Abstract
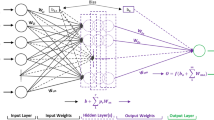
This paper uses the function of neural network-based nonlinear mapping and particle group optimization algorithm to optimize the system, and then uses the particle group optimization algorithm of inertia weight, so as to achieve the goal of optimizing the weight of neural network training. By choosing to encode the geological parameters of the coastline with mpeg-4 and obtain the relevant data, the relevant data of the beach motion image can be obtained, so that the simulation experiment can be carried out. This paper introduces the process of establishing a multi-modal pore size distribution fitting model based on probability density function, and conducts an experimental analysis on the geological parameters and pore structure of two typical shale storage layer samples in China. Finally, the multi-peak opening distribution fitting model and the pore size distribution are obtained through quantitative fitting curves, and the geological parameters of the marine continental shale that affect the pore size distribution are investigated, and the pore size distribution of the shale and the geology of the shale are investigated. In-depth parameter analysis is to explore the thermal maturity of organic matter, and the relationship between its content and mineral composition. In addition, the coastal image simulation is researched focusing on the characteristics of coastal beach recreational sports, the problems existing in the development process, and future development countermeasures. Finally, it is pointed out that the future development trend of coastal beach leisure sports, through the integration of local leisure sports-related characteristics and professional development, so as to achieve the implantation of culture in sports, and the organic combination of the two promotes the economic and ecological environment.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
13 December 2021
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-09276-5
28 September 2021
An Editorial Expression of Concern to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08471-8
References
Barma SD, Sathish R, Baskey PK (2018) Ultrasonic-assisted cleaning of Indian low-grade coal for clean and sustainable energy. J Clean Prod 195(10):1203–1213
Catcheside DEA, Ralph JP (2002) Bioconversion of coal by fungi. In: Bioconversion of coal by fungi. Springer, Berlin
Chang C, Huang C, Chen C, Wang G (2020) Assessing the potential effect of extreme weather on water quality and disinfection by-product formation using laboratory simulation. Water Res 170:115296
Chen M, Chyou Y, Wang T (2019) Simulation of coal gasification in a low-temperature, high-pressure entrained-bed reactor with a volatiles condensation and re-evaporation model. Appl Sci 9(3):510
Chen W, Westerhoff P, Leenheer JA, Booksh K (2003) Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 37(24):5701–5710
Chen TY, Zheng H, Hamilton S, Rodrigues S, Golding SD, Rudolph V (2017) Characterisation of bioavailability of Surat Basin Walloon coals for biogenic methane production using environmental microbial consortia. Int J Coal Geol 179:92–112
Ghosh S, Jha P, Vidyarthi AS (2014) Unraveling the microbial interactions in coal organic fermentation for generation of methane-a classical to metagenomic approach. Int J Coal Geol 125:36–44
Gupta P, Gupta A (2014) Biogas production from coal via anaerobic fermentation. Fuel 118:238–242
Haider R, Ghauri MA, SanFilipo JR, Jones EJ, Orem WH, Tatu CA, Akhtar K, Akhtar N (2013) Fungal degradation of coal as a pretreatment for methane production. Fuel 104:717–725
Hamidi H, Haddad AS, Mohammadian E, Rafati R, Azdarpour A, Ghahri P, Ombewa P, Neuert T, Zink A (2017) Ultrasound-assisted CO2 flooding to improve oil recovery. Ultrason Sonochem 35:243–250
Hamidi H, Haddad AS, Otumudia EW, Rafati R, Mohammadian E, Azdarpour A, Pilcher WG, Fuehrmann PW, Sosa LR, Cota N, García DC, Ibrahim RM, Damiev M, Tanujaya E (2021) Recent applications of ultrasonic waves in improved oil recovery: a review of techniques and results. Ultrasonics 110:106288
Haq SR, Tamamura S, Igarashi T, Kaneko K (2018) Characterization of organic substances in lignite before and after hydrogen peroxide treatment: implications for microbially enhanced coalbed methane. Int J Coal Geol 185:1–11
Huang Z, Urynowicz MA, Colberg PJS (2013) Stimulation of biogenic methane generation in coal samples following chemical treatment with potassium permanganate. Fuel 111:813–819
Jian K, Chen G, Guo C, Ma G, Ru Z (2019) Biogenic gas simulation of low-rank coal and its structure evolution. J Pet Sci Eng 173:1284–1288
Jones EJP, Voytek MA, Corum MD, Orem WH (2010) Stimulation of methane generation from nonproductive coal by addition of nutrients or a microbial consortium. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(21):7013–7022
Klein J, Pfeifer F, Schacht S, Sinder C (1997) Environmental aspects of bioconversion processes. Fuel Process Technol 52(1-3):17–25
Li X, Li C, Bai Y, Shi X, Su R (2019) Composition variations and spatiotemporal dynamics of dissolved organic matters during the occurrence of green tide (Ulva prolifera blooms) in the Southern Yellow Sea, China. Mar Pollut Bull 146:619–630
Li X, Pu CS, Chen X, Huang F, Zheng H (2021) Study on frequency optimization and mechanism of ultrasonic waves assisting water flooding in low-permeability reservoirs. Ultrason Sonochem 70:105291
Liu J, Wang B, Tai C, Wu L, Zhao H, Guan J, Chen L (2016) An effective method to detect volatile intermediates generated in the bioconversion of coal to methane by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry after in-situ extraction using headspace solid-phase micro-extraction under strict anaerobic conditions. PLoS One 11(10):0163949
Lupton N, Connell LD, Heryanto D, Sander R, Camilleri M, Down DI, Pan ZJ (2020) Enhancing biogenic methane generation in coalbed methane reservoirs-core flooding experiments on coals at in-situ conditions. Int J Coal Geol 219:103377
Machnikowska H, Pawelec K, Podgórska A (2002) Microbial degradation of low rank coals. Fuel Process Technol 77-78(2):17–23
Mullakaev MS, Abramov VO, Abramova AV (2017) Ultrasonic piezoceramic module and technology for stimulating low-productivity wells. J Pet Sci Eng 158:529–534
Nguyen V, Pierens X, Benhabib K (2019) Experimental and numerical study of methylparaben decomposition in aqueous solution using the UV/H2O2 process. J Environ Sci Heal 54(5):357–365
Funding
Novel coronavirus pneumonia development path reconstruction of Jiangxi National Fitness (Grant No. 2020028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sheldon Williamson
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Environment and Low Carbon Transportation
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-09276-5
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, L. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Coastline geological parameters and beach motion image simulation based on particle swarm optimization. Arab J Geosci 14, 1097 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07404-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07404-9