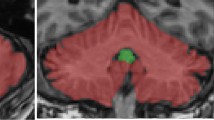
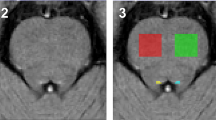
Abstract
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is now having a strong momentum in research to evaluate the neural fibers of the CNS. This technique can study white matter (WM) microstructure in neurodegenerative disorders, including Parkinson’s disease (PD). Previous neuroimaging studies have suggested cerebellar involvement in the pathogenesis of PD, and these cerebellum alterations can correlate with PD symptoms and stages. Using the PRISMA 2020 framework, PubMed and EMBASE were searched to retrieve relevant articles. Our search revealed 472 articles. After screening titles and abstracts, and full-text review, and implementing the inclusion criteria, 68 papers were selected for synthesis. Reviewing the selected studies revealed that the patterns of reduction in cerebellum WM integrity, assessed by fractional anisotropy, mean diffusivity, radial diffusivity, and axial diffusivity measures can differ symptoms and stages of PD. Cerebellar diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) changes in PD patients with “postural instability and gait difficulty” are significantly different from “tremor dominant” PD patients. Freezing of the gate is strongly related to cerebellar involvement depicted by DTI. The “reduced cognition,” “visual disturbances,” “sleep disorders,” “depression,” and “olfactory dysfunction” are not related to cerebellum microstructural changes on DTI, while “impulsive-compulsive behavior” can be linked to cerebellar WM alteration. Finally, higher PD stages and longer disease duration are associated with cerebellum white matter alteration depicted by DTI. Depiction of cerebellar white matter involvement in PD is feasible by DTI. There is an association with disease duration and severity and several clinical presentations with DTI findings. This clinical-imaging association may eventually improve disease management.


Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
07 April 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-022-01402-7
References
Kalia LV, Lang AE. Parkinson's disease. Lancet (London, England). 2015;386(9996):896–912.
Elbaz A, Carcaillon L, Kab S, Moisan F. Epidemiology of Parkinson's disease. Rev Neurol. 2016;172(1):14–26.
Lefaivre SC, Brown MJN, Almeida QJ. Cerebellar involvement in Parkinson’s disease resting tremor. Cereb Ataxias. 2016;3(1):13.
Bloem BR, Okun MS, Klein C. Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 2021;397(10291):2284–303.
Bares M, Apps R, Kikinis Z, Timmann D, Oz G, Ashe JJ, et al. Proceedings of the workshop on Cerebellum, Basal Ganglia and Cortical Connections Unmasked in Health and Disorder held in Brno, Czech Republic, October 17th, 2013. Cerebellum (London, England). 2015;14(2):142–50.
Haghshomar M, Dolatshahi M, Ghazi Sherbaf F, Sanjari Moghaddam H, Shirin Shandiz M, Aarabi MH. Disruption of inferior longitudinal fasciculus microstructure in Parkinson's disease: a systematic review of diffusion tensor imaging studies. Front Neurol 2018;9:598-.
Shen B, Pan Y, Jiang X, Wu Z, Zhu J, Dong J, et al. Altered putamen and cerebellum connectivity among different subtypes of Parkinson's disease. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2020;26(2):207–14.
Mirdamadi JL. Cerebellar role in Parkinson's disease. J Neurophysiol. 2016;116(3):917–9.
Wu T, Hallett M. The cerebellum in Parkinson's disease. Brain. 2013;136(Pt 3):696–709.
Roostaei T, Nazeri A, Sahraian MA, Minagar A. The human cerebellum: a review of physiologic neuroanatomy. Neurol Clin. 2014;32(4):859–69.
Rolland AS, Tande D, Herrero MT, Luquin MR, Vazquez-Claverie M, Karachi C, et al. Evidence for a dopaminergic innervation of the pedunculopontine nucleus in monkeys, and its drastic reduction after MPTP intoxication. J Neurochem. 2009;110(4):1321–9.
