hazama GI, Nakagome K (2011) Hippocampal astrocytes are necessary for antidepressant treatment of learned helplessness rats. Hippocampus 21(8):877–884. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.20803
Joca SR, Ferreira FR, Guimaraes FS (2007) Modulation of stress consequences by hippocampal monoaminergic, glutamatergic and nitrergic neurotransmitter systems. Stress 10(3):227–249
Joca SR, Padovan CM, Guimaraes FS (2003) Activation of post-synaptic 5-HT(1A) receptors in the dorsal hippocampus prevents learned helplessness development. Brain Res 978(1–2):177–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(03)02943-3
Kirchhoff F (2010) Neuroscience. Questionable calcium. Science 327(5970):1212–1213. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1187420
Krishnan V, Nestler EJ (2008) The molecular neurobiology of depression. Nature 455(7215):894–902
Kuhn R (1958) The treatment of depressive states with G 22355 (imipramine hydrochloride). Am J Psychiatry 115(5):459–464
Kumar A, Garg R, Gaur V, Kumar P (2009) Nitric oxide mechanism in protective effect of imipramine and venlafaxine against acute immobilization stress-induced behavioral and biochemical alteration in mice. Neurosci Lett 467(2):72–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2009.10.004
Li B, Zhang S, Zhang H, Nu W, Cai L, Hertz L, Peng L (2008a) Fluoxetine-mediated 5-HT2B receptor stimulation in astrocytes causes EGF receptor transactivation and ERK phosphorylation. Psychopharmacology 201(3):443–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1306-5
Li G, Comte M, Wollheim CB, Cox JA (1989) Mode of activation of bovine brain inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase by calmodulin and calcium. Biochem J 260(3):771–775. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2600771
Li Y, Luikart BW, Birnbaum S, Chen J, Kwon CH, Kernie SG, Parada LF (2008b) TrkB regulates hippocampal neurogenesis and governs sensitivity to antidepressive treatment. Neuron 59(3):399–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2008.06.023
Liu SH, Lai YL, Chen BL, Yang FY (2017) Ultrasound enhances the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in astrocyte through activation of TrkB-Akt and calcium-CaMK signaling pathways. Cereb Cortex 27(6):3152–3160. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhw169
Lonze BE, Ginty DD (2002) Function and regulation of CREB family transcription factors in the nervous system. Neuron 35(4):605–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00828-0
Ma Z, Zang T, Birnbaum SG, Wang Z, Johnson JE, Zhang CL, Parada LF (2017) TrkB dependent adult hippocampal progenitor differentiation mediates sustained ketamine antidepressant response. Nat Commun 8(1):1668. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01709-8
Madara JC, Levine ES (2008) Presynaptic and postsynaptic NMDA receptors mediate distinct effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on synaptic transmission. J Neurophysiol 100(6):3175–3184. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.90880.2008
Manna V (1991) Bipolar affective disorders and role of intraneuronal calcium. Therapeutic effects of the treatment with lithium salts and/or calcium antagonist in patients with rapid polar inversion. Minerva Med 82(11):757–763
Meng F, Liu J, Dai J, Wu M, Wang W, Liu C, Li C (2020) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in 5-HT neurons regulates susceptibility to depression-related behaviors induced by subchronic unpredictable stress. J Psychiatr Res 126:55–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.05.003
Mihanovic M, Restek-Petrovic B, Bodor D, Molnar S, Oreskovic A, Presecki P (2010) Suicidality and side effects of antidepressants and antipsychotics. Psychiatr Danub 22(1):79–84
Mochida S (2011) Ca/Calmodulin and presynaptic short-term plasticity. ISRN Neurol 2011:919043. https://doi.org/10.5402/2011/919043
Moussavi S, Chatterji S, Verdes E, Tandon A, Patel V, Ustun B (2007) Depression, chronic diseases, and decrements in health: results from the World Health Surveys. Lancet 370(9590):851–858. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61415-9
Paul IA (2001) Antidepressant activity and calcium signaling cascades. Hum Psychopharmacol 16(1):71–80. https://doi.org/10.1002/hup.186
Paxinos G, Watson C (1997) The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 3rd edn. (Pp. xxxiii+ 80; illustrated; f$ 69. 95 paperback; ISBN 0 12 547623; comes with CD-ROM.) San Diego: Academic Press. 1996
Peters O, Schipke CG, Hashimoto Y, Kettenmann H (2003) Different mechanisms promote astrocyte Ca2+ waves and spreading depression in the mouse neocortex. J Neurosci 23(30):9888–9896
Pirttimaki TM, Parri HR (2013) Astrocyte plasticity: implications for synaptic and neuronal activity. Neuroscientist 19(6):604–615. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858413504999
Porsolt RD, Bertin A, Jalfre M (1977) Behavioral despair in mice: a primary screening test for antidepressants. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 229(2):327–336
Quesseveur G, David DJ, Gaillard MC, Pla P, Wu MV, Nguyen HT, Guiard BP (2013a) BDNF overexpression in mouse hippocampal astrocytes promotes local neurogenesis and elicits anxiolytic-like activities. Transl Psychiatry 3:e253. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2013.30
Quesseveur G, Gardier AM, Guiard BP (2013b) The monoaminergic tripartite synapse: a putative target for currently available antidepressant drugs. Curr Drug Targets 14(11):1277–1294. https://doi.org/10.2174/13894501113149990209
Rafa-Zablocka K, Kreiner G, Baginska M, Nalepa I (2018) Selective depletion of CREB in serotonergic neurons affects the upregulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor evoked by chronic fluoxetine treatment. Front Neurosci 12:637. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00637
Reus GZ, Stringari RB, de Souza B, Petronilho F, Dal-Pizzol F, Hallak JE, Quevedo J (2010) Harmine and imipramine promote antioxidant activities in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Oxid Med Cell Longev 3(5):325–331
