Abstract
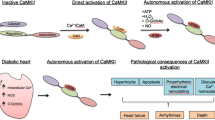
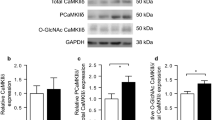
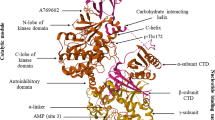
The increase in blood glucose causes a myriad of pathways and molecular components to malfunction, leading to diabetes. Diabetes affects each organ differently by activating distinct pathways. It has an impact on the liver, pancreas, kidney (nephropathy), eyes (retinopathy), and nervous system (neuropathy). Understanding the effects of diabetes on each organ is the first step in developing a sustained treatment for the disease. Among the many cellular molecules impacted by diabetes is Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), a complex Ca2+/calmodulin-activated serine/threonine-protein kinase. When intracellular [Ca2+] rises, it binds to calmodulin (CaM) to produce Ca2+/CaM, which activates CaMKIIs. This factor is involved in the pancreas, liver, heart, muscles, and various organs. Thus, Understanding CaMKII action in each organ is critical for gaining a complete picture of diabetic complications. Therefore, this review covers CaMKII’s functions in many organs and how it affects and has been affected by diabetes.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CaMKII:
-
Ca2+/CaM-dependent protein kinase II
- IP3Rs:
-
Inositol 3-phosphate receptors
- IR:
-
Insulin receptor
- IRS:
-
Insulin receptor substrate
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase
- AKT:
-
Serine/threonine kinase
- FoxO1:
-
Forkhead box O1
- cAMP:
-
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
- PKA:
-
Protein kinase A
- CREB:
-
CAMP responsive element binding protein
- IP3R:
-
Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor
- IP3:
-
Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate
- CRTC2:
-
CREB-regulated transcription co-activators 2
- PGC-1α:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1 alpha
- ATF6:
-
Activating transcription factor 6
- HDAC4:
-
Histone deacetylase 4
- RyR2:
-
Ryanodine receptor 2
- mPTP:
-
Mitochondrial permeability transition pore
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-kappaB
- TGF-β1:
-
Transforming growth factor-beta 1
- PKCα:
-
Protein kinase C alpha
- ERK:
-
Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase
- PLB:
-
Phospholamban
- CaSR:
-
Calcium-sensing receptor
- CSE:
-
Cystathionine-gamma-lyase
- H2S:
-
Hydrogen sulfide
References
Bao SL, Pan J, Sun HX, Liu WT (2018) Valsartan improves cardiac function in mice with diabetes mellitus by CaMKII/AngII. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:5327–5334
Castro AJG, Frederico MJS, Cazarolli LH et al (2015) The mechanism of action of ursolic acid as insulin secretagogue and insulinomimetic is mediated by cross-talk between calcium and kinases to regulate glucose balance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1850:51–61
Chen Y, Hua Y, Li X et al (2020) Distinct types of cell death and the implication in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Front Pharmacol 11:42
Chen J, Fleming T, Katz S et al (2021) CaM kinase II-δ is required for diabetic hyperglycemia and retinopathy but not nephropathy. Diabetes 70:616–626
Chou C, Ho C, Lee H et al (2017) Roles of impaired intracellular calcium cycling in arrhythmogenicity of diabetic mouse model. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 40:1087–1095
Dadi PK, Vierra NC, Ustione A et al (2014) Inhibition of pancreatic β-cell Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II reduces glucose-stimulated calcium influx and insulin secretion, impairing glucose tolerance. J Biol Chem 289:12435–12445
Dai W, Choubey M, Patel S et al (2021) Adipocyte CAMK2 deficiency improves obesity-associated glucose intolerance. Mol Metab 53:101300
Erickson JR, Pereira L, Wang L et al (2013) Diabetic hyperglycaemia activates CaMKII and arrhythmias by O-linked glycosylation. Nature 502:372–376
