Abstract
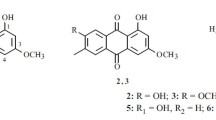
The endophytic fungus Trichothecium roseum LZ93 from Maytenus hookeri was found to antagonize other pathogenic fungi in vitro. To identify which compound contributed substantially to the antagonism, we fermented the strain and purified its fermentation products. Eleven compounds were obtained, including two trichothecenes, five rosenonolactones, two cardiotonic cyclodepsipeptides, and two sterols. Compound 11β-hydroxyrosenonolactone (1) was assigned according to 1D and 2D-NMR data for the first time. At the same time, the 1H and 13C-NMR assignments for 6β-hydroxyrosenonolactone (2) were revised. Of all of them, only trichothecin (6) showed strong antifungal activity. Based on our observations of the antagonistic activity and the other experimental results, we suggest that the antifungal compound trichothecin was the main contributor to the antagonistic action of T. roseum LZ93.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajit, N.S., R. Verma, and V. Shanmugam. 2006. Extracellular chitinases of fluorescent pseudomonads antifungal to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. dianthi causing carnation wilt. Curr. Microbiol. 52, 310–316.
Al-Heeti, M.B. and J.B. Sinclair. 1988. Antagonism between Gliodadium roseum, Trichoderma harzianum, or Trichothecium roseum and Phytophthora megasperma f. sp. glydnea. Mycopathologia 103, 135–140.
Amiguet, T.V., P. Petit, C.A. Ta, R. Nunez, P. Sanchez-Vindas, L.P. Alvarez, M.L. Smith, J.T. Arnason, and T. Durst. 2006. Phytochemistry and antifungal properties of the newly discovered tree pleodendron costaricense. J. Nat. Prod. 69, 1005–1009.
Bawden, F.C. and G.G. Freeman. 1952. The nature and behaviour of inhibitors of plant viruses produced by Trichothecium roseum Link. J. Gen. Microbiol. 7, 154–168.
Bok, J.W., L. Lermer, J. Chilton, H.G. Klingeman, and G.H.N. Towers. 1999. Antitumor sterols from the mycelia of Cordyceps sinensis. Phytochemistry 51, 891–898.
Dockerill, B., J.R. Hanson, and M. Siverns. 1978. The 13C NMR spectra of some rosane diterpenoids. Phytochemistry 17, 572–573.
Engstrom, G.W., J.V. DeLance, J.L. Richard, and A.L. Baetz. 1975. Purification and characterization of roseotoxin b, a toxic cyclodepsipeptide from Trichothecium roseum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 23, 244–253.
Freeman, G.G. and R.I. Morrison. 1949. The isolation and chemical properties of trichothecin, an antifungal substance from Trichothecium roseum Link. Biochem. J. 44, 1–5.
George, D.G. 1995. Biological and chemicalcontrol of rice blast disease (Pyricularia oryzae) in Northern Greece. Cah. Mediterr. 15, 61–68.
Guttormson, R., P. Main, A.J. Allison, and K.H. Overton. 1970. Structure of rosein III: X-ray analysis without a heavy atom. J. Chem. Soc. D 719–720.
Hanson, J.R., P.B. Hitchcock, I. Pibiri, and F. Piozzi. 2003. The biotransformation of the diterpenoid, rosenonolactone by Mucor plumbeus. J. Chem. Research(S) 147–149.
Hong, L.J., G.H. Li, W. Zhou, X.B. Wang, and K.Q. Zhang. 2007. Screening and isolation of a nematicidal sesquiterpene from Magnolia grandiflora L. Pest Manag. Sci. 63, 301–305.
Huang, H.C. and R.S. Erickson. 2008. Factors affecting biological control of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum by fungal antagonists. J. Phytopathol. 156, 628–634.
Kiriyama, N., Y. Yamamoto, and Y. Tsuda. 1971. Chemical correlation of rosein III (11-hydroxyrosenonolactone) and rosenonolactone. J. Chem. Soc. D 37–39.
