Abstract
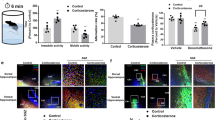
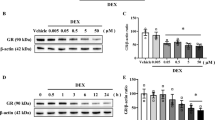
Prenatal glucocorticoid (GC) overexposure impacts fetal hippocampal neural stem cells (NSCs) and increases the risk for relative cognitive and mood disorders in offspring. However, the precise underlying mechanisms remain elusive. Here, we treated mouse hippocampal NSCs with dexamethasone (DEX) in vitro and found that DEX inhibited cell proliferation and Sirt7 expression. In addition, prenatal mouse overexposure to DEX induced the suppression of Sirt7 in the hippocampus of offspring. Sirt7 knockdown significantly decreased the percentage of proliferating cells but did not further reduce the NSC proliferation rate in the presence of DEX, whereas Sirt7 overexpression rescued DEX-induced inhibition of hippocampal NSC proliferation. Moreover, DEX inhibited Sirt7 expression through the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), and p21 was found to mediate the functional effect of DEX-induced Sirt7 suppression. In conclusion, our data demonstrate for the first time the effect of DEX on the Sirt7-p21 pathway in hippocampal NSCs, identifying a new potential therapeutic target for prenatal GC overexposure–related neurodevelopmental disorders in offspring.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
20 April 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-021-00360-y
Abbreviations
- NSCs:
-
Neural stem cells
- DEX:
-
Dexamethasone
- DG:
-
Dentate gyrus
- GR:
-
Glucocorticoid receptor
- GC:
-
Glucocorticoid
- P3W:
-
Postnatal 3 week
- GREs:
-
GC-responsive elements
- CDK:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase
- MR:
-
Mineralocorticoid receptor
References
Anacker C, Hen R (2017) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive flexibility—linking memory and mood. Nat Rev Neurosci 18:335–346
Bertoli C, Skotheim JM, De Bruin RA (2013) Control of cell cycle transcription during G1 and S phases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14:518–528
Bose R, Moors M, Tofighi R, Cascante A, Hermanson O, Ceccatelli S (2010) Glucocorticoids induce long-lasting effects in neural stem cells resulting in senescence-related alterations. Cell Death Dis 1:e92–e92
Cha HH, Cram EJ, Wang EC, Huang AJ, Kasler HG, Firestone GL (1998) Glucocorticoids stimulate p21 gene expression by targeting multiple transcriptional elements within a steroid responsive region of the p21 waf1/cip1 promoter in rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem 273:1998–2007
Choy KHC, de Visser Y, Nichols NR, van den Buuse M (2008) Combined neonatal stress and young-adult glucocorticoid stimulation in rats reduce BDNF expression in hippocampus: effects on learning and memory. Hippocampus 18:655–667
Cole TJ (2006) Glucocorticoid action and the development of selective glucocorticoid receptor ligands. Biotechnol Annu Rev 12:269–300
Cram EJ, Ramos RA, Wang EC, Cha HH, Nishio Y, Firestone GL (1998) Role of the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-α transcription factor in the glucocorticoid stimulation of p21 waf1/cip1 gene promoter activity in growth-arrested rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem 273:2008–2014
de los Angeles GAM, del Carmen ROM, Wendy PM, Socorro R-M (2016) Tactile stimulation effects on hippocampal neurogenesis and spatial learning and memory in prenatally stressed rats. Brain Res Bull 124:1–11
Diaz-Perdigon T, Belloch FB, Ricobaraza A, Elboray EE, Suzuki T, Tordera RM, Puerta E (2020) Early sirtuin 2 inhibition prevents age-related cognitive decline in a senescence-accelerated mouse model. Neuropsychopharmacology 45:347–357
Eichenbaum H, Cohen NJ (2014) Can we reconcile the declarative memory and spatial navigation views on hippocampal function? Neuron 83:764–770
Eto I (2010) Upstream molecular signaling pathways of p27 (Kip1) expression: effects of 4-hydroxytamoxifen, dexamethasone, and retinoic acids. Cancer Cell Int 10:3
Fusco S, Leone L, Barbati SA, Samengo D, Piacentini R, Maulucci G, Toietta G, Spinelli M, McBurney M, Pani G, Grassi C (2016) A CREB-Sirt1-Hes1 circuitry mediates neural stem cell response to glucose availability. Cell Rep 14:1195–1205
