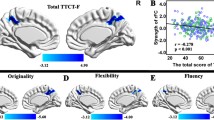
Abstract
In the present study, we hypothesized that the frontoparietal control network played important roles in effectively inhibiting the low creative ideas when performing the creative tasks. To test this hypothesis, the alternative uses task was used to obtain the creative score and the low-creative ideas ratio (LCIR), and the resting-state electroencephalogram (RS-EEG) microstates were used to measure the temporal characteristics of the frontoparietal control network. The results showed that the creative score plays moderating roles in the relationships between the LCIR and the parameters of the fourth microstate (MS4) which is generated from the frontoparietal control network. Specifically, for the individuals with higher creative score, the LCIR were negatively associated with the coverage rate of the MS4 and the possibilities of transitions between MS4 and MS1 (related to the semantic network), while the relationships were not observed for the individuals with lower creative score. Thus, we thought that the frontoparietal control network might be easier to sequentially activate the semantic network for the individuals with higher creative score, which make them more effectively inhibiting the low creative ideas under the creative tasks.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data and code availability
The data that support the findings of this study are included in the Supplementary Materials.
References
Acar, S., Runco, M. A., & Park, H. (2020). What should people be told when they take a divergent thinking test? A meta-analytic review of explicit instructions for divergent thinking. Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts,14(1), 39–49.
Beaty, R. E., & Silvia, P. J. (2012). Why do ideas get more creative across time? An executive interpretation of the serial order effect in divergent thinking tasks. Psychology of Aesthetics Creativity and the Arts, 6(4), 309–319.
Beaty, R. E., Silvia, P. J., Nusbaum, E. C., Jauk, E., & Benedek, M. (2014). The roles of associative and executive processes in creative cognition. Memory & Cognition,42(7), 1186–1197.
Beaty, R. E., Benedek, M., Kaufman, S. B., & Silvia, P. J. (2015). Default and executive network coupling supports creative idea production. Scientific Reports,5, 10964.
Beaty, R. E., Benedek, M., Silvia, P. J., & Schacter, D. L. (2016). Creative cognition and brain network dynamics. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 20, 87–95.
Beaty, R. E., Kenett, Y. N., Christensen, A. P., Rosenberg, M. D., Benedek, M., Chen, Q., Silvia, P. J., Beaty, R. E., Kenett, Y. N., Christensen, A. P., Rosenberg, M. D., Benedek, M., Chen, Q., Fink, A., Qiu, J., Kwapil, T. R., Kane, M. J., & Silvia, P. J. (2018). Robust prediction of individual creative ability from brain functional connectivity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,115, 1087–1092.
Benedek, M., & Neubauer, A. C. (2013). Revisiting mednick’s model on creativity-related differences in associative hierarchies. Evidence for a common path to uncommon thought. The Journal of Creative Behavior, 47(4), 273–289.
Benedek, M., Bergner, S., Könen, T., Fink, A., & Neubauer, A. C. (2011). EEG alpha synchronization is related to top-down processing in convergent and divergent thinking. Neuropsychologia, 49(12), 3505–3511.
Benedek, M., Jauk, E., Fink, A., Koschutnig, K., Reishofer, G., Ebner, F., & Neubauer, A. C. (2014). To create or to recall? Neural mechanisms underlying the generation of creative new ideas. Neuroimage,88, 125–133.
Benedek, M., Kenett, Y. N., Umdasch, K., Anaki, D., Faust, M., & Neubauer, A. C. (2017). How semantic memory structure and intelligence contribute to creative thought: a network science approach. Thinking & Reasoning, 23(2), 158–183.
Benedek, M., Schües, T., Beaty, R. E., Jauk, E., Koschutnig, K., Fink, A., & Neubauer, A. C. (2018). To create or to recall original ideas: brain processes associated with the imagination of novel object uses. Cortex; A Journal Devoted to the Study of the Nervous System and Behavior,99, 93–102.
Britz, J., Van De Ville, D., & Michel, C. M. (2010). BOLD correlates of EEG topography reveal rapid resting-state network dynamics. Neuroimage,52(4), 1162–1170.
Chen, C., Kasof, J., Himsel, A., Dmitrieva, J., Dong, Q., & Xue, G. (2005). Effects of explicit instruction to “be creative” across domains and cultures. The Journal of Creative Behavior,39(2), 89–110.
Chen, Q., Beaty, R. E., Wei, D., Yang, J., Sun, J., Liu, W., Qiu, J., Chen, Q., Beaty, R. E., Wei, D., Yang, J., Sun, J., Liu, W., Yang, W., Zhang, Q., & Qiu, J. (2018). Longitudinal alterations of frontoparietal and frontotemporal networks predict future creative cognitive ability. Cerebral Cortex,28(1), 103–115.
