Abstract
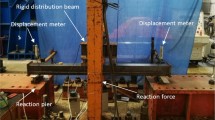
The combination of self-compacting rubberized concrete (SCRC) and rectangular steel tubes to be a composite structure is a new attempt to apply it to a broader range of engineering fields while making up for the shortcomings of SCRC. This study presents experimental and analytical studies on the bonding behavior of rectangular self-compacting rubber concrete-filled steel tubes (SCRCFST). A total of 17 SCRCFST specimens were performed on push-out test with different parameters of 1) interface bonding length, 2) rubber aggregate replacement rate, 3) rubber particle size, and 4) water-cement ratio (W/C). Based on the failure mode, strain analysis, and the evolution of damage on the interface between the SCRC and steel tubes, test results determined the effects of the parameters, and a prediction equation for the bond strength was derived from developing a relationship of bond-slip. The results indicated that the increase of rubber content, rubber particle size, W/C harmed the bond strength of SCRCFST, and bond length had little effect on bonding strength. Furthermore, the strain distribution of the rectangular steel tube was not uniformly distributed. The achievement of this research is the investigation of the bonding properties of the new structure, to provide guidance for future research scholars.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a g :
-
Maximum particle size of rubber aggregate
- A s :
-
Cross-sectional area of steel tubes
- B :
-
Side length of the rectangular section
- B l :
-
Side length of the long side of the rectangular section
- B s :
-
Side length of the short side of the rectangular section
- C a :
-
Length around the contact interface between the interior face of the steel tubes and the core concrete
- E s :
-
Elastic modulus of steel
- f cu :
-
Cube compressive strength of concrete
- f u :
-
Ultimate strength of steel
- f y :
-
Yield strength of steel
- k :
-
The amount of expansion agent
- L :
-
Length of steel tubes
- L a :
-
Bonding length of steel tubes
- P :
-
Load measured by the push-out test
- P u :
-
Ultimate load
- S :
-
Slip
- S r :
-
Slip represented by the residual bond strength τr
- S u :
-
Slip represented by the ultimate bond strength τu
- t :
-
Wall thickness of steel tubes
- T 500 :
-
Expansion time of SCRC
- β :
-
Water cement ratio
- γ :
-
Rubber content
- ε :
-
Strain
- ε(x):
-
Bond strain at location x
- σ(x):
-
Stress at location x
- τ :
-
Bond strength
- τ u-act :
-
Ultimate actual bond strength
- τ u-equ :
-
Ultimate bond strength of calculation results
- τ r :
-
Residual bond strength
- τ r-equ :
-
Residual bond strength of calculation results
- τ u τ u-typ :
-
Ultimate bond strength
References
AbdelAleem BH, Hassan AAA (2018) Development of self-consolidating rubberized concrete incorporating silica fume. Construction and Building Materials 161:389–397, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.11.146
Abendeh R, Ahmad HS, Hunaiti YM (2016) Experimental studies on the behavior of concrete-filled steel tubes incorporating crumb rubber. Journal of Constructional Steel Research 122:251–260, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2016.03.022
Aslani F, Ma G, Wan DLY, Muselin G (2018) Development of highperformance self-compacting concrete using waste recycled concrete aggregates and rubber granules. Journal of Cleaner Production 182:553–566, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.074
Belabdelouahab F, Trouzine H, Hellal H, Rahali B, Kaci SO, Medine M (2016) Comparative analysis of estimated young’s modulus of rubberized mortar and concrete. International Journal of Civil Engineering 16(2):243–253, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40999-016-0119-x
Chen ZP, Liu X, Xu JJ (2017) Study on interface bond behavior of high strength concrete filled square steel tube after high temperatures. Journal of Building Engineering 38(6):133–143, DOI: https://doi.org/10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2017.06.015 (in Chinese)
Fawzy H, Mustafa S, AbdEl-Badie A (2020) Thermal effect on bond strength of rubberized concrete filled steel tubular sections. Frattura ed Integrita Strutturale 53:353–371, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3221/IGF-ESIS.53.28
Fraile-Garcia E, Ferreiro-Cabello J, Defez, Peris-Fajanes G (2016) Acoustic behavior of hollow blocks and bricks made of concrete doped with waste tire rubber. Materials 9(12):962, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9120962
GB8076-2008 (2008) Concrete admixtures. GB8076-2008, Chinese Standardization Administration, Beijing, China (in Chinese)
