Abstract
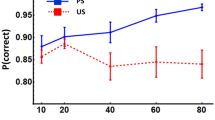
It is widely agreed upon that hippocampal function is linked to episodic-like and spatial memory across various species, for example, rodents. However, the interplay between hippocampal function and other types of learning and memory, like procedural stimulus–response or sequential learning, is less clear. Recently (Eckart et al. in Hippocampus 22:1202–1214, 2012), we showed that excitotoxic hippocampal lesions, which mainly affected its dorsal part, led not only to the expected deficits in a spatial and episodic-like memory task, namely the object place recognition test, but also to substantial improvements in terms of speed and accuracy in a rat adaption of the human sequential reaction time task (SRTT). The design of that experiment, however, which included fixed test durations per training day, led to the fact that lesioned animals gained more instrumental experience, which may partly have accounted for their enhanced performance. In order to rule out such a potential confound, we performed the present experiment on rats with similar ibotenic lesions aiming at the dorsal hippocampus, but we now kept the amount of correct instrumental responses and reinforcements on the same level as in controls. Our data revealed that lesioned animals were still able to complete the SRTT in a substantially smaller amount of time, when compared to control and sham-operated animals, although no differences were observable in terms of speed or accuracy. Also, the animals with lesions showed impaired extinction in a subsequent test where rewards were omitted. The former effect can primarily be attributed to shorter post-reinforcement pauses in the lesioned animals, and the possible mechanisms of this and the extinction effect will be addressed in the discussion.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams FS, Schwarting RK, Huston JP (1994) Behavioral and neurochemical asymmetries following unilateral trephination of the rat skull: is this control operation always appropriate? Physiol Behav 55:947–952
Altman J, Brunner RL, Bayer SA (1973) The hippocampus and behavioral maturation. Behav Biol 8:557–596
Amaral DG, Witter MP (1989) The three-dimensional organization of the hippocampal formation: a review of anatomical data. Neuroscience 31:571–591
Amaral DG, Witter MP (1995) Hippocampal formation. In: Paxinos G (ed) The rat nervous system. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 443–493
Bast T, Feldon J (2003) Hippocampal modulation of sensorimotor processes. Prog Neurobiol 70:319–345
Bast T, Zhang WN, Feldon J (2001) The ventral hippocampus and fear conditioning in rats. Different anterograde amnesias of fear after tetrodotoxin inactivation and infusion of the GABA(A) agonist muscimol. Exp Brain Res 139:39–52
Bast T, Wilson IA, Witter MP, Morris RGM (2009) From rapid place learning to behavioral performance: a key role for the intermediate hippocampus. PLoS Biol 7:e1000089
Bevins RA, Besheer J (2006) Object recognition in rats and mice: a one-trial non-matching-to-sample learning task to study ‘recognition memory’. Nat Protoc 1:1306–1311
Cameron HA, Glover LR (2015) Adult neurogenesis: beyond learning and memory. Annu Rev Psychol 66:53–81
Chang Q, Gold PE (2003a) Intra-hippocampal lidocaine injections impair acquisition of a place task and facilitate acquisition of a response task in rats. Behav Brain Res 144:19–24
Chang Q, Gold PE (2003b) Switching memory systems during learning: changes in patterns of brain acetylcholine release in the hippocampus and striatum in rats. J Neurosci 23:3001–3005
Cheung THC, Cardinal RN (2005) Hippocampal lesions facilitate instrumental learning with delayed reinforcement but induce impulsive choice in rats. BMC Neurosci 6:36
Chudasama Y, Wright KS, Murray EA (2008) Hippocampal lesions in rhesus monkeys disrupt emotional responses but not reinforcer devaluation effects. Biol Psychiatry 63:1084–1091