Rushlow WJ, Seah C, Sutton LP, Bjelica A, Rajakumar N (2009) Antipsychotics affect multiple calcium calmodulin dependent proteins. Neuroscience 161(3):877–886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.03.011
Schindelin J, Arganda-Carreras I, Frise E, Kaynig V, Longair M, Pietzsch T, Cardona A (2012) Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat Methods 9(7):676–682. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2019
Schipke CG, Heuser I, Peters O (2011) Antidepressants act on glial cells: SSRIs and serotonin elicit astrocyte calcium signaling in the mouse prefrontal cortex. J Psychiatr Res 45(2):242–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2010.06.005
Shi Y, Yuan Y, Xu Z, Pu M, Wang C, Zhang Y, Zhang Z (2012) Genetic variation in the calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaMK) pathway is associated with antidepressant response in females. J Affect Disord 136(3):558–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2011.10.030
Smith BC, Underbakke ES, Kulp DW, Schief WR, Marletta MA (2013) Nitric oxide synthase domain interfaces regulate electron transfer and calmodulin activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(38):E3577-3586. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1313331110
Smith MA, Makino S, Kvetnansky R, Post RM (1995) Stress and glucocorticoids affect the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 mRNAs in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 15(3 Pt 1):1768–1777
Soderling TR (2000) CaM-kinases: modulators of synaptic plasticity. Curr Opin Neurobiol 10(3):375–380
Suzuki N, Kanno T, Nagata Y, Kato T (1986) Inhibition of proliferative growth in glioma cells by calmodulin antagonists. J Neurosurg 65(1):74–79. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1986.65.1.0074
Takasaki I, Takarada S, Tatsumi S, Azegami A, Yasuda M, Fukuchi M, Tsuda M (2008) Extracellular adenosine 5’-triphosphate elicits the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor exon IV mRNA in rat astrocytes. Glia 56(13):1369–1379. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.20704
Tiscornia G, Singer O, Verma IM (2006a) Design and cloning of lentiviral vectors expressing small interfering RNAs. Nat Protoc 1(1):234–240
Tiscornia G, Singer O, Verma IM (2006b) Production and purification of lentiviral vectors. Nat Protoc 1(1):241–245
Toescu EC (2005) Normal brain ageing: models and mechanisms. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 360(1464):2347–2354. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2005.1771
Toescu EC, Verkhratsky A (2000) Parameters of calcium homeostasis in normal neuronal ageing. J Anat 197(Pt 4):563–569
Toescu EC, Verkhratsky A (2004) Ca2+ and mitochondria as substrates for deficits in synaptic plasticity in normal brain ageing. J Cell Mol Med 8(2):181–190
Toescu EC, Verkhratsky A (2007) Role of calcium in normal aging and neurodegeneration. Aging Cell 6(3):265. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2007.00299.x
Toescu EC, Vreugdenhil M (2010) Calcium and normal brain ageing. Cell Calcium 47(2):158–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2009.11.013
Walden J, Fritze J, Van Calker D, Berger M, Grunze H (1995) A calcium antagonist for the treatment of depressive episodes: single case reports. J Psychiatr Res 29(1):71–76
Wang Q, Jie W, Liu JH, Yang JM, Gao TM (2017) An astroglial basis of major depressive disorder? An overview. Glia 65(8):1227–1250. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23143
Wayman GA, Lee YS, Tokumitsu H, Silva AJ, Soderling TR (2008) Calmodulin-kinases: modulators of neuronal development and plasticity. Neuron 59(6):914–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2008.08.021
Wei L, Kan LY, Zeng HY, Tang YY, Huang HL, Xie M, Tang XQ (2018) BDNF/TrkB pathway mediates the antidepressant-like role of H2S in CUMS-exposed rats by inhibition of hippocampal ER stress. Neuromolecular Med 20(2):252–261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-018-8489-7
Willner P, Scheel-Kruger J, Belzung C (2012) The neurobiology of depression and antidepressant action. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.12.007
Wolf F, Kirchhoff F (2008) Neuroscience. Imaging astrocyte activity. Science 320(5883):1597–1599. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1160122
Zafra F, Castren E, Thoenen H, Lindholm D (1991) Interplay between glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid transmitter systems in the physiological regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor synthesis in hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88(22):10037–10041
Zafra F, Lindholm D, Castren E, Hartikka J, Thoenen H (1992) Regulation of brain- derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor mRNA in primary cultures ofhippocampal neurons and astrocytes. J Neurosci 12(12):4793–4799
Zarate CA Jr, Mathews DC, Furey ML (2013) Human biomarkers of rapid antidepressant effects. Biol Psychiatry 73(12):1142–1155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.11.031
Zhang Z, Chen G, Zhou W, Song A, Xu T, Luo Q, Duan S (2007) Regulated ATP release from astrocytes through lysosome exocytosis. Nat Cell Biol 9(8):945–953. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1620
Zhou L, Zhu DY (2009) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase: structure, subcellular localization, regulation, and clinical implications. Nitric Oxide 20(4):223–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2009.03.001
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Frank Rhode for helpful technical support.
Funding
This study was supported by São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (FAPESP), National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), and Oswaldo Cruz Foundation (PON-FIOCRUZ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferreira, F.R., Cupido, A., Catalin, B. et al. Astrocyte Intracellular Ca2+and TrkB Signaling in the Hippocampus Could Be Involved in the Beneficial Behavioral Effects of Antidepressant Treatment. Neurotox Res 39, 860–871 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-021-00334-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-021-00334-0