GB/T 50152-2012 (2012) Metallic materials - Tensile testing - Part 1: Method of test at room temperature. GB/T 50152-2012, Standards Press of China, Beijing, China (in Chinese)
Gheni AA, Alghazali HH, Elgawady MA, Myers JJ, Feys D (2019) Durability properties of cleaner cement mortar with by-products of tire recycling. Journal of Cleaner Production 213:1135–1146, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.260
Gholampour A, Ozbakkaloglu T, Hassanli R (2017) Behavior of rubberized concrete under active confinement. Construction and Building Materials 138:372–382, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.01.105
Güneyisi E (2010) Fresh properties of self-compacting rubberized concrete incorporated with fly ash. Materials and Structures 43(8):1037–1048, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-009-9564-1
Güneyisi E, Gesoglu M, Naji N, Ipek S (2016) Evaluation of the rheological behavior of fresh self-compacting rubberized concrete by using the Herschel-Bulkley and modified Bingham models. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering 16(1):9–19, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2015.09.003
Hall MR, Najim KB (2014) Structural behaviour and durability of steel-reinforced structural Plain/Self-Compacting Rubberised Concrete (PRC/SCRC). Construction and Building Materials 73:490–497, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.09.063
Hilal NN (2017) Hardened properties of self-compacting concrete with different crumb rubber size and content. International Journal of Sustainable Built Environment 6(1):191–206, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsbe.2017.03.001
Huang W, Huang X, Xing Q, Zhou Z (2020) Strength reduction factor of crumb rubber as fine aggregate replacement in concrete. Journal of Building Engineering 32:101346, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101346
Hunaiti YM (1996) Composite action of foamed and lightweight aggregate concrete. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 8(3):111–113, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(1996)8:3(111)
Ismail MK, Hassan AAA (2016) Use of metakaolin on enhancing the mechanical properties of self-consolidating concrete containing high percentages of crumb rubber. Journal of Cleaner Production 125: 282–295, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.03.044
JGJ/T 283-2012 (2012) Technical specification for application of self-compacting concrete. JGJ/T 283-2012, China Architecture & Building Press Beijing, Beijing, China (in Chinese)
Kang XL (2008) Study on compositing mechanical performance and bond-slip performance of concrete filled steel tube. Xian University of Architecture and Technology, Xian, China (in Chinese)
Khaksefidi S, Ghalehnovi M, De Brito J (2021) Bond behaviour of high-strength steel rebars in normal (NSC) and ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC). Journal of Building Engineering 33:101592, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101592
Khalil E, Abd-Elmohsen M, Anwar AM (2015) Impact resistance of rubberized self-compacting concrete. Water Science 29(1):45–53, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wsj.2014.12.002
Lai D, Demartino C, Xiao Y (2022) High-strain rate compressive behavior of fiber-reinforced rubberized concrete. Construction and Building Materials 319:125739, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125739
Li XY, Zhang JW, Liu J, Cao WL (2019) Bond behavior of spiral ribbed ultra-high strength steel rebar embedded in plain and steel fiber reinforced high-strength concrete. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 23(10):4417–4430, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-019-2449-0
Liu YJ, Chi JJ (2005) Experiment research on the bond behaviors of concrete-filled rectangular tubes. Architecture Technology 36(2): 97–98+107 (in Chinese)
Liu C, Fan ZY, Chen XN, Zhu C, Wang HY, Bai GL (2019) Experimental study on bond behavior between section steel and RAC under full replacement ratio. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 23(3):1159–1170, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-019-0702-1
Liu L, He L, Cheng Z, Wang XY, Ma Z, Cheng XR (2021) Interface bonding behavior of concrete-filled steel tube blended with circulating fluidized bed bottom ash. Materials 14(6):1529, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14061529
Liu QZ, Jiang HJ (2017) Experimental study on a new type of earthquake resilient shear wall. Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics 46(14):2479–2497, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/eqe.2914