Erickson JR, Nichols CB, Uchinoumi H et al (2015) S-nitrosylation induces both autonomous activation and inhibition of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II δ. J Biol Chem 290:25646–25656
Ersoy BA, Maner-Smith KM, Li Y et al (2018) Thioesterase-mediated control of cellular calcium homeostasis enables hepatic ER stress. J Clin Invest 128:141–156
Federico M, Portiansky EL, Sommese L et al (2017) Calcium-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase mediates the intracellular signalling pathways of cardiac apoptosis in mice with impaired glucose tolerance. J Physiol 595:4089–4108
Ferhatovic L, Jelicic Kadic A, Boric M, Puljak L (2014) Changes of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II expression in dorsal root ganglia during maturation in long-term diabetes. Histol Histopathol 29(5):649–58
Gao M, Ji S, Li J, Zhang S (2019) DL-3-n-butylphthalide (NBP) ameliorates cognitive deficits and CaMKII-mediated long-term potentiation impairment in the hippocampus of diabetic db/db mice. Neurol Res 41:1024–1033
Gbr AA, Baky NAA, Mohamed EA, Zaky HS (2021) Cardioprotective effect of pioglitazone and curcumin against diabetic cardiomyopathy in type 1 diabetes mellitus: impact on CaMKII/NF-κB/TGF-β1 and PPAR-γ signaling pathway. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 394:349–360
Gerhart-Hines Z, Dominy JE Jr, Blättler SM et al (2011) The cAMP/PKA pathway rapidly activates SIRT1 to promote fatty acid oxidation independently of changes in NAD+. Mol Cell 44:851–863
Hegyi B, Borst JM, Bailey LRJ et al (2020) Hyperglycemia regulates cardiac K+ channels via O-GlcNAc-CaMKII and NOX2-ROS-PKC pathways. Basic Res Cardiol 115:1–19
Hwang H, Park K, Choi JH et al (2018) Zafirlukast promotes insulin secretion by increasing calcium influx through L-type calcium channels. J Cell Physiol 233:8701–8710
Jankyova S, Rubintova D, Janosikova L et al (2016) The effects of Pycnogenol® as add-on drug to metformin therapy in diabetic rats. Phyther Res 30:1354–1361
Jensen TE, Rose AJ, Hellsten Y et al (2007) Caffeine-induced Ca2+ release increases AMPK-dependent glucose uptake in rodent soleus muscle. Am J Physiol Metab 293:E286–E292
Jerić M, Vuica A, Borić M et al (2015) Diabetes mellitus affects activity of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alpha in rat trigeminal ganglia. J Chem Neuroanat 64:12–19
Joseph JS, Ayeleso AO, Mukwevho E (2017a) Exercise increases hyper-acetylation of histones on the cis-element of NRF-1 binding to the Mef2a promoter: implications on type 2 diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 486:83–87
Joseph JS, Ayeleso AO, Mukwevho E (2017b) Role of exercise-induced calmodulin protein kinase (CAMK) II activation in the regulation of omega-6 fatty acids and lipid metabolism genes in rat skeletal muscle. Physiol Res 66:969–977
Katano T, Nakazawa T, Nakatsuka T et al (2011) Involvement of spinal phosphorylation cascade of Tyr1472-NR2B, Thr286-CaMKII, and Ser831-GluR1 in neuropathic pain. Neuropharmacology 60:609–616
Kato M, Tani T, Terahara N, Tsuda T (2015) The anthocyanin delphinidin 3-rutinoside stimulates glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion in murine GLUTag cell line via the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II pathway. PLoS ONE 10:e0126157
Kido K, Ato S, Yokokawa T et al (2018) Resistance training recovers attenuated APPL1 expression and improves insulin-induced Akt signal activation in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic rats. Am J Physiol Metab 314:E564–E571
Kim H, Kang H, Heo RW et al (2016) Caloric restriction improves diabetes-induced cognitive deficits by attenuating neurogranin-associated calcium signaling in high-fat diet-fed mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36:1098–1110
Koyani CN, Trummer C, Shrestha N et al (2018) Saxagliptin but not sitagliptin inhibits CaMKII and PKC via DPP9 inhibition in cardiomyocytes. Front Physiol 9:1622
Kronlage M, Dewenter M, Grosso J et al (2019) O-GlcNAcylation of histone deacetylase 4 protects the diabetic heart from failure. Circulation 140:580–594
