Abstract
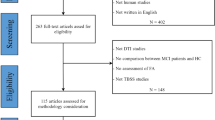
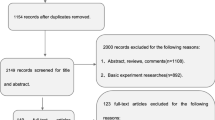
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is associated with the impairment of white matter (WM) tracts. The current study aimed to verify the utility of WM as the neuroimaging marker of AD with multisite diffusion tensor imaging datasets [321 patients with AD, 265 patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), 279 normal controls (NC)], a unified pipeline, and independent site cross-validation. Automated fiber quantification was used to extract diffusion profiles along tracts. Random-effects meta-analyses showed a reproducible degeneration pattern in which fractional anisotropy significantly decreased in the AD and MCI groups compared with NC. Machine learning models using tract-based features showed good generalizability among independent site cross-validation. The diffusion metrics of the altered regions and the AD probability predicted by the models were highly correlated with cognitive ability in the AD and MCI groups. We highlighted the reproducibility and generalizability of the degeneration pattern of WM tracts in AD.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scheltens P, De Strooper B, Kivipelto M, Holstege H, Chételat G, Teunissen CE. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397: 1577–1590.
Masters CL, Bateman R, Blennow K, Rowe CC, Sperling RA, Cummings JL. Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2015, 1: 15056.
Petersen RC. Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J Intern Med 2004, 256: 183–194.
Leifer BP. Early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Clinical and economic benefits. J Am Geriatr Soc 2003, 51: S281–S288.
Long JM, Holtzman DM. Alzheimer disease: An update on pathobiology and treatment strategies. Cell 2019, 179: 312–339.
Brun A, Englund E. A white matter disorder in dementia of the Alzheimer type: A pathoanatomical study. Ann Neurol 1986, 19: 253–262.
Agosta F, Pievani M, Sala S, Geroldi C, Galluzzi S, Frisoni GB, et al. White matter damage in Alzheimer disease and its relationship to gray matter atrophy. Radiology 2011, 258: 853–863.
Zlokovic BV. Neurovascular pathways to neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and other disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 2011, 12: 723–738.
Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Wilson RS, Bienias JL, Arnold SE. Neurofibrillary tangles mediate the association of amyloid load with clinical Alzheimer disease and level of cognitive function. Arch Neurol 2004, 61: 378–384.
Zhu W, Huang H, Yang S, Luo X, Zhu W, Xu S, et al. Cortical and subcortical grey matter abnormalities in white matter hyperintensities and subsequent cognitive impairment. Neurosci Bull 2021, 37: 789–803.
Fellgiebel A, Dellani PR, Greverus D, Scheurich A, Stoeter P, Müller MJ. Predicting conversion to dementia in mild cognitive impairment by volumetric and diffusivity measurements of the hippocampus. Psychiatry Res 2006, 146: 283–287.
Amlien IK, Fjell AM. Diffusion tensor imaging of white matter degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neuroscience 2014, 276: 206–215.
Delbeuck X, Van der Linden M, Collette F. Alzheimer’s disease as a disconnection syndrome? Neuropsychol Rev 2003, 13: 79–92.
Mayo CD, Mazerolle EL, Ritchie L, Fisk JD, Gawryluk JR. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Longitudinal changes in microstructural white matter metrics in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage Clin 2017, 13: 330–338.
Sun H, Lui S, Yao L, Deng W, Xiao Y, Zhang W, et al. Two patterns of white matter abnormalities in medication-naive patients with first-episode schizophrenia revealed by diffusion tensor imaging and cluster analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72: 678–686.
Yin RH, Tan L, Liu Y, Wang WY, Wang HF, Jiang T, et al. Multimodal voxel-based meta-analysis of white matter abnormalities in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2015, 47: 495–507.
Le Bihan D, Mangin JF, Poupon C, Clark CA, Pappata S, Molko N, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging: Concepts and applications. J Magn Reson Imaging 2001, 13: 534–546.
Beaulieu C. The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system - a technical review. NMR Biomed 2002, 15: 435–455.
Song SK, Sun SW, Ju WK, Lin SJ, Cross AH, Neufeld AH. Diffusion tensor imaging detects and differentiates axon and myelin degeneration in mouse optic nerve after retinal ischemia. NeuroImage 2003, 20: 1714–1722.
Medina D, DeToledo-Morrell L, Urresta F, Gabrieli JD, Moseley M, Fleischman D, et al. White matter changes in mild cognitive impairment and AD: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Neurobiol Aging 2006, 27: 663–672.
Zhang Y, Schuff N, Du AT, Rosen HJ, Kramer JH, Gorno-Tempini ML, et al. White matter damage in frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer’s disease measured by diffusion MRI. Brain 2009, 132: 2579–2592.
Xie S, Xiao JX, Gong GL, Zang YF, Wang YH, Wu HK, et al. Voxel-based detection of white matter abnormalities in mild Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2006, 66: 1845–1849.
Araque Caballero MÁ, Suárez-Calvet M, Duering M, Franzmeier N, Benzinger T, Fagan AM, et al. White matter diffusion alterations precede symptom onset in autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2018, 141: 3065–3080.
