Abstract
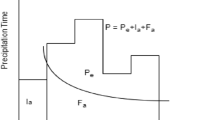
In semiarid areas, rainfall is often intense on dry soils with poor vegetation which might lead to high soil erosion susceptibility. Therefore, an appropriate assessment of the rainfall erosivity is of particular importance due to negative effects caused by top soil depletion and excessive sediment loading to receiving waters of reservoirs. The present study was conducted on the Wadi K’sob watershed (1480 km2) in northeast Algeria with an aim to examine the rainfall erosivity. The calculation of such an index is based on rains exceeding a specific threshold and requires rainfall data with a fine temporal resolution, which, often, are rare or difficult to acquire. The examination of daily rains occurring before a flood event carrying sediment load showed a spatial variability of the thresholds of rainfall erosivity. The seasonal values of the thresholds are low and lying between 2 mm in summer and 6 mm in winter, highlighting an erosivity process characteristically high in semi-arid regions. Empirical relationships, established at seasonal scale, were proposed as an alternative solution to the R-index calculation derived from the Revised Soil Loss Equation. The determined models allowed us to simulate the erosivity of rainfall events as a function of daily rain. Between 68 and 78% of the variance of rainfall erosivity is explained by the daily rainfall giving rise to an erosive rainfall event. Then, the spatial mean of the annual erosivity index fluctuated between 228 and 386 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 year−1 with an interannual average of 302 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 year−1, which if underestimated by 6%, the erosivity index quantified according to the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation. Rainfall erosivity is the determining factor in sediment yield with a different degree of binding during the year. In autumn, 68% of the variance in sediment production is explained by rainfall erosivity, compared with only 42% in spring due to changes in soil conditions, including the presence of a vegetation cover that protects the soil against rainfall erosivity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achite M, Ouillon S (2007) Suspended sediment transport in a semiarid watershed, Wadi Abd, Algeria (1973-1995). J Hydrol 343:187–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.06.026
Achite M, Ouillon S (2016) Recent changes in climate, hydrology and sediment load in the Wadi Abd, Algeria (1970-2010). Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 20:1355–1372. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-20-1355-2016
Arnoldus HMJ (1980) An approximation of the rainfall factor in the Universal Soil Loss Equation. In: De Boodt M, Gabriels D (eds) Assessment of erosion. Wiley, Chichester, pp 127–132
Asselman NEM (2000) Fitting and interpretation of sediment rating curves. J Hydrol 234:228–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(00)00253-5
Ávila B, Ávila H (2015) Spatial and temporal estimation of the erosivity factor R based on daily rainfall data for the department of Atlántico, Colombia. Ing Investig 35:23–29. https://doi.org/10.15446/ing.investig.v35n2.47773
Ballabio C, Borrelli P, Spinoni J et al (2017) Mapping monthly rainfall erosivity in Europe. Sci Total Environ 579:1298–1315
Beguería S, Serrano-Notivoli R, Tomas-Burguera M (2018) Computation of rainfall erosivity from daily precipitation amounts. Sci Total Environ 637:359–373
Benchettouh A, Kouri L, Jebari S (2017) Spatial estimation of soil erosion risk using RUSLE/GIS techniques and practices conservation suggested for reducing soil erosion in Wadi Mina watershed (northwest, Algeria). Arab J Geosci 10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2875-6
Benkadja R, Benhadouga M, Benkadja A (2013) Quantification des matières en suspension et valorisation des sédiments de dragage à l’échelle d’un bassin semi-aride: Cas du barrage du K’sob (Algérie). Bull Eng Geol Environ 72:523–531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-013-0516-1
Benkadja R, Boussag F, Benkadja A (2015) Identification et évaluation du risque d’érosion sur le bassin versant du K’sob (Est Algérien). Bull Eng Geol Environ 74:91–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-014-0611-y
