Abstract
Background
Deregulated expression of cell cycle regulators p27 and p16 is associated with cancer progression. p27kip1 and p16INKa are a cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor whose major target is the cyclinE/CDK2 and cyclinD/CDK4/6 complex, respectively, that governs cell cycle transition from late G1 to S phase.
Methods
We recruited biopsies of a total of 84 subjects including 72 primary tumor biopsies from histopathologically proven gastric carcinoma, 8 adjacent controls and 12 independent controls. We used gastric cancer cell line, AGS, for validation of our data. Expression profiling at transcript level was done by semi-quantitative RT-PCR and at proteome level by immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence. Receiver operator characteristics analysis was done for determining the diagnostic utility of p27 and p16 with respect to the sensitivity and specificity.
Results
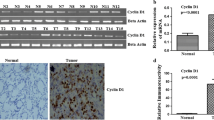
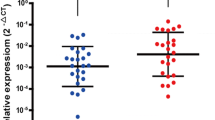
We demonstrate that p27 and p16 are frequently over expressed in early stages of gastric carcinoma. Our semi-quantitative data show a significant upregulation of p27 (Mean ± SEM, 0.4771 ± 0.0895; p = 0.0001) and p16 (Mean ± SEM, 0.4676 ± 0.04305; p = 0.0001) at mRNA level. Concordant to semi-quantitative data, immunohistochemistry data also showed a significant upregulation of p27 (Mean ± SEM, 196.4 ± 10.84; p < 0.0001) and p16 (Mean ± SEM, 100.4 ± 23.71; p < 0.0001) at protein level.
Conclusions
The present study showed that the significant upregulation of p27 and p16 were associated with early events in gastric carcinogenesis. Our data suggests that clinical correlation of these differentially expressed genes may be useful as diagnostic biomarkers for early detection of gastric carcinoma and promising therapeutics target for GC patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108.
Dikshit R, Gupta PC, Ramasundarahettige C, Gajalakshmi V, Aleksandrowicz L, Badwe R, et al. Cancer mortality in India: a nationally representative survey. Lancet. 2012;379:1807–16.
Chu IM, Hengst L, Slingerland JM. The Cdk inhibitor p27 in human cancer: prognostic potential and relevance to anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:253–67.
Yasui W, Oue N, Kuniyasu H, Ito R, Tahara E, Yokozaki H. Molecular diagnosis of gastric cancer: present and future. Gastric Cancer. 2001;4:113–21.
Viglietto G, Motti ML, Fusco A. Understanding p27(kip1) deregulation in cancer: down-regulation or mislocalization. Cell Cycle. 2002;1:394–400.
Lloyd RV, Erickson LA, Jin L, Kulig E, Qian X, Cheville JC, et al. p27kip1: a multifunctional cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor with prognostic significance in human cancers. Am J Pathol. 1999;154:313–23.
Loda M, Cukor B, Tam SW, Lavin P, Fiorentino M, Draetta GF, et al. Increased proteasome-dependent degradation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 in aggressive colorectal carcinomas. Nat Med. 1997;3:231–4.
Tan P, Cady B, Wanner M, Worland P, Cukor B, Magi- Galluzzi C, et al. The cell cycle inhibitor p27 is an independent prognostic marker in small (T1a, b) invasive breast carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1997;57:1259–63.
Masciullo V, Sgambato A, Pacilio C, Pucci B, Ferrandina G, Palazzo J, et al. Frequent loss of expression of the cyclindependent kinase inhibitor p27 in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 1999;59:3790–4.
Gillett CE, Smith P, Peters G, Lu X, Barnes DM. Cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 expression and interaction with other cell cycle-associated proteins in mammary carcinoma. J Pathol. 1999;187:200–6.
Barbareschi M, van Tinteren H, Mauri FA, Veronese S, Peterse H, Maisonneuve P, et al. p27(kip1) expression in breast carcinomas: an immunohistochemical study on 512 patients with long-term follow-up. Int J Cancer. 2000;89:236–41.
Sgambato A, Ratto C, Faraglia B, Merico M, Ardito R, Schinzari G, et al. Reduced expression and altered subcellular localization of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(Kip1) in human colon cancer. Mol Carcinog. 1999;26:172–9.
Zhang H, Sun XF. Loss of p27 expression predicts poor prognosis in patients with Dukes’ B stage or proximal colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol. 2001;19:49–52.