Cogdell-Brooke, L. S., Sowden, P. T., Violante, I. R., & Thompson, H. E. (2020). A meta-analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging studies of divergent thinking using activation likelihood estimation. Human Brain Mapping,41(17), 5057–5077.
Curran, P. J., West, S. G., & Finch, J. F. (1996). The robustness of test statistics to nonnormality and specification error in confirmatory factor analysis. Psychological Methods,1(1), 16–29.
Dewhurst, S. A., Thorley, C., Hammond, E. R., & Ormerod, T. C. (2011). Convergent, but not divergent, thinking predicts susceptibility to associative memory illusions. Personality and Individual Differences,51(1), 73–76.
Dumas, D., & Runco, M. (2018). Objectively scoring divergent thinking tests for originality: a re-analysis and extension. Creativity Research Journal,30(4), 466–468.
Fink, A., & Benedek, M. (2014). EEG alpha power and creative ideation. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews,44, 111–123.
Fink, A., Benedek, M., Koschutnig, K., Pirker, E., Berger, E., Meister, S., & Weiss, E. M. (2015). Training of verbal creativity modulates brain activity in regions associated with language-and memory‐related demands. Human Brain Mapping,36(10), 4104–4115.
Fink, A., Grabner, R. H., Gebauer, D., Reishofer, G., Koschutnig, K., & Ebner, F. (2010). Enhancing creativity by means of cognitive stimulation: evidence from an fMRI study. Neuroimage,52(4), 1687–1695.
Fink, A., Koschutnig, K., Benedek, M., Reishofer, G., Ischebeck, A., Weiss, E. M., & Ebner, F. (2012). Stimulating creativity via the exposure to other people’s ideas. Human Brain Mapping,33(11), 2603–2610.
Gao, Z. K., Cai, Q., Yang, Y. X., Dong, N., & Zhang, S. S. (2017). Visibility graph from adaptive optimal kernel time-frequency representation for classification of epileptiform EEG. International Journal of Neural Systems,27(04), 1750005.
Gilhooly, K. J., Fioratou, E., Anthony, S. H., & Wynn, V. (2007). Divergent thinking: strategies and executive involvement in generating novel uses for familiar objects. British Journal of Psychology, 98(4), 611–625.
Guilford, J. P. (1967). The nature of human intelligence. McGraw-Hill.
Guilford, J. P. (1950). Creativity. American Psychologist,5(9), 444–454.
Hayes, A. F. (2018). Partial, conditional, and moderated moderated mediation: Quantification, inference, and interpretation. Communication Monographs, 85(1), 4–40.
Johnson-Frey, S. H. (2004). The neural bases of complex tool use in humans. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 8(2), 71–78.
Kaufman, J. C., & Sternberg, R. J. (Eds.) (2010). Cambridge handbook of creativity. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Khanna, A., Pascual-Leone, A., & Farzan, F. (2014). Reliability of resting-state microstate features in electroencephalography. PloS One,9(12), e114163.
Khanna, A., Pascual-Leone, A., Michel, C. M., & Farzan, F. (2015). Microstates in resting-state EEG: current status and future directions. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews,49, 105–113.
Koenig, T., Lehmann, D., Merlo, M. C., Kochi, K., Hell, D., & Koukkou, M. (1999). A deviant EEG brain microstate in acute, neuroleptic-naive schizophrenics at rest. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience,249(4), 205–211.
Kühn, S., Ritter, S. M., Müller, B. C., Van Baaren, R. B., Brass, M., & Dijksterhuis, A. (2014). The importance of the default mode network in creativity—a structural MRI study. The Journal of Creative Behavior,48(2), 152–163.
Lehmann, D., Ozaki, H., & Pál, I. (1987). EEG alpha map series: brain micro-states by space-oriented adaptive segmentation. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology,67(3), 271–288.
Lehmann, D., Strik, W. K., Henggeler, B., König, T., & Koukkou, M. (1998). Brain electric microstates and momentary conscious mind states as building blocks of spontaneous thinking: I. Visual imagery and abstract thoughts. International Journal of Psychophysiology,29(1), 1–11.
Lifshitz-Ben-Basat, A., & Mashal, N. (2021). Enhancing creativity by altering the frontoparietal control network functioning using transcranial direct current stimulation. Experimental Brain Research,239, 613–626.
Matheson, H. E., Buxbaum, L. J., & Thompson-Schill, S. L. (2017). Differential tuning of ventral and dorsal streams during the generation of common and uncommon tool uses. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience,29(11), 1791–1802.