Bertoni J, Lombardi Neto F (1985) Conservação do solo, 3rd edn. Ícone, São Paulo, Brasil, p 355
Bollinne A (1978) Study of the importance of splash and wash on cultivated loamy soils of Hesbaye (Belgium). Earth Surf Process 3:71–84
Bonilla CA, Vidal KL (2011) Rainfall erosivity in Central Chile. J Hydrol 410:126–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.09.022
Bouderbala D, Souidi Z, Hamimed A, Bouamar B (2019) Estimation of rainfall erosivity by mapping at the watershed of macta (Algeria). Rev Bras Cart 71:274–294
Bouguerra H, Bouanani A, Khanchoul K et al (2017) Mapping erosion prone areas in the Bouhamdane watershed (Algeria) using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation through GIS. J Water Land Dev 32:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1515/jwld-2017-0002
Brown LC, Foster GR (1987) Storm erosivity using idealized intensity distributions. Trans ASAE 30:379–386
Bruce JP, Clark RH (1966) Introduction to hydrometeorology. Pergamon Press, Long Island City, NY
Choukri F, Chikhaoui M, Naimi M et al (2016) Impact Du Changement Climatique Sur L’évolution De L’érosivité Des Pluies Dans Le Rif Occidental (Nord Du Maroc). Eur Sci Journal, ESJ 12
Da Silva AM (2004) Rainfall erosivity map for Brazil. Catena 57:251–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2003.11.006
De Santos Loureiro N, De Azevedo Coutinho M (2001) A new procedure to estimate the RUSLE EI30index, based on monthly rainfall data and applied to the Algarve region, Portugal. J Hydrol 250:12–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(01)00387-0
Denis MKA, Patil PL, Dasog GS, Manjunath MV (2013) Rainfall erosivity (R-factor) estimation for Singhanalli-Bogur micro-watershed in northern transition zone of Karnataka. Res J Agric Sci 4:644–647
Dutta S (2016) Soil erosion, sediment yield and sedimentation of reservoir: a review. Model Earth Syst Environ 2:123
Elangovan A, Seetharaman R (2011) Estimating rainfall erosivity of the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation from daily rainfall depth in Krishanagiri watershed region of Tamil Nadu. India Int Conf 19:48–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjca.2015.11.019
Farhan Y, Alnawaiseh S (2018) Spatio-temporal variation in rainfall erosivity over Jordan using annual and seasonal precipitation. Nat Resour 9:242
Fernandez H, Martins F, Isidoro JMGP (2019) Mapping rainfall aggressiveness from physiographical data: application to the Grândola Mountain range (Alentejo, Portugal). Phys Geogr:1–16
Fournier F (1961) Climat et erosion. Soil Sci 92:151
Fournier F (1969) L’érosion hydrique et le climat. Bulletin technique d’information
Gaubi I, Chaabani A, Ben Mammou A, Hamza MH (2017) A GIS-based soil erosion prediction using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) (Lebna watershed, Cap Bon, Tunisia). Nat Hazards 86:219–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2684-3
Ghenim AN, Megnounif A (2016, 2016) Variability and trend of annual maximum daily rainfall in northern Algeria. Int J Geophys. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6820397
Hasbaia M, Zeroual S, Dougha M et al (2017) Prediction of dams silting in semi-arid region using erosion map under GIS environment, case of Ksob watershed in Hodna Region (Algeria). In: Euro-Mediterranean Conference for Environmental Integration. Springer, pp 781–783
Hassen B, Soufiane L, Chaouki C (2017) Mapping and modelling of areas at risk of erosion: case of Aures Center (Algeria). In: Water resources in arid areas: the way forward. Springer, pp 197–214
Heusch B (1970) Estimation et controle de l’érosion hydraulique. Soc ScPhys Maroc 1970. N spécial, pp. 41–54
Hicks DM, Gomez B, Trustrum NA (2000) Erosion thresholds and suspended sediment yields, Waipaoa River basin, New Zealand. Water Resour Res 36:1129–1142
Horowitz AJ (2003) An evaluation of sediment rating curves for estimating suspended sediment concentrations for subsequent flux calculations. Hydrol Process 17:3387–3409
Issa LK, Lech-Hab KBH, Raissouni A, El Arrim A (2016) Cartographie quantitative du risque d’erosion des sols par approche SIG/USLE au niveau du bassin versant kalaya (Maroc Nord Occidental). J Mater Environ Sci 7:2778–2795
