Abstract
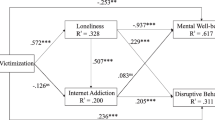
Internet addiction has rapidly become a prevalent concern among left-behind children in China. Using the hierarchical multiple regression analysis, this cross-sectional study aims to investigate the correlation among loneliness, psychological resilience, and Internet addiction, as well as determine whether the adverse impact of loneliness could be buffered by psychological resilience. The findings revealed that loneliness positively correlated with Internet addiction, while psychological resilience negatively correlated with Internet addiction. The moderating effect analysis suggested that resilience could alleviate the adverse impact of loneliness on Internet addiction. Specifically, a statistically significantly positive effect of loneliness was noted on Internet addiction among children with low resilience, whereas no significant association between loneliness and Internet addiction was found among those with a high level of resilience. In conclusion, this study sheds light on the psychosocial mechanisms how loneliness might affect Internet addiction among left-behind children in China.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data linking to the present study could be obtained by sending email to cql1086@126.com.
References
Ai, H., & Hu, J. (2016). Psychological resilience moderates the impact of social support on loneliness of “left-behind” children. Journal of Health Psychology, 21(6), 1066–1073.
Aiken, L. S., & West, S. G. (1991). Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Newbury Park: Sage.
Asher, S. R., Hymel, S., & Renshaw, P. D. (1984). Loneliness in children. Child Development, 55, 1456–1464.
Bai, Y., Zhang, L., Liu, C., Shi, Y., Mo, D., & Rozelle, S. (2018). Effect of parental migration on the academic performance of left behind children in North Western China. The Journal of Development Studies, 54(7), 1154–1170.
Bozoglan, B., Demirer, V., & Sahin, I. (2013). Loneliness, self-esteem, and life satisfaction as predictors of internet addiction: A cross-sectional study among Turkish university students. Scandinavian Journal of Psychology, 54(4), 313–319.
Campbell-Sills, L., & Stein, M. B. (2007). Psychometric analysis and refinement of the connor-Davidson resilience scale (CD-RISC): Validation of a 10-item measure of resilience. Journal of Traumatic Stress: Official Publication of the International Society for Traumatic Stress Studies, 20(6), 1019–1028.
Canale, N., Marino, C., Griffiths, M. D., Scacchi, L., Monaci, M. G., & Vieno, A. (2019). The association between problematic online gaming and perceived stress: The moderating effect of psychological resilience. Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 8(1), 174–180.
Caplan, S. E. (2003). Preference for online social interaction. Communication Research, 30(6), 625–648.
Chang, M. K., & Law, S. P. M. (2008). Factor structure for Young’s internet addiction test: A confirmatory study. Computers in Human Behavior, 24(6), 2597–2619.
Cheng, C., & Li, A. Y. L. (2014). Internet addiction prevalence and quality of (real) life: A meta-analysis of 31 nations across seven world regions. Cyberpsychology, Behavior and Social Networking, 17(12), 755–760.
Chou, C., & Hsiao, M. C. (2000). Internet addiction, usage, gratification, and pleasure experience: The Taiwan college students’ case. Computers & Education, 35(1), 65–80.
Cohen, J., Cohen, P., West, S. G., & Aiken, L. S. (2003). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Connor, K. M., & Davidson, J. R. (2003). Development of a new resilience scale: The Connor-Davidson resilience scale (CD-RISC). Depression and Anxiety, 18(2), 76–82.
Czincz, J., & Hechanova, R. (2009). Internet addiction: Debating the diagnosis. Journal of Technology in Human Services, 27(4), 257–272.
Davis, R. A. (2001). A cognitive-behavioral model of pathological internet use. Computers in Human Behavior, 17(2), 187–195.
Dong, B., Zhao, F., Wu, X. S., Wang, W. J., Li, Y. F., Zhang, Z. H., & Sun, Y. H. (2018). Social anxiety may modify the relationship between internet addiction and its determining factors in Chinese adolescents. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 1-13.