G V, M L (2020) Genetics in endocrinology: glucocorticoid resistance syndrome. Eur J Endocrinol 182:R15–R27
Gao J, Wang W-Y, Mao Y-W, Gräff J, Guan J-S, Pan L, Mak G, Kim D, Su SC, Tsai LH (2010) A novel pathway regulates memory and plasticity via SIRT1 and miR-134. Nature 466:1105–1109
Han D, Gao J, Gu X, Hengstler JG, Zhang L, Shahid M, Ali T, Han B (2018) P21 Waf1/Cip1 depletion promotes dexamethasone-induced apoptosis in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells by inhibiting the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Arch Toxicol 92:679–692
Hauser J, Feldon J, Pryce CR (2009) Direct and dam-mediated effects of prenatal dexamethasone on emotionality, cognition and HPA axis in adult Wistar rats. Horm Behav 56:364–375
Hauser J, Knapman A, Zürcher NR, Pilloud S, Maier C et al (2008) Effects of prenatal dexamethasone treatment on physical growth, pituitary-adrenal hormones, and performance of motor, motivational, and cognitive tasks in juvenile and adolescent common marmoset monkeys. Endocrinology 149:6343–6355
Holmes MC, Abrahamsen CT, French KL, Paterson JM, Mullins JJ, Seckl JR (2006) The mother or the fetus? 11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 null mice provide evidence for direct fetal programming of behavior by endogenous glucocorticoids. J Neurosci 26:3840–3844
Islam MS, Wei F-Y, Ohta K, Shigematsu N, Fukuda T, Tomizawa K, Yoshizawa T, Yamagata K (2018) Sirtuin 7 is involved in the consolidation of fear memory in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 495:261–266
Kawata M (1995) Roles of steroid hormones and their receptors in structural organization in the nervous system. Neurosci Res 24:1–46
Kim J-H, Kim D, Cho SJ, Jung K-Y, Kim J-H, Lee JM, Jung HJ, Kim KR (2019) Identification of a novel SIRT7 inhibitor as anticancer drug candidate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 508:451–457
Kim JB, Ju JY, Kim JH, Kim T-Y, Yang B-H, Lee Y-S, Son H (2004) Dexamethasone inhibits proliferation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Brain Res 1027:1–10
Kino T (2015) Stress, glucocorticoid hormones, and hippocampal neural progenitor cells: implications to mood disorders. Front Physiol 6:230
Lautarescu A, Pecheva D, Nosarti C, Nihouarn J, Zhang H, Victor S, Craig M, Edwards AD, Counsell SJ (2020) Maternal prenatal stress is associated with altered uncinate fasciculus microstructure in premature neonates. Biol Psychiatry 87:559–569
Li W, Zhang B, Tang J, Cao Q, Wu Y, Wu C, Guo J, Ling EA, Liang F (2007) Sirtuin 2, a mammalian homolog of yeast silent information regulator-2 longevity regulator, is an oligodendroglial protein that decelerates cell differentiation through deacetylating α-tubulin. J Neurosci 27:2606–2616
Lu NZ, Cidlowski JA (2006) Glucocorticoid receptor isoforms generate transcription specificity. Trends Cell Biol 16:301–307
Lucassen PJ, Müller MB, Holsboer F, Bauer J, Holtrop A, Wouda J, Hoogendijk WJG, de Kloet ER, Swaab DF (2001) Hippocampal apoptosis in major depression is a minor event and absent from subareas at risk for glucocorticoid overexposure. Am J Pathol 158:453–468
Ma C-y, Yao M-j, Zhai Q-w, J-w J, Yuan X-b, Poo M-m (2014) SIRT1 suppresses self-renewal of adult hippocampal neural stem cells. Development 141:4697–4709
MacQueen G, Frodl T (2011) The hippocampus in major depression: evidence for the convergence of the bench and bedside in psychiatric research? Mol Psychiatry 16:252–264
Mirescu C, Peters JD, Gould E (2004) Early life experience alters response of adult neurogenesis to stress. Nat Neurosci 7:841–846
Mohamed Ariff I, Mitra A, Basu A (2012) Epigenetic regulation of self-renewal and fate determination in neural stem cells. J Neurosci Res 90:529–539
Moisiadis VG, Matthews SG (2014) Glucocorticoids and fetal programming part 1: outcomes. Nat Rev Endocrinol 10:391–402
Mutsaers HA, Tofighi R (2012) Dexamethasone enhances oxidative stress-induced cell death in murine neural stem cells. Neurotox Res 22:127–137