Kefi M, Yoshino K (2010) Evaluation of the economic effects of soil erosion risk on agricultural productivity using remote sensing: case of watershed in Tunisia. Int Arch Photogramm Remote Sens Spat Inf Sci—ISPRS Arch 38:930–935
Lal R (2001) Soil degradation by erosion. Land Degrad Dev 12:519–539
Langbein WB, Schumm SA (1958) Yield of sediment in relation to mean annual precipitation. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 39:1076–1084
Lee MH, Lin HH (2015, 2015) Evaluation of annual rainfall erosivity index based on daily, monthly, and annual precipitation data of rainfall station network in Southern Taiwan. Int J Distrib Sens Netw. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/214708
Louamri A, Mebarki A, Laignel B (2013) Variabilité interannuelle et intra-annuelle des transports solides de l’Wadi Bouhamdane, à l’amont du barrage Hammam Debagh (Algérie orientale). Hydrol Sci J 58:1559–1572. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2013.824089
Mannaerts CM, Gabriels D (2000) Rainfall erosivity in Cape Verde. Soil Tillage Res 55:207–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00118052
McGregor KC, Bingner RL, Bowie AJ, Foster GR (1995) Erosivity index values for northern Mississippi. Trans ASAE 38:1039–1047
Meddi M, Toumi S, Assani AA (2016) Spatial and temporal variability of the rainfall erosivity factor in northern Algeria. Arab J Geosci 9:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2303-8
Medhioub E, Bouaziz M, Bouaziz S (2017) Assessment of soil erosion by water using RUSLE, remote sensing and GIS in Gabes Coast-Southern Tunisia: study case of Wadi El Sourrag watershed. In: Euro-Mediterranean Conference for Environmental Integration. Springer, pp 1805–1806
Meghraoui M, Habi M, Morsli B et al (2017) Mapping of soil erodibility and assessment of soil losses using the RUSLE model in the Sebaa Chioukh Mountains (northwest of Algeria). J Water Land Dev 34:205–213. https://doi.org/10.1515/jwld-2017-0055
Megnounif A, Ghenim AN (2016) Rainfall irregularity and its impact on the sediment yield in Wadi Sebdou watershed, Algeria. Arab J Geosci 9:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2280-y
Megnounif A, Ouillon S (2018) Empirical and analytical methods to characterize the efficiency of floods to move sediment in a small semi-arid basin. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 22:6335–6355. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-22-6335-2018
Megnounif A, Terfous A, Bouanani A (2003) Production et transport des matières solides en suspension dans le bassin versant de la Haute-Tafna (Nord-Ouest Algérien). Rev Sci L’eau 16:369. https://doi.org/10.7202/705513ar
Megnounif A, Terfous A, Ouillon S (2013) A graphical method to study suspended sediment dynamics during flood events in the Wadi Sebdou, NW Algeria (1973-2004). J Hydrol 497:24–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.05.029
Meliho M, Khattabi A, Mhammdi N, Hongming Z (2016) Impact of land use and vegetation cover on risks of erosion in the Ourika watershed (Morocco). Am J Eng Res (AJER):75–82
Oduro-Afriyie K (1996) Rainfall erosivity map for Ghana. Geoderma 74:161–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(96)00054-7
Olías M, Cánovas CR, Nieto JM, Sarmiento AM (2006) Evaluation of the dissolved contaminant load transported by the Tinto and Odiel rivers (South West Spain). Appl Geochem 21:1733–1749
Panagos P, Ballabio C, Borrelli P, Meusburger K (2016) Spatio-temporal analysis of rainfall erosivity and erosivity density in Greece. Catena 137:161–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.09.015
Probst JL, Amiotte-Suchet P (1992) Fluvial suspended sediment transport and mechanical erosion in the Maghreb (North Africa). Hydrol Sci J 37:621–637. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626669209492628
Remini B (2008) La surélévation des barrages: une technique de lutte contre l’envasement-exemples algériens. La Houille Blanche:103–108
Renard KG, Freimund JR (1994) Using monthly precipitation data to estimate the R-factor in the revised USLE. J Hydrol 157:287–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(94)90110-4