Chudasama Y, Izquierdo A, Murray EA (2009) Distinct contributions of the amygdala and hippocampus to fear expression. Eur J Neurosci 30:2327–2337
Compton DM (2004) Behavior strategy learning in rat. effects of lesions of the dorsal striatum or dorsal hippocampus. Behav Process 67:335–342
Coover GD, Goldman L, Levine S (1971) Plasma corticosterone levels during extinction of a lever-press response in hippocampectomized rats. Physiol Behav 7:727–732
Coutureau E, Killcross S (2003) Inactivation of the infralimbic prefrontal cortex reinstates goal-directed responding in overtrained rats. Behav Brain Res 146:167–174
Domenger D, Schwarting RK (2005) Sequential behavior in the rat. A new model using food-reinforced instrumental behavior. Behav Brain Res 160:197–207
Domenger D, Schwarting RK (2006) The serial reaction time task in the rat. Effects of D1 and D2 dopamine-receptor antagonists. Behav Brain Res 175:212–222
Domenger D, Schwarting RK (2007) Sequential behavior in the rat. Role of skill and attention. Exp Brain Res 182:223–231
Domenger D, Schwarting RK (2008) Effects of neostriatal 6-OHDA lesion on performance in a rat sequential reaction time task. Neurosci Lett 444:212–216
Douglas RJ (1967) The hippocampus and behavior. Psychol Bull 67:416–422
Eckart MT, Huelse-Matia MC, Loer D, Schwarting RK (2010a) Acquisition and performance in a rat sequential reaction time task is not affected by subtotal ventral striatal 6-OHDA lesions. Neurosci Lett 476:21–31
Eckart MT, Huelse-Matia MC, McDonald RS, Schwarting RK (2010b) 6-Hydroxydopamine lesions in the rat neostriatum impair sequential learning in a serial reaction time task. Neurotox Res 17:287–298
Eckart MT, Huelse-Matia MC, Schwarting RKW (2012) Dorsal hippocampal lesions boost performance in the rat sequential reaction time task. Hippocampus 22:1202–1214
Fanselow MS, Dong HW (2010) Are the dorsal and ventral hippocampus functionally distinct structures? Neuron 65:7–19
Ferbinteanu J, McDonald RJ (2000) Dorsal and ventral hippocampus: same or different? Psychobiology 28:314–324
Flicker C, Geyer MA (1982a) Behavior during hippocampal microinfusions. II: muscarinic locomotor activation. Brain Res 257:105–127
Flicker C, Geyer MA (1982b) Behavior during hippocampal microinfusions. III: lidocaine versus picrotoxin. Brain Res 257:129–136
Gilbert PE, Kesner RP (2002) The amygdala but not the hippocampus is involved in pattern separation based on reward value. Neurobiol Learn Mem 77:338–353
Gray JA, McNaughton N (2000) The neuropsychology of anxiety. An enquiry into the functions of the septo-hippocampal system. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Graybiel AM (2008) Habits, rituals, and the evaluative brain. Annu Rev Neurosci 31:359–387
Grossman R, Shohami E, Alexandrovich A, Yatsiv I, Kloog Y, Biegon A (2003) Increase in peripheral benzodiazepine receptors and loss of glutamate NMDA receptors in a mouse model of closed head injury: a quantitative autoradiographic study. Neuroimage 20:1971–1981
Gruber AJ, McDonald RJ (2012) Context, emotion, and the strategic pursuit of goals: interactions among multiple brain systems controlling motivated behavior. Front Behav Neurosci 6:50
Hirsh R (1974) The hippocampus and contextual retrieval of information from memory: a theory. Behav Biol 12:421–444
Hirshler YK, Polat U, Biegon A (2010) Intracranial electrode implantation produces regional neuroinflammation and memory deficits in rats. Exp Neurol 222:42–50
Hopkins RO, Waldram K, Kesner RP (2004) Sequences assessed by declarative and procedural tests of memory in amnesic patients with hippocampal damage. Neuropsychologia 42:1877–1886
Isaacson RL, Kimble DP (1972) Lesions of the limbic system: their effects upon hypotheses and frustration. Behav Biol 7:767–793
Ito R, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (2005) The hippocampus and appetitive Pavlovian conditioning: effects of excitotoxic hippocampal lesions on conditioned locomotor activity and autoshaping. Hippocampus 15:713–721
Jacobson TK, Gruenbaum BF, Markus EJ (2012) Extensive training and hippocampus or striatum lesions: effect on place and response strategies. Physiol Behav 105:645–652
