Abstract
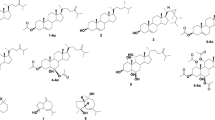
Chemical investigation of an Antarctic deep-sea derived fungus Penicillium sp. PR19 N-1 yielded five new eremophilane-type sesquiterpenes 1–5 and a new rare lactam-type eremophilane 6, together with three known compounds 7–9. The structures of these diverse sesquiterpenes were determined by extensive NMR and mass spectroscopic analyses. Compounds 1, 2, 4–6, 8 and 9 were evaluated for their cytotoxities against HL-60 and A-549 human cancer cell lines, and 5 was the most active one with IC50 value of 5.2 μM against the A-549 cells.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bohlmann, F., and K. Knoll. 1979. Natürlich vorkommende terpen-derivate, 200 zwei neue eremophilan-derivate aus senecio suaveolens. Liebigs Annalen der Chemie 4: 470–472.
Fraga, B.M. 2012. Natural sesquiterpenoids. Natural Products Reports 29: 1334–1366.
Fraga, B.M. 2011. Natural sesquiterpenoids. Natural Products Reports 28: 1580–1610.
Guerriero, A., V. Cuomo, F. Vanzanella, and F. Pietra. 1990. A novel glyceryl ester (glyceryl dendryphiellate A), a trinor-eremophilane (dendryphiellin A1), and eremophilanes (dendryphiellin E1 and E2) from the marine deutermycete Dendryphiella salina (Sutherland) puch et nicot. Helvetica Chimica Acta 73: 2090–2096.
Isaka, M., U. Srisanoh, S. Veeranondha, W. Choowong, and S. Lumyong. 2009. Cytotoxic eremophilane sesquiterpenoids from the saprobic fungus Berkleasmium nigroapicale BCC 8220. Tetrahedron 65: 8808–8815.
Khasawneh, M.A., Y.P. Xiong, J. Peralta-Cruz, and J.J. Karchesy. 2011. Biologically Important eremophilane sesquiterpenes from alaska cedar heartwood essential oil and their semi-synthetic derivatives. Molecules 16: 4775–4785.
Kurihara, K., R. Shinei, Y. Kurata, Y. Tabata, K. Tanabe, and T. Okonogi. 1998. Novel tetrahydrobenzindolone derivatives: tetrahdrobenzindolon-derivate nouveaux derives de la tetrahydrobenzindolone. Appl: PCT Int.
Mohamed, A.E.H., and A.A. Ahmed. 2005. Eremophilane-type sesquiterpene derivatives from Senecio aegyptius var.discoideus. Journal of Natural Products 68: 439–442.
Moreau, S., M. Cacan, and C. Eremofortin. 1977. A new metabolite obtained from Penicillium roqueforti cultures and from biotransformation of PR toxin. Journal of Organic Chemistry 42: 2632–2633.
Moreau, S., and J. Biguet. 1980. Structures et stereochimie des sesquiterpenes de Penicillium roqueforti PR toxine et eremofortines A, B, C, D, E. Tetrahedron 36: 2989–2997.
Mosmann, T. 1983. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. Journal of Immunological Methods 65: 55–63.
Shinei, R., K. Kurihara, K. Tanabe, Y. Tabata, Y. Kurata, S. Hoshiko, and T. Okonogi. 2006. Nonsteroidal progesterone receptor ligands (I): synthesis and SAR of new tetrahydronaphthofuranone derivatives. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 14: 4850–4861.
Shoji, N., A. Umeyama, Y. Asakawa, T. Takemoto, K. Nomoto, and Y. Ohizumi. 1984. Structural determination of nootkatol, a new sesquiterpene isolated from Alpinia oxyphylla miquel possessing calcium-antagonistic activity. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 73: 843–844.
Skehan, P., R. Storeng, D. Scudiero, A. Monks, J. McMahon, D. Vistica, and T. Jonathan. 1990. New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 82: 1107–1112.
Sørensen, D., A. Raditsis, L.A. Trimble, B.A. Blackwell, and M.W. Sumarah. 2007. David Miller, J. Isolation and structure elucidation by LC-MS-SPE/NMR; PR toxin- and cuspidatol-related eremophilane sesquiterpenes from Penicillium roqueforti. Journal of Natural Products 70: 121–123.
Tabata, Y., M. Hatsu, Y. Kurata, K. Miyajima, M. Tani, T. Sasaki, Y. Kodama, T. Tsuruoka, and S. Omoto. 1997. PF1092A, B and C, new nonsteroidal progesterone receptor ligands produced by Penicillium oblatum. II.physicochemical properties and structure elucidation. Journal of Antibiotics 50: 309–313.
Tori, M., K. Otose, H. Fukuyama, J. Murata, Y. Shiotani, S. Takaoka, K. Katsuyuki Nakashima, M. Sono, and M. Tanaka. 2010. New eremophilanes from Farfugium japonicum. Tetrahedron 66: 5235–5243.
Torres, P., J. Ayala, C. Grande, J. Anaya, and M. Grande. 1999. Furanoeremophilane derivatives from Senecio flavus. Phytochemistry 52: 1507–1513.
Wei, R.D., P.E. Still, E.B. Smalley, H.K. Schnoes, and F.M. Strong. 1973. Isolation and partial characterization of a mycotoxin from Penicillium roquefoti. Applied Microbiology 25: 111–114.
Wu, G.W., Aq Lin, Q.Q. Gu, T.J. Zhu, and D.H. Li. 2013. Four new chloro-eremophilane sesquiterpenes from an Antarctic deep-sea derived fungus, Penicillium sp. PR19 N-1. Marine Drugs 11: 1399–1408.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Fundation of China (Nos. 41376147 and 41176120), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2013AA092901), the Chinese Polar Environment Comprehensive Investigation & Assessment Programmes (CHINARE2013-01-06-06), and the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (No. NCET-12-0499), the public Projects of State Oceanic Administration (No. 2010418022-3), the Promotive Research Fund for Excellent Young and Middle-aged Scientisits of Shandong Province (No. BS2010HZ027), and the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (No. IRT0944). We also thank A.R. Pereira (Scripps Institution of Oceanography, La Jolla) for helping with the manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, A., Wu, G., Gu, Q. et al. New eremophilane-type sesquiterpenes from an Antarctic deep-sea derived fungus, Penicillium sp. PR19 N-1. Arch. Pharm. Res. 37, 839–844 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0246-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0246-8