Acosta-Cabronero J, Nestor PJ. Diffusion tensor imaging in Alzheimer’s disease: Insights into the limbic-diencephalic network and methodological considerations. Front Aging Neurosci 2014, 6: 266.
Yeatman JD, Dougherty RF, Myall NJ, Wandell BA, Feldman HM. Tract profiles of white matter properties: Automating fiber-tract quantification. PLoS One 2012, 7: e49790.
Yeatman JD, Richie-Halford A, Smith JK, Keshavan A, Rokem A. A browser-based tool for visualization and analysis of diffusion MRI data. Nat Commun 2018, 9: 940.
Dou X, Yao H, Feng F, Wang P, Zhou B, Jin D, et al. Characterizing white matter connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: An automated fiber quantification analysis with two independent datasets. Cortex 2020, 129: 390–405.
Zhang X, Sun Y, Li W, Liu B, Wu W, Zhao H, et al. Characterization of white matter changes along fibers by automated fiber quantification in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage Clin 2019, 22: 101723.
Jin Y, Huang C, Daianu M, Zhan L, Dennis EL, Reid RI, et al. 3D tract-specific local and global analysis of white matter integrity in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Brain Mapp 2017, 38: 1191–1207.
Sexton CE, Kalu UG, Filippini N, MacKay CE, Ebmeier KP. A meta-analysis of diffusion tensor imaging in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 2011, 32: 2322.e5-2322.e18.
Clerx L, Visser PJ, Verhey F, Aalten P. New MRI markers for Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis of diffusion tensor imaging and a comparison with medial temporal lobe measurements. J Alzheimers Dis 2012, 29: 405–429.
Qin L, Guo Z, McClure MA, Mu Q. White matter changes from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis. Acta Neurol Belg 2021, 121: 1435–1447.
Rathore S, Habes M, Iftikhar MA, Shacklett A, Davatzikos C. A review on neuroimaging-based classification studies and associated feature extraction methods for Alzheimer’s disease and its prodromal stages. Neuroimage 2017, 155: 530–548.
Dyrba M, Grothe M, Kirste T, Teipel SJ. Multimodal analysis of functional and structural disconnection in Alzheimer’s disease using multiple kernel SVM. Hum Brain Mapp 2015, 36: 2118–2131.
Teipel S, Drzezga A, Grothe MJ, Barthel H, Chételat G, Schuff N, et al. Multimodal imaging in Alzheimer’s disease: Validity and usefulness for early detection. Lancet Neurol 2015, 14: 1037–1053.
Nir TM, Villalon-Reina JE, Prasad G, Jahanshad N, Joshi SH, Toga AW, et al. Diffusion weighted imaging-based maximum density path analysis and classification of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 2015, 36: S132–S140.
Jin D, Wang P, Zalesky A, Liu B, Song C, Wang D, et al. Grab-AD: Generalizability and reproducibility of altered brain activity and diagnostic classification in Alzheimer’s Disease. Hum Brain Mapp 2020, 41: 3379–3391.
Li J, Jin D, Li A, Liu B, Song C, Wang P, et al. ASAF: Altered spontaneous activity fingerprinting in Alzheimer’s disease based on multisite fMRI. Sci Bull 2019, 64: 998–1010.
Jin D, Zhou B, Han Y, Ren J, Han T, Liu B, et al. Generalizable, reproducible, and neuroscientifically interpretable imaging biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Adv Sci (Weinh) 2020, 7: 2000675.
Chen P, Yao H, Tijms BM, Wang P, Wang D, Song C, et al. Four distinct subtypes of Alzheimer’s disease based on resting-state connectivity biomarkers. Biol Psychiatry 2022, 2022: S0006-S3223.
Qu Y, Wang P, Liu B, Song C, Wang D, Yang H, et al. AI4AD: Artificial intelligence analysis for Alzheimer’s disease classification based on a multisite DTI database. Brain Disord 2021, 1: 100005.
Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. 2nd ed. Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1988.
Yu M, Linn KA, Cook PA, Phillips ML, McInnis M, Fava M, et al. Statistical harmonization corrects site effects in functional connectivity measurements from multi-site fMRI data. Hum Brain Mapp 2018, 39: 4213–4227.
Fan L, Li H, Zhuo J, Zhang Y, Wang J, Chen L, et al. The human brainnetome atlas: A new brain atlas based on connectional architecture. Cereb Cortex 2016, 26: 3508–3526.
Yeo BT, Krienen FM, Sepulcre J, Sabuncu MR, Lashkari D, Hollinshead M, et al. The organization of the human cerebral cortex estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity. J Neurophysiol 2011, 106: 1125–1165.
Jones DK, Christiansen KF, Chapman RJ, Aggleton JP. Distinct subdivisions of the cingulum bundle revealed by diffusion MRI fibre tracking: Implications for neuropsychological investigations. Neuropsychologia 2013, 51: 67–78.