Kelley AE, Domesick VB (1982) The distribution of the projection from the hippocampal formation to the nucleus accumbens in the rat: an anterograde- and retrograde-horseradish peroxidase study. Neuroscience 7:2321–2335
Killcross S, Coutureau E (2003) Coordination of actions and habits in the medial prefrontal cortex of rats. Cereb Cortex 13:400–408
Kimble DP (1968) Hippocampus and internal inhibition. Psychol Bull 70:285–295
Machado CJ, Bachevalier J (2008) Behavioral and hormonal reactivity to threat: effects of selective amygdala, hippocampal or orbital frontal lesions in monkeys. Psychoneuroendocrino 33:926–941
Mariano TY, Bannerman DM, McHugh SB, Preston TJ, Rudebeck PH, Rudebeck SR, Rawlins JNP, Walton ME, Rushworth MFS, Baxter MG, Campbell TG (2009) Impulsive choice in hippocampal but not orbitofrontal cortex-lesioned rats on a nonspatial decision-making maze task. Eur J Neurosci 30:472–484
McDonald RJ, White NM (1993) A triple dissociation of memory systems: hippocampus, amygdala, and dorsal striatum. Behav Neurosci 107:3–22
McDonald RJ, White NM (1994) Parallel information processing in the water maze: evidence for independent memory systems involving dorsal striatum and hippocampus. Behav Neural Biol 61:260–270
McDonald RJ, White NM (2013) A triple dissociation of memory systems: hippocampus, amygdala, and dorsal striatum. Behav Neurosci 127:835–853
McDonald RJ, Foong N, Hong NS (2004) Incidental information acquired by the amygdala during acquisition of a stimulus-response habit task. Exp Brain Res 159:72–83
McDonald RJ, Foong N, Ray C, Rizos Z, Hong NS (2007) The role of medial prefrontal cortex in context-specific inhibition during reversal learning of a visual discrimination. Exp Brain Res 177:509–519
McHugh SB, Campbell TG, Taylor AM, Rawlins JNP, Bannerman DM (2008) A role for dorsal and ventral hippocampus in inter-temporal choice cost-benefit decision making. Behav Neurosci 122:1–8
Mittleman G, LeDuc PA, Whishaw IQ (1993) The role of D1 and D2 receptors in the heightened locomotion induced by direct and indirect dopamine agonists in rats with hippocampal damage: an animal analogue of schizophrenia. Behav Brain Res 55:253–267
Mogenson GJ, Nielsen M (1984) A study of the contribution of hippocampal-accumbens-subpallidal projections to locomotor activity. Behav Neural Biol 42:38–51
Nagy H, Keri S, Myers CE, Benedek G, Shohamy D, Gluck MA (2007) Cognitive sequence learning in Parkinson’s disease and amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Dissociation between sequential and non-sequential learning of associations. Neuropsychologia 45:1386–1392
Nazar M, Siemiatkowski M, Członkowska A, Sienkiewicz-Jarosz H, Płaźnik A (1999) The role of the hippocampus and 5-HT/GABA interaction in the central effects of benzodiazepine receptor ligands. J Neural Transm 106:369–381
Nissen MJBP (1987) Attentional requirements of learning. Evidence from performance measures. Cognit Psychol 19:1–32
Peters H, Hunt M, Harper D (2010) An animal model of slot machine gambling: the effect of structural characteristics on response latency and persistence. J Gambl Stud 26:521–531
Pitkänen A, Pikkarainen M, Nurminen N, Ylinen A (2000) Reciprocal connections between the amygdala and the hippocampal formation, perirhinal cortex, and postrhinal cortex in rat. A review. Ann N Y Acad Sci 911:369–391
Raghavendra Rao VL, Dogan A, Bowen KK, Dempsey RJ (2000) Traumatic brain injury leads to increased expression of peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors, neuronal death, and activation of astrocytes and microglia in rat thalamus. Exp Neurol 161:102–114
Rawlins JN, Feldon J, Gray JA (1980) The effects of hippocampectomy and of fimbria section upon the partial reinforcement extinction effect in rats. Exp Brain Res 38:273–283
Reed J, Johnson P (1994) Assessing implicit learning with indirect tests: determining what is learned about sequence structure. J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cognit 20:585–594