Lewis SJG, O’Callaghan C, Shine JM, Hornberger M, Balsters JH, Halliday GM. Cerebellar atrophy in Parkinson’s disease and its implication for network connectivity. Brain. 2016;139(3):845–55.
Mori S, Zhang J. Principles of diffusion tensor imaging and its applications to basic neuroscience research. Neuron. 2006;51(5):527–39.
Beaulieu C. The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system - a technical review. NMR Biomed. 2002;15(7-8):435–55.
Lebel C, Treit S, Beaulieu C. A review of diffusion MRI of typical white matter development from early childhood to young adulthood. NMR in biomedicine.e3778-n/a.
Ghazi Sherbaf F, Aarabi MH, Hosein Yazdi M, Haghshomar M. White matter microstructure in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: a systematic review of diffusion tensor imaging studies. Hum Brain Mapp. 2018.
Acosta-Cabronero J, Nestor PJ. Diffusion tensor imaging in Alzheimer's disease: insights into the limbic-diencephalic network and methodological considerations. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014;6:266.
Mahlknecht P, Krismer F, Poewe W, Seppi K. Meta-analysis of dorsolateral nigral hyperintensity on magnetic resonance imaging as a marker for Parkinson's disease. Movement disorders : official journal of the Movement Disorder Society. 2017;32(4):619–23.
Ghazi Sherbaf F, Mojtahed Zadeh M, Haghshomar M, Aarabi MH. Posterior limb of the internal capsule predicts poor quality of life in patients with Parkinson's disease: connectometry approach. Acta Neurol Belg. 2019;119(1):95–100.
Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell Da, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. Oxford; 2000.
Disease MDSTFoRSfPs. The Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS): status and recommendations. 2003;18(7):738-50.
Goetz CG, Poewe W, Rascol O, Sampaio C, Stebbins GT, Counsell C, et al. Movement Disorder Society Task Force report on the Hoehn and Yahr staging scale: status and recommendations. Mov Disord. 2004;19(9):1020–8.
Marsili L, Rizzo G, Colosimo C. Diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease: from James Parkinson to the concept of prodromal disease. 2018;9(156).
Barbagallo G, Caligiuri ME, Arabia G, Cherubini A, Lupo A, Nistico R, et al. Structural connectivity differences in motor network between tremor-dominant and nontremor Parkinson's disease. Hum Brain Mapp. 2017;38(9):4716–29.
Canu E, Agosta F, Markovic V, Petrovic I, Stankovic I, Imperiale F, et al. White matter tract alterations in Parkinson's disease patients with punding. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2017;43:85–91.
Canu E, Agosta F, Sarasso E, Volonte MA, Basaia S, Stojkovic T, et al. Brain structural and functional connectivity in Parkinson's disease with freezing of gait. Hum Brain Mapp. 2015;36(12):5064–78.
Fling BW, Cohen RG, Mancini M, Nutt JG, Fair DA, Horak FB. Asymmetric pedunculopontine network connectivity in parkinsonian patients with freezing of gait. Brain. 2013;136(Pt 8):2405–18.
Gu Q, Huang P, Xuan M, Xu X, Li D, Sun J, et al. Greater loss of white matter integrity in postural instability and gait difficulty subtype of Parkinson's disease. Can J Neurol Sci. 2014;41(6):763–8.
Lee E, Lee JE, Yoo K, Hong JY, Oh J, Sunwoo MK, et al. Neural correlates of progressive reduction of bradykinesia in de novo Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014;20(12):1376–81.
Lenfeldt N, Hansson W, Larsson A, Nyberg L, Birgander R, Forsgren L. Diffusion tensor imaging and correlations to Parkinson rating scales. J Neurol. 2013;260(11):2823–30.
Luo C, Song W, Chen Q, Yang J, Gong Q, Shang HF. White matter microstructure damage in tremor-dominant Parkinson's disease patients. Neuroradiology. 2017;59(7):691–8.
Peterson DS, Fling BW, Mancini M, Cohen RG, Nutt JG, Horak FB. Dual-task interference and brain structural connectivity in people with Parkinson's disease who freeze. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015;86(7):786–92.
