Abstract
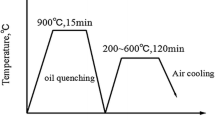
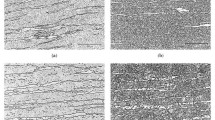
The microstructures and impact absorbed energies at various temperatures were investigated for steel strips hot rolled to thickness reductions of 95.5%, 96.0%, 96.5%, 97.0%, and 97.5%. Results indicate that grain refinement can be realized with an increase in hot rolling reduction. Besides, finer precipitates can be achieved with an increase in hot rolling reduction from 95.5% to 97.0%. The impact absorbed energy decreases with a decrease in testing temperature for steel strips hot rolled to 95.5%, 96.0%, and 96.5% reductions in thickness. However, in the case of steel strips hot rolled to 97.0% and 97.5% reductions in thickness, the impact absorbed energy remained almost constant with a decrease in testing temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Straffelini, V. Fontanari, and A. Molinari, Impact fracture toughness of porous alloys between room temperature and −60°C, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 272(1999), No. 2, p. 389.
R.Z. Valiev, R.K. Islamgaliev, and I.V. Alexandrov, Bulk nanostructured materials from severe plastic deformation, Prog. Mater. Sci., 45(2000), No. 2, p. 103.
C.C. Koch, D.G. Morris, K. Lu, and A. Inoue, Ductility of nanostructured materials, MRS Bull., 24(1999), No. 2, p. 54.
C.C. Koch, Optimization of strength and ductility in nanocrystalline and ultrafine grained metals, Scripta Mater., 49(2003), No. 7, p. 657.
E. Ma, Instabilities and ductility of nanocrystalline and ultrafine-grained metals, Scripta Mater., 49(2003), No. 7, p. 663.
E.W. Qin, L. Lu, N.R. Tao, and K. Lu, Enhanced fracture toughness of bulk nanocrystalline Cu with embedded nanoscale twins, Scripta Mater., 60(2009), No. 7, p. 539.
Y.H. Zhao, X.Z. Liao, S. Cheng, E. Ma, and Y.T. Zhu, Simultaneously increasing the ductility and strength of nanostructured alloys, Adv. Mater., 18(2006), No. 17, p. 2280.
S. Cheng, Y.H. Zhao, Y.T. Zhu, and E. Ma, Optimizing the strength and ductility of fine structured 2024 Al alloy by nano-precipitation, Acta Mater., 55(2007), No. 17, p. 5822.
Y.H. Zhao, X.Z. Liao, Z. Jin, R.Z. Valiev, and Y.T. Zhu, Microstructures and mechanical properties of ultrafine grained 7075 Al alloy processed by ECAP and their evolutions during annealing, Acta Mater., 52(2004), No. 15, p. 4589.
D.P. Fairchild, D.G. Howden, and W.A.T. Clark, The mechanism of brittle fracture in a microalloyed steel: Part I. Inclusion-induced cleavage, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 31(2000), No. 3, p. 641.
I. Sabirov and O. Kolednik, The effect of inclusion size on the local conditions for void nucleation near a crack tip in a mild steel, Scripta Mater., 53(2005), No. 12, p. 1373.
S. Maropoulos and N. Ridley, Inclusions and fracture characteristics of HSLA steel forgings, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 384(2004), No. 1–2, p. 64.
V.V. Stolyarov, R.Z. Valiev, and Y.T. Zhu, Enhanced low-temperature impact toughness of nanostructured Ti, Appl. Phys. Lett., 88(2006), No. 4, art No. 041905.
X.P. Mao, X.D. Huo, X.J. Sun, and Y.Z. Chai, Strengthening mechanisms of a new 700 MPa hot-rolled Ti-microalloyed steel produced by compact strip production, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 210(2010), No. 12, p. 1660.
K. Wallin, Upper shelf energy normalisation for sub-sized Charpy-V specimens, Int. J. Pressure Vessels Piping, 78(2001), No. 7, p. 463.
Y.J. Chao, J.D. Ward Jr., and R.G. Sands, Charpy impact energy, fracture toughness and ductile-brittle transition temperature of dual-phase 590 Steel, Mater. Des., 28(2007), No. 2, p. 551.
R. Kasada, H. Ono, and A. Kimura, Small specimen test technique for evaluating fracture toughness of blanket structural materials, Fusion Eng. Des., 81(2006), No. 8–14, p. 981.
G.P. Cherepanov, A.S. Balankin, and V.S. Ivanova, Fractal fracture mechanics-a review, Eng. Fract. Mech., 51(1995), No. 6, p. 997.
R.A. Ainsworth, D.G. Hooton, and D. Green, Failure assessment diagrams for high temperature defect assessment, Eng. Fract. Mech., 62(1999), No. 1, p. 95.
S. Cicero, R. Lacalle, R. Cicero, and D. Ferreño, Assessment of local thin areas in a marine pipeline by using the FITNET FFS corrosion module, Int. J. Pressure Vessels Piping, 86(2009), No. 5, p. 329.
G. Lewis and S. Mladsi, Correlation between impact strength and fracture toughness of PMMA-based bone cements, Biomaterials, 21(2000), No. 8, p. 775.
B. Hwang, Y.G. Kim, S. Lee, Y.M. Kim, N.J. Kim, and J.Y. Yoo, Effective grain size and Charpy impact properties of high-toughness X70 pipeline steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 36(2005), No. 8, p. 2107.
A.S. Kumar, B.R. Kumar, G.L. Datta, and V.R. Ranganath, Effect of microstructure and grain size on the fracture toughness of a micro-alloyed steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527(2010), No. 4–5, p. 954.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Jj., Wu, R., Liang, W. et al. Effect of hot rolling on the microstructure and impact absorbed energy of the strip steel by CSP. Int J Miner Metall Mater 21, 674–681 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-014-0957-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-014-0957-y