Rich EL, Shapiro ML (2007) Prelimbic/infralimbic inactivation impairs memory for multiple task switches, but not flexible selection of familiar tasks. J Neurosci 27:4747–4755
Rich EL, Shapiro M (2009) Rat prefrontal cortical neurons selectively code strategy switches. J Neurosci 29:7208–7219
Schmelzeis MC, Mittleman G (1996) The hippocampus and reward: effects of hippocampal lesions on progressive-ratio responding. Behav Neurosci 110:1049–1066
Schwarting RK (2009) Rodent models of serial reaction time tasks and their implementation in neurobiological research. Behav Brain Res 199:76–88
Silveira JM, Kimble DP (1968) Brightness discrimination and reversal in hippocampally-lesioned rats. Physiol Behav 3:625–630
Simonov PV (1974) On the role of the hippocampus in the integrative activity of the brain. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 34:33–41
Simonov PV (1991) Thwarted action needed—informational theories of emotions. Int J Comp Psychol 5(2):103–107
Spanswick SC, Sutherland RJ (2010) Object/context-specific memory deficits associated with loss of hippocampal granule cells after adrenalectomy in rats. Learn Mem 17:241–245
Tait DS, Brown VJ (2007) Difficulty overcoming learned non-reward during reversal learning in rats with ibotenic acid lesions of orbital prefrontal cortex. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1121:407–420
Tam SK, Jennings DJ, Bonardi C (2015) Effects of dorsal hippocampal damage on conditioning and conditioned-response timing: a pooled analysis. Hippocampus 25:444–459
Taylor JR, Robbins TW (1984) Enhanced behavioural control by conditioned reinforcers following microinjections of d-amphetamine into the nucleus accumbens. Psychopharmacology 84:405–412
Verwer RW, Meijer RJ, van Uum HF, Witter MP (1997) Collateral projections from the rat hippocampal formation to the lateral and medial prefrontal cortex. Hippocampus 7:397–402
Wallace RJ, Tigner JC (1972) Effect of cortical and hippocampal lesions on hoarding behavior in the albino rat. Physiol Behav 8:937–942
White NM, McDonald RJ (2002) Multiple parallel memory systems in the brain of the rat. Neurobiol Learn Mem 77:125–184
White NM, Packard MG, McDonald RJ (2013) Dissociation of memory systems: the story unfolds. Behav Neurosci 127:813–834
Wilkinson LS, Mittleman G, Torres E, Humby T, Hall FS, Robbins TW (1993) Enhancement of amphetamine-induced locomotor activity and dopamine release in nucleus accumbens following excitotoxic lesions of the hippocampus. Behav Brain Res 55:143–150
Will JL, Eckart MT, Rosenow F, Bauer S, Oertel WH, Schwarting RKW, Norwood BA (2013) Enhanced sequential reaction time task performance in a rat model of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with classic hippocampal sclerosis. Behav Brain Res 247:65–72
Wirth S, Ferry B, Di Scala G (1998) Facilitation of olfactory recognition by lateral entorhinal cortex lesion in rats. Behav Brain Res 91:49–59
Wise SP, Murray EA (2000) Arbitrary associations between antecedents and actions. Trends Neurosci 23:271–276
Wishart T, Brohman L, Mogenson G (1969) Effects of lesions of the hippocampus and septum on hoarding behaviour. Anim Behav 17:781–784
Zhang WN, Bast T, Feldon J (2001) The ventral hippocampus and fear conditioning in rats: different anterograde amnesias of fear after infusion of N-methyl-d-aspartate or its noncompetitive antagonist MK-801 into the ventral hippocampus. Behav Brain Res 126:159–174
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grant SCHW 559/12-1 from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. Thanks to Janine Roscher for support in data acquisition and analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Busse, S., Schwarting, R.K.W. Procedural Performance Benefits after Excitotoxic Hippocampal Lesions in the Rat Sequential Reaction Time Task. Neurotox Res 29, 54–68 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-015-9551-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-015-9551-y