Vercruysse S, Leunissen I, Vervoort G, Vandenberghe W, Swinnen S, Nieuwboer A. Microstructural changes in white matter associated with freezing of gait in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2015;30(4):567–76.
Vervoort G, Leunissen I, Firbank M, Heremans E, Nackaerts E, Vandenberghe W, et al. Structural brain alterations in motor subtypes of Parkinson’s disease: evidence from probabilistic tractography and shape analysis. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(6):e0157743.
Wang M, Jiang S, Yuan Y, Zhang L, Ding J, Wang J, et al. Alterations of functional and structural connectivity of freezing of gait in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol. 2016;263(8):1583–92.
Wen M-C, Heng HSE, Lu Z, Xu Z, Chan LL, Tan EK, et al. Differential white matter regional alterations in motor subtypes of early drug-naive Parkinson’s disease patients. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2018;32(2):129–41.
Wu JY, Zhang Y, Wu WB, Hu G, Xu Y. Impaired long contact white matter fibers integrity is related to depression in Parkinson's disease. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018;24(2):108–14.
Blain CR, Barker GJ, Jarosz JM, Coyle NA, Landau S, Brown RG, et al. Measuring brain stem and cerebellar damage in parkinsonian syndromes using diffusion tensor MRI. Neurology. 2006;67(12):2199–205.
Nair SR, Tan LK, Mohd Ramli N, Lim SY, Rahmat K, Mohd NH. A decision tree for differentiating multiple system atrophy from Parkinson's disease using 3-T MR imaging. Eur Radiol. 2013;23(6):1459–66.
Prodoehl J, Li H, Planetta PJ, Goetz CG, Shannon KM, Tangonan R, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of Parkinson's disease, atypical parkinsonism, and essential tremor. Mov Disord. 2013;28(13):1816–22.
Abos A, Baggio HC, Segura B, Campabadal A, Uribe C, Giraldo DM, et al. Differentiation of multiple system atrophy from Parkinson's disease by structural connectivity derived from probabilistic tractography. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):16488.
Lucas-Jimenez O, Ojeda N, Pena J, Diez-Cirarda M, Cabrera-Zubizarreta A, Gomez-Esteban JC, et al. Altered functional connectivity in the default mode network is associated with cognitive impairment and brain anatomical changes in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016;33:58–64.
Melzer TR, Watts R, MacAskill MR, Pitcher TL, Livingston L, Keenan RJ, et al. White matter microstructure deteriorates across cognitive stages in Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2013;80(20):1841–9.
Koshimori Y, Segura B, Christopher L, Lobaugh N, Duff-Canning S, Mizrahi R, et al. Imaging changes associated with cognitive abnormalities in Parkinson's disease. Brain Struct Funct. 2015;220(4):2249–61.
Kamagata K, Motoi Y, Tomiyama H, Abe O, Ito K, Shimoji K, et al. Relationship between cognitive impairment and white-matter alteration in Parkinson's disease with dementia: tract-based spatial statistics and tract-specific analysis. Eur Radiol. 2013;23(7):1946–55.
Agosta F, Canu E, Stefanova E, Sarro L, Tomic A, Spica V, et al. Mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease is associated with a distributed pattern of brain white matter damage. Hum Brain Mapp. 2014;35(5):1921–9.
Baggio HC, Segura B, Ibarretxe-Bilbao N, Valldeoriola F, Marti MJ, Compta Y, et al. Structural correlates of facial emotion recognition deficits in Parkinson's disease patients. Neuropsychologia. 2012;50(8):2121–8.
Chondrogiorgi M, Astrakas LG, Zikou AK, Weis L, Xydis VG, Antonini A, et al. Multifocal alterations of white matter accompany the transition from normal cognition to dementia in Parkinson's disease patients. Brain Imaging Behav. 2019;13(1):232–40.
Duncan GW, Firbank MJ, Yarnall AJ, Khoo TK, Brooks DJ, Barker RA, et al. Gray and white matter imaging: a biomarker for cognitive impairment in early Parkinson's disease? Mov Disord. 2016;31(1):103–10.