Musso, F., Brinkmeyer, J., Mobascher, A., Warbrick, T., & Winterer, G. (2010). Spontaneous brain activity and EEG microstates. A novel EEG/fMRI analysis approach to explore resting-state networks. Neuroimage,52(4), 1149–1161.
Niu, W., & Liu, D. (2009). Enhancing creativity: a comparison between effects of an indicative instruction “to be creative” and a more elaborate heuristic instruction on chinese student creativity. Psychology of Aesthetics Creativity and the Arts,3(2), 93–98.
Pascual-Marqui, R. D., Michel, C. M., & Lehmann, D. (1995). Segmentation of brain electrical activity into microstates: model estimation and validation. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,42(7), 658–665.
Shi, L., Beaty, R. E., Chen, Q., Sun, J., Wei, D., Yang, W., & Qiu, J. (2020). Brain entropy is associated with divergent thinking. Cerebral Cortex,30(2), 708–717.
Silvia, P. J., Winterstein, B. P., Willse, J. T., Barona, C. M., Cram, J. T., Hess, K. I., Richard, C. A., Silvia, P. J., Winterstein, B. P., Willse, J. T., Barona, C. M., Cram, J. T., Hess, K. I., Martinez, J. L., & Richard, C. A. (2008). Assessing creativity with divergent thinking tasks: exploring the reliability and validity of new subjective scoring methods. Psychology of Aesthetics Creativity and the Arts,2, 68–85.
Sternberg, R. J. (1999). A propulsion model of types of creative contributions. Review of General Psychology, 3(2), 83–100.
Sun, J., Shi, L., Chen, Q., Yang, W., Wei, D., Zhang, J., Qiu, J., Sun, J., Shi, L., Chen, Q., Yang, W., Wei, D., Zhang, J., Zhang, Q., & Qiu, J. (2019). Openness to experience and psychophysiological interaction patterns during divergent thinking. Brain Imaging and Behavior,13(6), 1580–1589.
Tibshirani, R., & Walther, G. (2005). Cluster validation by prediction strength. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics,14(3), 511–528.
Van de Ville, D., Britz, J., & Michel, C. M. (2010). EEG microstate sequences in healthy humans at rest reveal scale-free dynamics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,107(42), 18179–18184.
Wagner, A. D., Paré-Blagoev, E. J., Clark, J., & Poldrack, R. A. (2001). Recovering meaning: left prefrontal cortex guides controlled semantic retrieval. Neuron,31(2), 329–338.
Whitney, C., Kirk, M., O’Sullivan, J., Lambon Ralph, M. A., & Jefferies, E. (2011). The neural organization of semantic control: TMS evidence for a distributed network in left inferior frontal and posterior middle temporal gyrus. Cerebral Cortex,21(5), 1066–1075.
Wu, X., Guo, J., Wang, Y., Zou, F., Guo, P., Lv, J., & Zhang, M. (2020). The relationships between trait creativity and resting-state EEG microstates were modulated by self-esteem. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 14, 576114.
Wu, X., Yang, W., Tong, D., Sun, J., Chen, Q., Wei, D., et al. (2015). A meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies on divergent thinking using activation likelihood estimation. Human Brain Mapping,36(7), 2703–2718.
Xiao, Z., & Huang, J. (2022). The relation between college students’ social anxiety and mobile phone addiction: the mediating role of regulatory emotional self-efficacy and subjective well-being. Frontiers in Psychology,13, 861527–861527.
Yilmaz, S., Seifert, C. M., & Gonzalez, R. (2010). Cognitive heuristics in design: instructional strategies to increase creativity in idea generation. Ai Edam,24(3), 335–355.
Yuan, H., Zotev, V., Phillips, R., Drevets, W. C., & Bodurka, J. (2012). Spatiotemporal dynamics of the brain at rest—exploring EEG microstates as electrophysiological signatures of BOLD resting state networks. Neuroimage,60(4), 2062–2072.
Zmigrod, S., Colzato, L. S., & Hommel, B. (2015). Stimulating creativity: modulation of convergent and divergent thinking by transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS). Creativity Research Journal,27(4), 353–360.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31600927, 81830040), the Youth Foundation of Social Science and Humanity, China Ministry of Education (19YJCZH179), and the Key scientific research projects of colleges and universities in Henan province (20A190001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they had no conflicts of interest with respect to their authorship or the publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Zhang, X., Yang, X. et al. Temporal characteristics of frontoparietal control network related to inhibiting low creative ideas in creative tasks. Curr Psychol 43, 11413–11421 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-04858-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-04858-w