Lv J, Zhou TH, Li KL, Sun K (2019) Shrinkage properties of self-compacting rubber lightweight aggregate concrete: Experimental and analytical studies. Materials 12(24):4059, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12244059
Meng WJ, Liu HX, Liu GJ, Kong XQ, Wang XZ (2016) Bond-slip constitutive relation between BFRP bar and basalt fiber recycled-aggregate concrete. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 20(5):1996–2006, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-015-0350-z
Najim KB, Hall MR (2013) Crumb rubber aggregate coatings/pretreatments and their effects on interfacial bonding, air entrapment, and fracture toughness in self-compacting rubberized concrete (SCRC). Materials and Structures 46(12):2029–2043, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-013-0034-4
Nezamian A, Al-Mahaidi R, Grundy P (2006) Bond strength of concrete plugs embedded in tubular steel piles under cyclic loading. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering 33(2):111–125, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1139/L05-091
Qu XS, Liu Q (2017) Bond strength between steel and self-compacting lower expansion concrete in composite columns. Journal of Constructional Steel Research 139:176–187, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2017.09.017
Ren SH, Zhao HT, Xue JY (2011) Experiment research on bond strength of concrete-filled square steel tubes. Building Structure 41(6):68–70
Roeder CW, Cameron B, Brown CB (1999) Composite action in concrete filled tubes. Journal of Structural Engineering 125(5):477–484, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1999)125:5(477)
Sindhuja S, Bhuvaneshwari P (2021) Push-out test on low-density concrete filled stiffened steel tubular columns. International Journal of Civil Engineering 19(12):1399–1413, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40999-021-00638-4
Song H, Liu JP, Yang YL, Chen YF (2018) Study on mechanical behavior of integrated multi-cell concrete-filled steel tubular stub columns under concentric compression. International Journal of Civil Engineering 17(3A):361–376, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40999-018-0367-z
Turatsinze A, Bonnet S, Granju JL (2005) Potential of rubber aggregates to modify properties of cement based-mortars: Improvement in cracking shrinkage resistance. Construction and Building Materials 21(1): 176–181, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2005.06.036
Wang FC, Wu XM, Guo C, Song W (2018) Experimental study on bond strength of deformed steel bars in recycled glass aggregate concrete. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 22(9):3409–3418, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-018-0051-5
Wang YB, Zhao RD (2019) Experimental study on time-dependent behavior of concrete filled steel tubes in ambient environment. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 23(1):200–209, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-018-1070-y
Xiong Z, Wei W, Liu F, Cui CY, Li LJ, Zou R, Zeng Y (2021) Bond behaviour of recycled aggregate concrete with basalt fibre-reinforced polymer bars. Composite Structures 256:113078
Youssf O, ElGawady MA, Mills JE, Ma X (2014) An experimental investigation of crumb rubber concrete confined by fibre reinforced polymer tubes. Construction and Building Materials 53:522–532, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.12.007
Yu F, Chen TY, Niu K, Wang SL, Kong ZY, Fang Y (2020) Study on bond-slip behaviors of self-stressing steel slag concrete-filled steel tube. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 24(11):3309–3319, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-1596-7
Yung WH, Yung LC, Hua LH (2013) A study of the durability properties of waste tire rubber applied to self-compacting concrete. Construction and Building Materials 41:665–672, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.11.019
Zhang JH, Chen CG, Li XJ, Chen XD, Zhang YY (2021) Dynamic mechanical property of self-compacting rubber concrete under high strain rates. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 33(2):04020458, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0003560
Zhao YC, Liu J (2011) The compute method of concrete filled rectangular steel tube bond stress. Science & Technology Information 5:732–733 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 51668007 and 51508112), and the financial support is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ke, X., Tang, Z., Shen, J. et al. Investigation on Bond Behavior between Self-compacting Rubberized Concrete and Rectangular Steel Tubes. KSCE J Civ Eng 26, 3504–3519 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-022-1998-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-022-1998-9