Hattori T, Orimo S, Aoki S, Ito K, Abe O, Amano A, et al. Cognitive status correlates with white matter alteration in Parkinson's disease. Hum Brain Mapp. 2012;33(3):727–39.
Price CC, Tanner J, Nguyen PT, Schwab NA, Mitchell S, Slonena E, et al. Gray and white matter contributions to cognitive frontostriatal deficits in non-demented Parkinson's disease. PLoS One. 2016;11(1):e0147332-e.
Theilmann RJ, Reed JD, Song DD, Huang MX, Lee RR, Litvan I, et al. White-matter changes correlate with cognitive functioning in Parkinson's disease. Front Neurol. 2013;4:37.
Diez-Cirarda M, Ojeda N, Pena J, Cabrera-Zubizarreta A, Gomez-Beldarrain MA, Gomez-Esteban JC, et al. Neuroanatomical correlates of theory of mind deficit in Parkinson's disease: a multimodal imaging study. PLoS One. 2015;10(11):e0142234.
Gallagher C, Bell B, Bendlin B, Palotti M, Okonkwo O, Sodhi A, et al. White matter microstructural integrity and executive function in Parkinson's disease. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2013;19(3):349–54.
Liu Z, Zhang Y, Wang H, Xu D, You H, Zuo Z, et al. Altered cerebral perfusion and microstructure in advanced Parkinson's disease and their associations with clinical features. Neurol Res. 2021;1-10.
Holtbernd F, Romanzetti S, Oertel WH, Knake S, Sittig E, Heidbreder A, et al. Convergent patterns of structural brain changes in rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder and Parkinson’s disease on behalf of the German rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder study group. Sleep. 2021;44(3):zsaa199.
Lim JS, Shin SA, Lee JY, Nam H, Lee JY, Kim YK. Neural substrates of rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016;23:31–6.
Ford AH, Duncan GW, Firbank MJ, Yarnall AJ, Khoo TK, Burn DJ, et al. Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder in Parkinson's disease: magnetic resonance imaging study. Mov Disord. 2013;28(6):832–6.
Chung SJ, Choi YH, Kwon H, Park YH, Yun HJ, Yoo HS, et al. Sleep disturbance may alter white matter and resting state functional connectivities in Parkinson's disease. Sleep. 2017;40(3).
Gou L, Zhang W, Li C, Shi X, Zhou Z, Zhong W, et al. Structural brain network alteration and its correlation with structural impairments in patients with depression in de novo and drug-naive Parkinson's disease. Front Neurol. 2018;9:608.
Huang P, Xu X, Gu Q, Xuan M, Yu X, Luo W, et al. Disrupted white matter integrity in depressed versus non-depressed Parkinson's disease patients: a tract-based spatial statistics study. J Neurol Sci. 2014;346(1-2):145–8.
Prange S, Metereau E, Maillet A, Lhommée E, Klinger H, Pelissier P, et al. Early limbic microstructural alterations in apathy and depression in de novo Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2019;34(11):1644–54.
Garcia-Diaz AI, Segura B, Baggio HC, Marti MJ, Valldeoriola F, Compta Y, et al. Structural brain correlations of visuospatial and visuoperceptual tests in Parkinson's disease. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2018;24(1):33–44.
Lee WW, Yoon EJ, Lee JY, Park SW, Kim YK. Visual hallucination and pattern of brain degeneration in Parkinson's disease. Neurodegener Dis. 2017;17(2-3):63–72.
Arrigo A, Calamuneri A, Milardi D, Mormina E, Rania L, Postorino E, et al. Visual system involvement in patients with newly diagnosed Parkinson disease. Radiology. 2017;285(3):885–95.
Imperiale F, Agosta F, Canu E, Markovic V, Inuggi A, Jecmenica-Lukic M, et al. Brain structural and functional signatures of impulsive-compulsive behaviours in Parkinson's disease. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23(2):459–66.
Yoo HB, Lee JY, Lee JS, Kang H, Kim YK, Song IC, et al. Whole-brain diffusion-tensor changes in parkinsonian patients with impulse control disorders. J Clin Neurol. 2015;11(1):42–7.