Duan, C. R., Lai, M. H., & Qin, M. (2017). Research on the change trend of left-behind children in rural China since the 21st century. China Youth Study, 6, 52–60.
Ge, Y., Se, J., & Zhang, J. (2015). Research on relationship among internet-addiction, personality traits and mental health of urban left-behind children. Global Journal of Health Science, 7(4), 60–69.
Ge, Y., Zhong, X., & Luo, W. (2017). Recognition of facial expressions by urban internet-addicted left-behind children in China: An eye-movement study. Psychological Reports, 120(3), 391–407.
Gosling, S. D., & Mason, W. (2015). Internet research in psychology. Annual Review of Psychology, 66, 877–902.
Ha, Y. M., & Hwang, W. J. (2014). Gender differences in internet addiction associated with psychological health indicators among adolescents using a national web-based survey. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 12(5), 660–669.
Hawi, N. S. (2012). Internet addiction among adolescents in Lebanon. Computers in Human Behavior, 28(3), 1044–1053.
Heinrich, L. M., & Gullone, E. (2006). The clinical significance of loneliness: A literature review. Clinical Psychology Review, 26(6), 695–718.
Hou, X., Wang, H., Guo, C., Gaskin, J., Rost, D. H., & Wang, J. (2017). Psychological resilience can help combat the effect of stress on problematic social networking site usage. Personality and Individual Differences, 109, 61–66.
Hu, H., Lu, S., & Huang, C. C. (2014). The psychological and behavioral outcomes of migrant and left-behind children in China. Children and Youth Services Review, 46, 1–10.
Jenaro, C., Flores, N., Gómez-Vela, M., González-Gil, F., & Caballo, C. (2009). Problematic internet and cell-phone use: Psychological, behavioral, and health correlates. Addiction Research & Theory, 15(3), 309–320.
Ji, Y., Xu, H., Zhang, Y., & Liu, Q. (2017). Heterogeneity of health-risk behaviours in left-behind children in rural western China: A cross-sectional survey. The Lancet, 390, S4.
Jia, Z., & Tian, W. (2010). Loneliness of left-behind children: A cross-sectional survey in a sample of rural China. Child: Care, Health and Development, 36(6), 812–817.
Jiangsu Provincial Bureau of Statistics. (2019, June 16). Retrieved from: http://tj.jiangsu.gov.cn/.
Kim, J., LaRose, R., & Peng, W. (2009). Loneliness as the cause and the effect of problematic internet use: The relationship between internet use and psychological well-being. Cyberpsychology & Behavior, 12(4), 451–455.
Kostak, M. A., Dindar, İ., & Dinçkol, R. Z. (2018). Loneliness, depression, social support levels, and other factors involving the internet use of high school students in Turkey. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 1-14.
Lee, J. Y., Ko, D. W., & Lee, H. (2019). Loneliness, regulatory focus, inter-personal competence, and online game addiction: A moderated mediation model. Internet Research, 29(2), 381–394.
Ling, H., Fu, E., & Zhang, J. R. (2015). Effects of separation age and separation duration among left-behind children in China. Social Behavior and Personality: An International Journal, 43(2), 241–253.
Malak, M. Z., Khalifeh, A. H., & Shuhaiber, A. H. (2017). Prevalence of internet addiction and associated risk factors in Jordanian school students. Computers in Human Behavior, 70, 556–563.
Milošević-Đorđević, J. S., & Žeželj, I. L. (2014). Psychological predictors of addictive social networking sites use: The case of Serbia. Computers in Human Behavior, 32, 229–234.
Ren, Y., Yang, J., & Liu, L. (2017). Social anxiety and internet addiction among rural left-behind children: The mediating effect of loneliness. Iranian Journal of Public Health, 46(12), 1659–1668.
Robertson, T. W., Yan, Z., & Rapoza, K. A. (2018). Is resilience a protective factor of internet addiction? Computers in Human Behavior, 78, 255–260.