Preti MG, Baglio F, Laganà MM, Griffanti L, Nemni R, Clerici M, et al. Assessing corpus callosum changes in Alzheimer’s disease: Comparison between tract-based spatial statistics and atlas-based tractography. PLoS One 2012, 7: e35856.
Lee SH, Coutu JP, Wilkens P, Yendiki A, Rosas HD, Salat DH, et al. Tract-based analysis of white matter degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 2015, 301: 79–89.
Mito R, Raffelt D, Dhollander T, Vaughan DN, Tournier JD, Salvado O, et al. Fibre-specific white matter reductions in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Brain 2018, 141: 888–902.
Buckner RL, DiNicola LM. The brain’s default network: Updated anatomy, physiology and evolving insights. Nat Rev Neurosci 2019, 20: 593–608.
Seguin C, Razi A, Zalesky A. Inferring neural signalling directionality from undirected structural connectomes. Nat Commun 2019, 10: 4289.
Eyler LT, Elman JA, Hatton SN, Gough S, Mischel AK, Hagler DJ, et al. Resting state abnormalities of the default mode network in mild cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Alzheimers Dis 2019, 70: 107–120.
Buckner RL, Sepulcre J, Talukdar T, Krienen FM, Liu H, Hedden T, et al. Cortical hubs revealed by intrinsic functional connectivity: Mapping, assessment of stability, and relation to Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 2009, 29: 1860–1873.
Huang J, Beach P, Bozoki A, Zhu DC. Alzheimer’s disease progressively reduces visual functional network connectivity. J Alzheimers Dis Rep 2021, 5: 549–562.
Mandal PK, Joshi J, Saharan S. Visuospatial perception: An emerging biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2012, 31: S117–S135.
Braak H, Del Tredici K. Spreading of tau pathology in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease along cortico-cortical top-down connections. Cereb Cortex 2018, 28: 3372–3384.
Catani M, Howard RJ, Pajevic S, Jones DK. Virtual in vivo interactive dissection of white matter fasciculi in the human brain. NeuroImage 2002, 17: 77–94.
Wakana S, Jiang H, Nagae-Poetscher LM, van Zijl PC, Mori S. Fiber tract-based atlas of human white matter anatomy. Radiology 2004, 230: 77–87.
Larroza A, Moratal D, D’ocón Alcañiz V, Arana E. por la Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Tractography of the uncinate fasciculus and the posterior cingulate fasciculus in patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurologia 2014, 29: 11–20.
Hau J, Sarubbo S, Perchey G, Crivello F, Zago L, Mellet E, et al. Cortical terminations of the inferior Fronto-occipital and uncinate fasciculi: Anatomical stem-based virtual dissection. Front Neuroanat 2016, 10: 58.
Teipel SJ, Bokde AL, Meindl T, Amaro E Jr, Soldner J, Reiser MF, et al. White matter microstructure underlying default mode network connectivity in the human brain. Neuroimage 2010, 49: 2021–2032.
Davatzikos C. Machine learning in neuroimaging: Progress and challenges. Neuroimage 2019, 197: 652–656.
Lian C, Liu M, Zhang J, Shen D. Hierarchical fully convolutional network for joint atrophy localization and Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis using structural MRI. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 2020, 42: 880–893.
Ding Y, Zhao K, Che T, Du K, Sun H, Liu S, et al. Quantitative radiomic features as new biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: An amyloid PET study. Cereb Cortex 2021, 31: 3950–3961.
Pinto MS, Paolella R, Billiet T, van Dyck P, Guns PJ, Jeurissen B, et al. Harmonization of brain diffusion MRI: Concepts and methods. Front Neurosci 2020, 14: 396.
Fortin JP, Cullen N, Sheline YI, Taylor WD, Aselcioglu I, Cook PA, et al. Harmonization of cortical thickness measurements across scanners and sites. Neuroimage 2018, 167: 104–120.
Fortin JP, Parker D, Tunç B, Watanabe T, Elliott MA, Ruparel K, et al. Harmonization of multi-site diffusion tensor imaging data. Neuroimage 2017, 161: 149–170.
Tax CM, Grussu F, Kaden E, Ning L, Rudrapatna U, John Evans C, et al. Cross-scanner and cross-protocol diffusion MRI data harmonisation: A benchmark database and evaluation of algorithms. Neuroimage 2019, 195: 285–299.
Dinsdale NK, Jenkinson M, Namburete AIL. Deep learning-based unlearning of dataset bias for MRI harmonisation and confound removal. Neuroimage 2021, 228: 117689.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the Science and Technology Innovation 2030 Major Projects (2022ZD0211600), the Beijing Natural Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholars (JQ20036), the Beijing Nova Program (20220484177), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2021XD-A03), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82172018 and 81871438). In addition, data collection and sharing for this project were funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61633018, 81571062, 81400890, 81471120, and 81701781).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Y., Wang, P., Yao, H. et al. Reproducible Abnormalities and Diagnostic Generalizability of White Matter in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurosci. Bull. 39, 1533–1543 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-023-01041-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-023-01041-w