Georgiopoulos C, Warntjes M, Dizdar N, Zachrisson H, Engström M, Haller S, et al. Olfactory impairment in Parkinson's disease studied with diffusion tensor and magnetization transfer imaging. 301-11.
Ibarretxe-Bilbao N, Junque C, Marti MJ, Valldeoriola F, Vendrell P, Bargallo N, et al. Olfactory impairment in Parkinson's disease and white matter abnormalities in central olfactory areas: a voxel-based diffusion tensor imaging study. 1888-94.
Wen MC, Xu Z, Lu Z, Chan LL, Tan EK, Tan LCS. Microstructural network alterations of olfactory dysfunction in newly diagnosed Parkinson's disease. 12559.
Zhang K, Yu C, Zhang Y, Wu X, Zhu C, Chan P, et al. Voxel-based analysis of diffusion tensor indices in the brain in patients with Parkinson's disease.269-73.
Haghshomar M, Rahmani F, Hadi Aarabi M, Shahjouei S, Sobhani S, Rahmani M. White matter changes correlates of peripheral neuroinflammation in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience. 2019;403:70–8.
Rossi ME, Ruottinen H, Saunamaki T, Elovaara I, Dastidar P. Imaging brain iron and diffusion patterns: a follow-up study of Parkinson's disease in the initial stages. Acad Radiol. 2014;21(1):64–71.
Kikuchi K, Hiwatashi A, Togao O, Yamashita K, Somehara R, Kamei R, et al. Structural changes in Parkinson's disease: voxel-based morphometry and diffusion tensor imaging analyses based on (123)I-MIBG uptake. Eur Radiol. 2017;27(12):5073–9.
Polli A, Weis L, Biundo R, Thacker M, Turolla A, Koutsikos K, et al. Anatomical and functional correlates of persistent pain in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2016;31(12):1854–64.
Kim HJ, Kim SJ, Kim HS, Choi CG, Kim N, Han S, et al. Alterations of mean diffusivity in brain white matter and deep gray matter in Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett. 2013;550:64–8.
Youn J, Lee JM, Kwon H, Kim JS, Son TO, Cho JW. Alterations of mean diffusivity of pedunculopontine nucleus pathway in Parkinson's disease patients with freezing of gait. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2015;21(1):12–7.
Karagulle Kendi AT, Lehericy S, Luciana M, Ugurbil K, Tuite P. Altered diffusion in the frontal lobe in Parkinson disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29(3):501–5.
Schweder PM, Joint C, Hansen PC, Green AL, Quaghebeur G, Aziz TZ. Chronic pedunculopontine nucleus stimulation restores functional connectivity. Neuroreport. 2010;21(17):1065–8.
Meijer FJ, van Rumund A, Tuladhar AM, Aerts MB, Titulaer I, Esselink RA, et al. Conventional 3T brain MRI and diffusion tensor imaging in the diagnostic workup of early stage parkinsonism. Neuroradiology. 2015;57(7):655–69.
Haller S, Badoud S, Nguyen D, Garibotto V, Lovblad KO, Burkhard PR. Individual detection of patients with Parkinson disease using support vector machine analysis of diffusion tensor imaging data: initial results. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33(11):2123–8.
Minett T, Su L, Mak E, Williams G, Firbank M, Lawson RA, et al. Longitudinal diffusion tensor imaging changes in early Parkinson's disease: ICICLE-PD study. J Neurol. 2018;265(7):1528–39.
Taylor KI, Sambataro F, Boess F, Bertolino A, Dukart J. Progressive decline in gray and white matter integrity in de novo Parkinson’s disease: an analysis of longitudinal Parkinson progression markers initiative diffusion tensor imaging data. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience. 2018;10(318).
Zhang K, Yu C, Zhang Y, Wu X, Zhu C, Chan P, et al. Voxel-based analysis of diffusion tensor indices in the brain in patients with Parkinson's disease. Eur J Radiol. 2011;77(2):269–73.
