Abstract
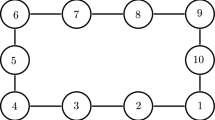
This paper investigates the event-triggered consensus problem of multi-agent systems with uncertainties and input saturation. First, a fully distributed robust consensus low-gain feedback control strategy is proposed, in which some global information, such as the communication graph and the scale of network, is not needed. Then, by defining an internal dynamic variable to memory the past state, an adaptive dynamic event-triggering mechanism is proposed, which contributes to reducing the usage of communication resources and also does not rely on any global information. Furthermore, Lyapunov-based consensus analysis results are presented, and it is also formally shown that Zeno behavior can be excluded with the proposed consensus protocols. Finally, a numerical example is provided to illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Tang and C. Li, “Distributed event-triggered containment control for discrete-time multi-agent systems,” International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, vol. 16, no. 6, pp. 2727–2732, October 2018.
X. Liu, C. Du, H. Liu, and P. Lu, “Distributed event-triggered consensus control with fully continuous communication free for general linear multi-agent systems under directed graph,” International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, vol. 28, no. 13, pp. 132–143, June 2017.
A. Zhang, D. Zhou, P. Yang, and M. Yang, “Event-triggered finite-time consensus with fully continuous communication free for second-order multi-agent systems,” International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, vol. 17, pp. 836–846, March 2019.
S. Islam and N. I. Xiros, “Robust asymptotic and finite-time tracking for second-order nonlinear multi-agent autonomous systems,” International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, vol. 17, no. 3, pp. 3069–3078, December 2019.
W. Liu and J. Huang, “Adaptive leader-following consensus for a class of higher-order nonlinear multi-agent systems with directed switching networks,” Automatica, vol. 79, pp. 84–92, January 2016.
H. Li, Y. Zhu, L. Jing, and Y. Wang, “Consensus of second-order delayed nonlinear multi-agent systems via node-based distributed adaptive completely intermittent protocols,” Applied Mathematics and Computation, vol. 326, pp. 1–15, June 2018.
X. Xie and X. Mu, “Observer-based intermittent consensus control of nonlinear singular multi-agent systems,” International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, vol. 17, no. 7, pp. 2321–2330, July 2019.
D. Zhang and G. Feng, “A new switched system approach to leader-follower consensus of heterogeneous linear multiagent systems with DoS attack,” IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2019.2895097
D. Zhang, Z. Xu, G. Feng, and H. Li, “Asynchronous resilient output consensus of switched heterogeneous linear multivehicle systems with communication delay,” IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, vol. 24, no. 6, pp. 2627–2640, December 2019.
W. P. M. H. Heemels, J. H. Sandee, and P. P. J. van den Bosch, “Analysis of event-driven controllers for linear systems,” International Journal of Control, vol. 81, no. 4, pp. 571–590, April 2008.
D. V. Dimarogonas, E. Frazzoli, and K. H. Johansson, “Distributed event triggered control for multi-agent systems,” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, vol. 57, no. 5, pp. 1291–1297, May 2012.
W. Zhu, Z. Jiang, and F. Gang, “Event-based consensus of multi-agent systems with general linear models,” Automatica, vol. 50, no. 2, pp. 552–558, February 2014.
W. Zhu and Z. P. Jiang, “Event-based leader-following consensus of multi-agent systems with input time delay,” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, vol. 60, no. 5, pp. 1362–1367, May 2015.
W. Hu, L. Liu, and G. Feng, “Consensus of linear multi-agent systems by distributed event-triggered strategy,” IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 46, no. 1, pp. 148–157, January 2016.
D. Yang, W. Ren, X. Liu, and W. Chen, “Decentralized event-triggered consensus for linear multi-agent systems under general directed graphs,” Automatica, vol. 69, pp. 242–249, July 2016.
S. Yu, H. Jiang, Z. Yu, and C. Hu, “Consensus of multiagent stsyems with feedforward nonlinear dynamics and digraph,” International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 1512–1520, July 2018.
Y. Liu, J. H. Park, B. Guo, F. Fang, and F. Zhou, “Event-triggered dissipative synchronization for Markovian jump neural networks with general transition probabilities,” International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, vol. 28, pp. 3893–3908, 2018.
X. Wang, H. Su, X. Wang, and G. Chen, “Fully distributed event-triggered semiglobal consensus of multi-agent systems with input saturation,” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 64, no. 6, pp. 5055–5064, June 2017.
B. Cheng and Z. Li, “Fully distributed event-triggered protocols for linear multiagent networks,” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, vol. 64, no. 4, pp. 1655–1662, April 2019.