Renard KG, Foster GR, Weesies GA, McCool DK, Yoder DC (1997) Predicting soil erosion by water: a guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). U.S. Government Printing Office, USA
Richardson CW, Foster GR, Wright DA (1983) Estimation of erosion index from daily rainfall amount. Trans ASAE 26(1):153–156
Sanchez-Moreno JF, Mannaerts CM, Jetten V (2014) Rainfall erosivity mapping for Santiago Island, Cape Verde. Geoderma 217–218:74–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.10.026
Scott SH (2006) Predicting sediment transport dynamics in ephemeral channels: a review of literature. Engineer Research and Development Center Vicksburg Ms Coastal and Hydraulics Lab
Seeger M, Errea M-P, Beguerıa S et al (2004) Catchment soil moisture and rainfall characteristics as determinant factors for discharge/suspended sediment hysteretic loops in a small headwater catchment in the Spanish Pyrenees. J Hydrol 288:299–311
Syvitski JPM, Vörösmarty C, Kettner AJ, Green P (2005) Impact of humans on the flux of terrestrial sediment to the global coastal ocean. Science 308:376–380
Tahiri M, Tabyaoui H, El Hammichi F et al (2014) Evaluation et quantification de l’érosion et la sédimentation à partir des modèles RUSLE, MUSLE et Déposition intégrés dans un SIG. Application au sous bassin de l’Wadi Sania (Bassin de Tahaddart, Rif nord occidental, Maroc). Eur J Sci Res 125:157–178
Terranova OG, Gariano SL (2015) Regional investigation on seasonality of erosivity in the Mediterranean environment. Environ Earth Sci 73:311–324
Toubal AK, Achite M, Ouillon S, Dehni A (2018) Soil erodibility mapping using the RUSLE model to prioritize erosion control in the Wadi Sahouat basin, North-West of Algeria. Environ Monit Assess 190:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6580-z
Vörösmarty CJ, Meybeck M, Fekete B et al (2003) Anthropogenic sediment retention: major global impact from registered river impoundments. Glob Planet Chang 39:169–190
Walling DE (1977) Assessing the accuracy of suspended sediment rating curves for a small basin. Water Resour Res 13:531–538
Walling DE (2006) Human impact on land–ocean sediment transfer by the world’s rivers. Geomorphology 79:192–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.06.019
Walling DE, Fang D (2003) Recent trends in the suspended sediment loads of the world’s rivers. Glob Planet Chang 39:111–126
Warrick JA (2015) Trend analyses with river sediment rating curves. Hydrol Process 29:936–949
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1958) Rainfall energy and its relationship to soil loss. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 39:285–291. https://doi.org/10.1029/TR039i002p00285
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1978) Predicting rainfall erosion losses. USDA agricultural research services handbook 537. USDA, Washington, DC, 57pp
Xie Y, Liu B, Nearing MA (2002) Practical thresholds for separating erosive and non-erosive storms. Trans ASAE (American Soc Agric Eng) 45:1843–1847
Xie Y, Yin SQ, Liu BY et al (2016) Models for estimating daily rainfall erosivity in China. J Hydrol 535:547–558
Yin S, Xie Y, Liu B, Nearing MA (2015) Rainfall erosivity estimation based on rainfall data collected over a range of temporal resolutions. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 19:4113–4126. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-19-4113-2015
Yin S, Nearing MA, Borrelli P, Xue X (2017) Rainfall erosivity: an overview of methodologies and applications. Vadose Zo J 16:0. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2017.06.0131
Yu B, Rosewell CJ (1996) Rainfall erosivity estimation using daily rainfall amounts for South Australia. Aust J Soil Res 34:721–733. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR9960721
Zhang XC, Nearing MA (2005) Impact of climate change on soil erosion, runoff, and wheat productivity in Central Oklahoma. Catena 61(2):185–195
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sheryl Luzzadder-Beach
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guesri, M., Megnounif, A. & Ghenim, A.N. Rainfall erosivity and sediment yield in Northeast Algeria: K’sob watershed case study. Arab J Geosci 13, 299 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-5276-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-5276-1