Tessa C, Giannelli M, Della Nave R, Lucetti C, Berti C, Ginestroni A, et al. A whole-brain analysis in de novo Parkinson disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29(4):674–80.
Wen MC, Heng HS, Ng SY, Tan LC, Chan LL, Tan EK. White matter microstructural characteristics in newly diagnosed Parkinson's disease: an unbiased whole-brain study. Sci Rep. 2016;6:35601.
Li X-R, Ren Y-D, Cao B, Huang X-L. Analysis of white matter characteristics with tract-based spatial statistics according to diffusion tensor imaging in early Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett. 2018;675:127–32.
Agosta F, Kostic VS, Davidovic K, Kresojevic N, Sarro L, Svetel M, et al. White matter abnormalities in Parkinson's disease patients with glucocerebrosidase gene mutations. Mov Disord. 2013;28(6):772–8.
Mormina E, Arrigo A, Calamuneri A, Granata F, Quartarone A, Ghilardi MF, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging parameters' changes of cerebellar hemispheres in Parkinson's disease. Neuroradiology. 2015;57(3):327–34.
Melzer TR, Myall DJ, MacAskill MR, Pitcher TL, Livingston L, Watts R, et al. Tracking Parkinson's disease over one year with multimodal magnetic resonance imaging in a group of older patients with moderate disease. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0143923.
Chondrogiorgi M, Astrakas LG, Zikou AK, Weis L, Xydis VG, Antonini A, et al. Multifocal alterations of white matter accompany the transition from normal cognition to dementia in Parkinson's disease patients. 232-40.
Chiang PL, Chen HL, Lu CH, Chen PC, Chen MH, Yang IH, et al. White matter damage and systemic inflammation in Parkinson's disease. BMC Neurosci. 2017;18(1):48.
Wen M-C, Xu Z, Lu Z, Chan LL, Tan EK, Tan LCS. Microstructural network alterations of olfactory dysfunction in newly diagnosed Parkinson’s disease. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):12559.
Bharti K, Suppa A, Pietracupa S, Upadhyay N, Giannì C, Leodori G, et al. Abnormal cerebellar connectivity patterns in patients with Parkinson's disease and freezing of gait. Cerebellum. 2019;18(3):298–308.
Chondrogiorgi M, Tzarouchi LC, Zikou AK, Astrakas LG, Kosta P, Argyropoulou MI, et al. Multimodal imaging evaluation of excessive daytime sleepiness in Parkinson's disease. Int J Neurosci. 2016;126(5):422–8.
Georgiopoulos C, Warntjes M, Dizdar N, Zachrisson H, Engstrom M, Haller S, et al. Olfactory impairment in Parkinson's disease studied with diffusion tensor and magnetization transfer imaging. J Parkinsons Dis. 2017;7(2):301–11.
Ibarretxe-Bilbao N, Junque C, Marti MJ, Valldeoriola F, Vendrell P, Bargallo N, et al. Olfactory impairment in Parkinson's disease and white matter abnormalities in central olfactory areas: a voxel-based diffusion tensor imaging study. Mov Disord. 2010;25(12):1888–94.
Chitnis T, Weiner HL. CNS inflammation and neurodegeneration. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(10):3577–87.
Olesen MN, Soelberg K, Nilsson AC, Jarius S, Madsen JS, Grauslund J, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of inflammation and neurodegeneration in acute optic neuritis. Mult Scler J. 2018;24(2):253–4.
Gartner LPP, Maria A. Textbook of Neuroanatomy; 2009.
Kwon HG, Hong JH, Jang SH. Anatomic location and somatotopic arrangement of the corticospinal tract at the cerebral peduncle in the human brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32(11):2116–9.
Merlini L, Vargas MI, De Haller R, Rilliet B, Fluss J. MRI with fibre tracking in Cogan congenital oculomotor apraxia. Pediatr Radiol. 2010;40(10):1625–33.
Mtui EG, Gregory; Dockery, Peter. Fitzgerald's Clinical Neuroanatomy and Neuroscience Elsevier; 2016.