Lacicowa, B. and D. Pieta. 1996. The efficiency of microbiological dressing of pea seeds (Pisum sativum L.) against pathogenic soilborn fungi. Rocz. Nauk. Roln. Ser. E 15–21.
Li, G.H., Y.M. Shen, and K.Q. Zhang. 2005. Nematicidal activity and chemical component of Poria cocos. J. Microbiol. 43, 17–20.
Liu, C., B.M. Tadayoni, L.A. Bourret, K.M. Mattocks, S.M. Derr, W.C. Widdison, N.L. Kedersha, P.D. Ariniello, V.S. Goldmacher, J.M. Lambert, W.A. Blättler, and R.V. Chari. 1996. Eradication of large colon tumor xenografts by targeted delivery of maytansinoids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 8618–8623.
Loukaci, A., O. Kayser, K. Bindseil, K. Siems, J. Frevert, and P.M. Abreu. 2000. New trichothecenes isolated from Holarrhena floribunda. J. Nat. Prod. 63, 52–56.
Mandal, S., K.D. Srivatava, A. Rashmi, D.V. Singh, S. Mandal, and R. Aggarwal. 1999. Mycoparasitic action of some fungi on spot blotch pathogen (Drechslera sorokiniana) of wheat. Indian Phytopathol. 52, 39–43.
Mosmann, T. 1983. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 65, 55–63.
Owen, N.L. and N. Hundley. 2004. Endophytes-The chemical synthesizers inside plants. Sci. Prog. 87, 79–99.
Rex, J.H., M.A. Pfaller, T.J. Walsh, V. Chaturvedi, A. Espinel-Ingroff, M.A. Ghannoum, L.L. Gosey, F.C. Odds, M.G. Rinaldi, D.J. Sheehan, and D.W. Warnock. 2001. Antifungal susceptibility testing: practical aspects and current challenges. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 14, 643–658.
Rod, J. 1984. Antagonistic effects of some fungi on fungal pathogens causing storage rots of onion (Allium cepa L.). Ceska Mykol. 38, 235–239.
Skidmore, A.M. and C.H. Dickinson. 1976. Colony interaction and hyphal interference between Septoria nodorurn and phylloplane fungi. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 66, 57–64.
Sturz, A.V., B.R. Christie, and J. Nowak. 2000. Bacterial endophytes: potential role in developing sustainable systems of crop production. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 19, 1–30.
Tan, R.X. and W.X. Zou. 2001. Endophytes: a rich source of functional metabolites. Nat. Prod. Rep. 18, 448–459.
Tsunoo, A., M. Kamijo, N. Taketomo, Y. Sato, and K. Ajisaka. 1997. Roseocardin, a novel cardiotonic cyclodepsipeptide from Trichothecium roseum TT103. J. Antibiot.(Tokyo) 50, 1007–1013.
Vanneste, J.L., R.A. Hill, S.J. Kay, R.L. Farrell, and P.T. Holland. 2002. Biological control of sapstain fungi with natural products and biological control agents: a review of the work carried out in New Zealand. Mycol. Res. 106, 228–232.
Yue, J.M., S.N. Chen, Z.W. Lin, and H.D. Sun. 2001. Sterols from the fungus Lactarium volemus. Phytochemistry 56, 801–806.
Zhao, P.J., L.M. Fan, G.H. Li, N. Zhu, and Y.M. Shen. 2005. Antibacterial and antitumor macrolides from Streptomyces sp. Is9131. Arch. Pharm. Res. 28, 1228–1232.
Zhao, P.J., G.H. Li, and Y.M. Shen. 2006. New chemical constituents from the endophyte Streptomyces species LR4612 cultivated on Maytenus hookeri. Chem. Biodivers. 3, 337–342.
Zhao, P.J., H.X. Wang, G.H. Li, H.D. Li, J. Liu, and Y.M. Shen. 2007. Secondary metabolites from endophytic Streptomyces sp. Lz531. Chem. Biodivers. 4, 899–904.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Li, G., Ma, J. et al. Endophytic fungus Trichothecium roseum LZ93 antagonizing pathogenic fungi in vitro and its secondary metabolites. J Microbiol. 48, 784–790 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-0173-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-0173-z