Singh SP, Lipman J, Goldman H, Ellis FH Jr, Aizenman L, Cangi MG, et al. Loss or altered subcellular localization of p27 in Barrett’s associated adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1998;58:1730–5.
Babaei M, Pourfarzi F, Yazdanbod A, Chiniforush MM, Derakhshan MH, Mousavi SM, et al. Gastric cancer in Ardabil, Iran–a review and update on cancer registry data. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2010;11:595–9.
Hansson LE, Baron J, Nyrén O, Bergström R, Wolk A, Adami HO. Tobacco, alcohol and the risk of gastric cancer. A population-based case-control study in Sweden. Int J Cancer. 1994;57:26–31.
Kulkarni S, Rader JS, Zhang F, Liapis H, Koki AT, Masferrer JL. Cyclooxygenase-2 over expressed in human cervical cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:429–34.
Prasad SB, Yadav SS, Das M, Modi A, Kumari S, Pandey LK, et al. PI3K/AKT pathway-mediated regulation of p27(Kip1) is associated with cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in cervical cancer. Cell Oncol. 2015;38:215–25.
Lee YY, Derakhshan MH. Environmental and lifestyle risk factors of gastric cancer. Arch Iran Med. 2013;16:358–65.
Chandanos E, Lagergren J. Oestrogen and the enigmatic male predominance of gastric cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2008;44:2397–403.
Qin J, Liu M, Ding Q, Ji X, Hao Y, Wu X, et al. The direct effect of estrogen on cell viability and apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;395:99–107.
Gamboa-Dominguez A, Seidl S, Reyes-Gutierrez E, Hermannstädter C, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Busch R, Höfler H, et al. Prognostic significance of p21WAF1/CIP1, p27Kip1, p53 and E-cadherin expression in gastric cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2007;60:756–61.
Sugai T, Tsukahara M, Endoh M, Shioi Y, Takebe N, Mue Y, et al. Analysis of cell cycle-related proteins in gastric intramucosal differentiated-type cancers based on mucin phenotypes: a novel hypothesis of early gastric carcinogenesis based on mucin phenotype. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010;10:55.
Kumari S, Puneet PSB, Yadav SS, Kumar M, Khanna A, et al. Cyclin D1 and cyclin E2 are differentially expressed in gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 2016;33:40.
Ito Y, Matsuura N, Sakon M, Miyoshi E, Noda K, Takeda T, et al. Expression and prognostic roles of the G1-S modulators in hepatocellular carcinoma: p27 independently predicts the recurrence. Hepatology. 1999;30:90–9.
Wang Y, Wang Y, Cheng C, Ji Y, Zhao Y, Zou L, et al. Expression of Jun activation domain-binding protein 1 and Ser10 phosphorylated p27 protein in human epithelial ovarian carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009;135:951–9.
Hwang CS, Ahn S, Lee BE, Lee SJ, Kim A, Choi CI, et al. Risk of lymph node metastasis in mixed-type early gastric cancer determined by the extent of the poorly differentiated component. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22:4020–6.
Baekelandt M, Holm R, Tropé CG, Nesland JM, Kristensen GB. Lack of independent prognostic significance of p21 and p27 expression in advanced ovarian cancer: an immunohistochemical study. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5:2848–53.
Kang HY, Kim N, Park YS, Hwang JH, Kim JW, Jeong SH, et al. Progression of atrophic gastritisand intestinal metaplasia drives Helicobacter pylori out of thegastric mucosa. Dig Dis Sci. 2006;51:2310–5.
Melck A, Masoudi H, Griffith OL, Rajput A, Wilkins G, Bugis S, et al. Cell cycle regulators show diagnostic and prognostic utility for differentiated thyroid cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:3403–11.
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge financial assistance from Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science and Technology, India to Dr. Puneet (BT/PR/11113/10/678/2008); Soni Kumari is thankful to DBT and Banaras Hindu University for Research Fellowships. Authors are thankful to Interdisciplinary School of Life Sciences, Banaras Hindu University and UGC-UPE programme of Banaras Hindu University for equipment facilities.
Funding
This study was funded by Department of Biotechnology, Government of India, vide Grant number BT/PR11113/BRB/10/678/ 2008 to Dr. Puneet and financial assistance from Banaras Hindu University to Soni Kumari.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration ethical standards and approved by the Institutional Ethical Committee of Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumari, S., Kumar, P., Kumar, M. et al. Expression of p27 and p16 and their clinical significance in gastric cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 23, 856–865 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-020-02479-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-020-02479-4