Gillig PM, Sanders RD. Psychiatry, neurology, and the role of the cerebellum. Psychiatry (Edgmont). 2010;7(9):38–43.
Bostan AC, Dum RP, Strick PL. The basal ganglia communicate with the cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(18):8452–6.
Ichinohe N, Mori F, Shoumura K. A di-synaptic projection from the lateral cerebellar nucleus to the laterodorsal part of the striatum via the central lateral nucleus of the thalamus in the rat. Brain Res. 2000;880(1-2):191–7.
Hoshi E, Tremblay L, Feger J, Carras PL, Strick PL. The cerebellum communicates with the basal ganglia. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8(11):1491–3.
Bostan AC, Strick PL. The cerebellum and basal ganglia are interconnected. Neuropsychol Rev. 2010;20(3):261–70.
Floris DL, Barber AD, Nebel MB, Martinelli M, Lai M-C, Crocetti D, et al. Atypical lateralization of motor circuit functional connectivity in children with autism is associated with motor deficits. Mol Autism. 2016;7(1):35.
Knecht S, Dräger B, Flöel A, Lohmann H, Breitenstein C, Deppe M, et al. Behavioural relevance of atypical language lateralization in healthy subjects. Brain. 2001;124(8):1657–65.
Biduła SP, Przybylski Ł, Pawlak MA, Króliczak G. Unique neural characteristics of atypical lateralization of language in healthy individuals. Front Neurosci 2017;11:525-.
Lefaivre SC, Brown MJN, Almeida QJJC, Ataxias. Cerebellar involvement in Parkinson’s disease resting tremor 2016;3(1):13.
Bedard P, Sanes JN. On a basal ganglia role in learning and rehearsing visual-motor associations. NeuroImage. 2009;47(4):1701–10.
Hanakawa T, Katsumi Y, Fukuyama H, Honda M, Hayashi T, Kimura J, et al. Mechanisms underlying gait disturbance in Parkinson's disease: a single photon emission computed tomography study. Brain. 1999;122(Pt 7):1271–82.
Huang C, Mattis P, Tang C, Perrine K, Carbon M, Eidelberg D. Metabolic brain networks associated with cognitive function in Parkinson's disease. NeuroImage. 2007;34(2):714–23.
Projection techniques for evaluating surgery in Parkinson's disease.Third Symposium on Parkinson's Disease, R Coll Surg Edinburgh 1996.
Berardelli A, Rothwell JC, Thompson PD, Hallett M. Pathophysiology of bradykinesia in Parkinson's disease. Brain. 2001;124(Pt 11):2131–46.
Jankovic J. Parkinson’s disease: clinical features and diagnosis. 2008;79(4):368-76.
Moustafa AA, Poletti M. Neural and behavioral substrates of subtypes of Parkinson's disease. Front Syst Neurosci. 2013;7:117.
Jankovic J, McDermott M, Carter J, Gauthier S, Goetz C, Golbe L, et al. Variable expression of Parkinson's disease: a base-line analysis of the DATATOP cohort. The Parkinson Study Group. Neurology. 1990;40(10):1529–34.
Nutt JG, Bloem BR, Giladi N, Hallett M, Horak FB, Nieuwboer A. Freezing of gait: moving forward on a mysterious clinical phenomenon. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10(8):734–44.
Nieuwboer A, Giladi N. Characterizing freezing of gait in Parkinson's disease: models of an episodic phenomenon. Mov Disord. 2013;28(11):1509–19.
Yang X, Huang Q, Yang H, Liu S, Chen B, Liu T, et al. Astrocytic damage in glial fibrillary acidic protein astrocytopathy during initial attack. Multiple Sclerosis Relat Disord. 2019;29:94–9.
Wager TD, Davidson ML, Hughes BL, Lindquist MA, Ochsner KN. Prefrontal-subcortical pathways mediating successful emotion regulation. Neuron. 2008;59(6):1037–50.
Roheger M, Kalbe E, Liepelt-Scarfone I. Progression of cognitive decline in Parkinson's disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 2018;8(2):183–93.