Neilson J (2007) Antenatal corticosteroids for accelerating fetal lung maturation for women at risk of preterm birth. Obstet Gynecol 109:189–190
Peaceman A, Bajaj K, Kumar P, Grobman W (2006) The interval between a single course of antenatal steroids and delivery and its association with neonatal outcomes. Midirs Midwifery Digest 16:112–113
Poulsen RC, Watts AC, Murphy RJ, Snelling SJ, Carr AJ, Hulley PA (2014) Glucocorticoids induce senescence in primary human tenocytes by inhibition of sirtuin 1 and activation of the p53/p21 pathway: in vivo and in vitro evidence. Ann Rheum Dis 73:1405–1413
Reagan-Shaw S, Nihal M, Ahmad N (2008) Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J 22:659–661
Scheinost D, Sinha R, Cross SN, Kwon SH, Sze G, Constable RT, Ment LR (2017) Does prenatal stress alter the developing connectome? Pediatr Res 81:214–226
Seckl JR (2001) Glucocorticoid programming of the fetus; adult phenotypes and molecular mechanisms. Mol Cell Endocrinol 185:61–71
Suzuki S, Iben JR, Coon SL, Kino T (2018) SIRT1 is a transcriptional enhancer of the glucocorticoid receptor acting independently to its deacetylase activity. Mol Cell Endocrinol 461:178–187
Uhlenhaut NH, Barish GD, Ruth TY, Downes M, Karunasiri M et al (2013) Insights into negative regulation by the glucocorticoid receptor from genome-wide profiling of inflammatory cistromes. Mol Cell 49:158–171
Wang G, Li S, Gilbert J, Gritton HJ, Wang Z, Li Z, Han X, Selkoe DJ, Man HY (2017) Crucial roles for SIRT2 and AMPA receptor acetylation in synaptic plasticity and memory. Cell Rep 20:1335–1347
Wang G, Wang F, Ren J, Qiu Y, Zhang W, Gao S, Yang D, Wang Z, Liang A, Gao Z, Xu J (2018) SIRT1 involved in the regulation of alternative splicing affects the DNA damage response in neural stem cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 48:657–669
Wyrwoll CS, Holmes MC, Seckl JR (2011) 11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases and the brain: from zero to hero, a decade of progress. Front Neuroendocrinol 32:265–286
Xu D, Luo HW, Hu W, Hu SW, Yuan C, Wang GH, Zhang L, Yu H, Magdalou J, Chen LB, Wang H (2018) Intrauterine programming mechanism for hypercholesterolemia in prenatal caffeine-exposed female adult rat offspring. FASEB J 32:5563–5576
Yoo DY, Kim DW, Kim MJ, Choi JH, Jung HY, Nam SM, Kim JW, Yoon YS, Choi SY, Hwang IK (2015) Sodium butyrate, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, ameliorates SIRT2-induced memory impairment, reduction of cell proliferation, and neuroblast differentiation in the dentate gyrus. Neurol Res 37:69–76
Zhang X, Shang-Guan Y, Ma J, Hu H, Wang L, Magdalou J, Chen L, Wang H (2016) Mitogen-inducible gene-6 partly mediates the inhibitory effects of prenatal dexamethasone exposure on endochondral ossification in long bones of fetal rats. Br J Pharmacol 173:2250–2262
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants 81530042, 31830059, 31721003, 31871495, 31701110) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (22120190149).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All mice were maintained and handled according to Tongji University institutional guidelines.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOC 121 kb)
Supplementary Figure 1.
Test of NSC proliferation by CFSE-based assay. (a) CFSE-based assay among DMSO- or DEX-treated NSCs. (b) CFSE-based assay in Sirt7-knockdown and control NSCs treated with DMSO or DEX. (c) CFSE-based assay in p21-knockdown and control NSCs treated with DMSO or DEX. (d) CFSE based-assay in shCtrl- or shSirt7 (shSirt7-1, shSirt7-2)-transfected NSCs following p21 knockdown. (e) CFSE-based assay in the DMSO+HA-Luc, DEX+HA-Luc, DEX+HA-SIRT7, DEX+HA-p21, and DEX+HA-SIRT7+HA-p21 groups. The data are shown as the mean ± SEM. Student’s t test. ***P<0.001. (JPG 706 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alnoud, M.A.H., Chen, W., Liu, N. et al. Sirt7-p21 Signaling Pathway Mediates Glucocorticoid-Induced Inhibition of Mouse Neural Stem Cell Proliferation. Neurotox Res 39, 444–455 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00294-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00294-x