W. Hu, C. Yang, T. Huang, and W. Gui, “A distributed dynamic event-triggered control approach to consensus of linear multiagent systems with directed networks,” IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 50, no. 2, pp. 869–874, February 2018.
B. Cheng and Z. Li, “Output consensus of heterogeneous linear multi-agent systems via fully distributed event-triggered protocols,” Proc. of IECON 2017 — 43rd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, pp. 5581–5586, December 2017.
H. Su, Y. Ye, Y. Qiu, Y. Cao, and M. Z. Q. Chen, “Semiglobal output consensus for discrete-time switching networked systems subject to input saturation and external disturbances,” IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 49, no. 11, pp. 3934–3945, November 2019.
B. Wang, W. Chen, and B. Zhang, “Semi-global robust tracking consensus for multi-agent uncertain systems with input saturation via metamorphic low-gain feedback,” Automatica, vol. 103, pp. 363–373, May 2019.
H. Su, M. Z. Q. Chen, J. Lam, and Z. Lin, “Semi-global leader-following consensus of linear multi-agent systems with input saturation via low gain feedback,” IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, vol. 60, no. 7, pp. 1881–1889, March 2013.
H. Su, M. Z. Q. Chen, X. Wang, and J. Lam, “Semiglobal observer-based leader-following consensus with input saturation,” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 61, no. 6, pp. 2842–2850, June 2014.
H. Zhou, Y. Yang, and H. Su, “Semi-global leader-following consensus of discrete-time linear multi-agent systems subject to actuator position and rate saturation,” International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, vol. 27, no. 16, pp. 2921–2936, November 2017.
H. Su, G. Jia, and M. Z. Q. Chen, “Semi-global containment control of multi-agent systems with input saturation,” IET Control Theory and Applications, vol. 8, no. 18, pp. 2229–2237, December 2014.
B. Wang, W. Chen, J. Wang, B. Zhang, Z. Zhang, and X. Qiu, “Accurate cooperative control for multiple leaders multiagent uncertain systems: A two-layer node-to-node communication framework,” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 14, no. 6, pp. 2395–2405, June 2018.
B. Wang, J. Wang, B. Zhang, W. Chen, and Z. Zhang, “Leader-follower consensus of multivehicle wirelessly networked uncertain systems subject to nonlinear dynamics and actuator fault,” IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 492–505, January 2018.
Y. Liu, J. H. Park, and F. Fang, “Global exponential stability of delayed neural networks based on a new integral inequality,” IEEE Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics Systems, vol. 49, no. 11, pp. 2318–2325, March 2019.
Y. Chen, H. Dong, J. Lü, X. Sun, and K. Liu, “Robust consensus of nonlinear multiagent systems with switching topology and bounded noises,” IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 46, no. 6, pp. 1276–1285, July 2016.
X. Lu, Y. Wang, X. Yu, and J. Lai, “Finite-time control for robust tracking consensus in MASs with an uncertain leader,” IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 47, no. 5, pp. 1210–1223, March 2017.
Y. Wang, L. Xie, and C. E. de Souza, “Robust control of a class of uncertain nonlinear systems,” Systems and Control Letters, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 139–149, August 1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Recommended by Associate Editor Yajuan Liu under the direction of Editor Fuchun Sun. This work was supported by National Defense Research Program (JCKY2019407D001), Key R & D Program of Hebei Province (20311803D), Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (F2020203016), National Natural Science Foundation of China (62073277, 61825304).
Guanglei Zhao received his Ph.D. degree in electrical engineering from Shanghai Jiaotong University, China, in 2015. He is currently an Associate Professor with the Institute of Electrical Engineering, Yanshan University, Qinhuangdao, China. From 2012 to 2013, he was a visiting scholar in The University of Melbourne. His research interests include networked control systems, hybrid systems and robust control.
Zhao Wang received his B.S. degree from the Anhui University of Science and Technology, Huainan, China, in 2018. He is currently pursuing an M.S. degree with the Yanshan University. His research interests include multi-agent systems, event-triggered control, adaptive control, and output regulation.
Xiuwei Fu received his Ph.D. degree in electrical engineering from Guilin University of Electronic Technology, China, in 2010. He is currently an Lecturer with the College of Information and Control Engineering, Jilin Institute of Chemical Technology, Jilin, China. His research interests include networked control systems, embedded systems and motor control.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, G., Wang, Z. & Fu, X. Fully Distributed Dynamic Event-Triggered Semiglobal Consensus of Multi-agent Uncertain Systems with Input Saturation via Low-gain Feedback. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 19, 1451–1460 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-019-1080-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-019-1080-7