Cosgrove J, Alty JE, Jamieson S. Cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease. 2015;91(1074):212-20.
Gouras P, Bishop PO. Neural basis of vision. Science (New York, NY). 1972;177(4044):188–9.
Harris S, Comi G, Cree BAC, Steinman L, Sheffield JK, Silva D, et al. Neurofilament light chains as a marker of concurrent and future active disease in relapsing multiple sclerosis: an analysis of baseline data from the phase 3 ozanimod clinical trials. Neurology. 2019;92(15).
Armstrong RA. Visual symptoms in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsons Dis. 2011;2011:908306.
Weil RS, Schrag AE, Warren JD, Crutch SJ, Lees AJ, Morris HR. Visual dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Brain. 2016;139(11):2827–43.
Kim CS, Sung YH, Kang MJ, Park KH. Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder in Parkinson's disease: a preliminary study. J Mov Disord. 2016;9(2):114–9.
Schrempf W, Brandt MD, Storch A, Reichmann H. Sleep disorders in Parkinson's disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 2014;4(2):211–21.
Sateia MJ. International Classification of Sleep Disorders-Third Edition. Chest. 2014;146(5):1387–94.
Sack RL, Auckley D, Auger RR, Carskadon MA, Wright KP Jr, Vitiello MV, et al. Circadian rhythm sleep disorders: part i, basic principles, shift work and jet lag disorders. Sleep. 2007;30(11):1460–83.
Kanter JW, Busch AM, Weeks CE, Landes SJ. The nature of clinical depression: symptoms, syndromes, and behavior analysis. Behav Anal. 2008;31(1):1–21.
Chaudhury D, Liu H, Han M-H. Neuronal correlates of depression. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015;72(24):4825–48.
Marsh L. Depression and Parkinson's disease: current knowledge. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2013;13(12):409.
Molde H, Moussavi Y, Kopperud ST, Erga AH, Hansen AL, Pallesen S. Impulse-control disorders in Parkinson's disease: a meta-analysis and review of case-control studies. Front Neurol. 2018;9:330.
Doty RL. Olfaction in Parkinson's disease and related disorders. Neurobiol Dis. 2012;46(3):527–52.
Calne DB, Snow BJ, Lee C. Criteria for diagnosing Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol. 1992;32(S1):S125–S7.
Caan MW, Khedoe HG, Poot DH, Arjan J, Olabarriaga SD, Grimbergen KA, et al. Estimation of diffusion properties in crossing fiber bundles. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2010;29(8):1504–15.
Metzler-Baddeley C, O'Sullivan MJ, Bells S, Pasternak O, Jones DK. How and how not to correct for CSF-contamination in diffusion MRI. Neuroimage. 2012;59(2):1394–403.
Pasternak O, Sochen N, Gur Y, Intrator N, Assaf Y. Free water elimination and mapping from diffusion MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2009;62(3):717–30.
Ofori E, Pasternak O, Planetta PJ, Burciu R, Snyder A, Febo M, et al. Increased free water in the substantia nigra of Parkinson's disease: a single-site and multi-site study. Neurobiol Aging. 2015;36(2):1097–104.
Planetta PJ, Ofori E, Pasternak O, Burciu RG, Shukla P, DeSimone JC, et al. Free-water imaging in Parkinson’s disease and atypical parkinsonism. Brain. 2016;139(2):495–508.
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank the authors of the included articles in this systematic review due to sharing the relevant data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: MH, PS, MHA; Literature search and data extraction: FA, AP; Formal analysis and investigation: MH, PS, HS; Writing - original draft preparation: MH; Writing - review and editing: PS, HS, AK; All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
This article does not contain any part with the requirement of informed consent for subjects.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haghshomar, M., Shobeiri, P., Seyedi, S.A. et al. Cerebellar Microstructural Abnormalities in Parkinson’s Disease: a Systematic Review of Diffusion Tensor Imaging Studies. Cerebellum 21, 545–571 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-021-01355-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-021-01355-3