Rutter, M. (2012). Resilience as a dynamic concept. Development and Psychopathology, 24(2), 335–344.
Shaw, L. H., & Gant, L. M. (2004). In defense of the internet: The relationship between internet communication and depression, loneliness, self-esteem, and perceived social support. Internet Research, 28(3).
Shek, D. T. L., & Yu, L. (2016). Adolescent internet addiction in Hong Kong: Prevalence, change, and correlates. Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology, 29, S22–S30.
Shettar, M., Karkal, R., Kakunje, A., Mendonsa, R. D., & Chandran, V. M. (2017). Facebook addiction and loneliness in the post-graduate students of a university in southern India. International Journal of Social Psychiatry, 63(4), 325–329.
Shi, X., Wang, J., & Zou, H. (2017). Family functioning and internet addiction among Chinese adolescents: The mediating roles of self-esteem and loneliness. Computers in Human Behavior, 76, 201–210.
Skues, J., Williams, B., Oldmeadow, J., & Wise, L. (2016). The effects of boredom, loneliness, and distress tolerance on problem internet use among university students. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 14(2), 167–180.
Wang, X. D., Wang, X. L., & Ma, H. (Eds.). (1999). The handbook of mental health rating scales [in Chinese]. Beijing, China: Chinese Mental Health Journal.
Wang, L., Shi, Z., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, Z. (2010). Psychometric properties of the 10-item Connor–Davidson resilience scale in Chinese earthquake victims. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 64(5), 499–504.
Wen, M., & Lin, D. (2012). Child development in rural China: Children left behind by their migrant parents and children of nonmigrant families. Child Development, 83(1), 120–136.
Wu, C. Y., Lee, M. B., Liao, S. C., & Chang, L. R. (2015). Risk factors of internet addiction among internet users: An online questionnaire survey. PLoS One, 10(10).
Wu, C. S. T., Wong, H. T., Yu, K. F., Fok, K. W., Yeung, S. M., Lam, C. H., & Liu, K. M. (2016a). Parenting approaches, family functionality, and internet addiction among Hong Kong adolescents. BMC Pediatrics, 16(1), 130.
Wu, X., Zhang, Z., Zhao, F., Wang, W., Li, Y., Bi, L., et al. (2016b). Prevalence of internet addiction and its association with social support and other related factors among adolescents in China. Journal of Adolescence, 52, 103–111.
Ye, Y., & Lin, L. (2015). Examining relations between locus of control, loneliness, subjective well-being, and preference for online social interaction. Psychological Reports, 116(1), 164–175.
Ying Ge, J. S., & Zhang, J. (2015). Research on relationship among internet-addiction, personality traits and mental health of urban left-behind children. Global Journal of Health Science, 7(4), 60.
Young, K. S. (1998). Internet addiction: The emergence of a new clinical disorder. Cyberpsychology & Behavior, 1(3), 237–244.
Young, K. S., & Rodgers, R. C. (1998). Internet addiction: Personality traits associated with its development. In 69th annual meeting of the Eastern Psychological Association pp. 40-50.
Zhao, X., Huang, C., Li, X., Zhao, X., & Peng, J. (2015). Dispositional optimism, self-framing and medical decision-making. International Journal of Psychology, 50(2), 121–127.
Acknowledgments
This paper is supported by the project of innovation and entrepreneurship of college students in Changzhou University of Jiangsu Province (ZMF19020225) and National Natural Science Foundation Project (71904019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CQ and JA drafted the manuscript and performed the statistical analysis. YY and PP conceived of the study and participated in its design and coordination and helped to draft the manuscript. XX and XH participated in the design of the study, XS performed the statistical analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Q., An, J., Yang, Y. et al. Correlation among psychological resilience, loneliness, and internet addiction among left-behind children in China: A cross-sectional study. Curr Psychol 41, 4566–4573 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-020-00970-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-020-00970-3