Li J, Wang P, Zhu Y et al (2015) Curcumin inhibits neuronal loss in the retina and elevates Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activity in diabetic rats. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther 31:555–562
Li J, Wang P, Ying J et al (2016) Curcumin attenuates retinal vascular leakage by inhibiting calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activity in streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Cell Physiol Biochem 39:1196–1208
Lin Y-W, Liu P-S, Pook KA, Wei L-N (2018) Glyburide and retinoic acid synergize to promote wound healing by anti-inflammation and RIP140 degradation. Sci Rep 8:1–8
Lisman J, Schulman H, Cline H (2002) The molecular basis of CaMKII function in synaptic and behavioural memory. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:175–190
Lu C-H, Shen C-Y, Hsieh DJ-Y et al (2019) Deep ocean minerals inhibit IL-6 and IGFIIR hypertrophic signaling pathways to attenuate diabetes-induced hypertrophy in rat hearts. J Appl Physiol 127:356–364
Luo M, Guan X, Luczak ED et al (2013) Diabetes increases mortality after myocardial infarction by oxidizing CaMKII. J Clin Invest 123:1262–1274
Matsumura S, Kunori S, Mabuchi T et al (2010) Impairment of CaMKII activation and attenuation of neuropathic pain in mice lacking NR2B phosphorylated at Tyr1472. Eur J Neurosci 32:798–810
Michael ES, Covic L, Kuliopulos A (2019) Trace amine–associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) promotes anti-diabetic signaling in insulin-secreting cells. J Biol Chem 294:4401–4411
Monnerat G, Alarcón ML, Vasconcellos LR et al (2016) Macrophage-dependent IL-1β production induces cardiac arrhythmias in diabetic mice. Nat Commun 7:1–15
Mukwevho E, Joseph JS (2014) Calmodulin dependent protein kinase II activation by exercise regulates saturated & unsaturated fatty acids and improves some metabolic syndrome markers. Life Sci 111:53–61
Ojuka EO, Goyaram V, Smith JAH (2012) The role of CaMKII in regulating GLUT4 expression in skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Metab 303:E322–E331
Ozcan L, Tabas I (2018) A new activator of hepatocyte CaMKII in fasting and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 67:1742–1744
Ozcan L, Wong CCL, Li G et al (2012) Calcium signaling through CaMKII regulates hepatic glucose production in fasting and obesity. Cell Metab 15:739–751
Ozcan L, De Souza JC, Harari AA et al (2013) Activation of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in obesity mediates suppression of hepatic insulin signaling. Cell Metab 18:803–815
Park D-R, Park K-H, Kim B-J et al (2015) Exercise ameliorates insulin resistance via Ca2+ signals distinct from those of insulin for GLUT4 translocation in skeletal muscles. Diabetes 64:1224–1234
Perry RJ, Zhang D, Guerra MT et al (2020) Glucagon stimulates gluconeogenesis by INSP3R1-mediated hepatic lipolysis. Nature 579:279–283
Pradhan D, Dasmohapatra T, Tripathy G (2018) Pharmacognostic evaluation of curcumin on diabetic retinopathy in alloxan-induced diabetes through NF-KB and Brn3a related mechanism. Pharmacogn J 10:324–332
Roe ND, He EY, Wu Z, Ren J (2013) Folic acid reverses nitric oxide synthase uncoupling and prevents cardiac dysfunction in insulin resistance: role of Ca2+/calmodulin-activated protein kinase II. Free Radic Biol Med 65:234–243
Sawada K, Yamashita Y, Zhang T et al (2014) Glabridin induces glucose uptake via the AMP-activated protein kinase pathway in muscle cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 393:99–108
Shen Y, Guo S, Chen G et al (2019) Hyperglycemia induces osteoclastogenesis and bone destruction through the activation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Calcif Tissue Int 104:390–401
Shioda N, Fukunaga K (2018) Physiological and pathological roles of CaMKII-PP1 signaling in the brain. Int J Mol Sci 19:20
Sommese L, Valverde CA, Blanco P et al (2016) Ryanodine receptor phosphorylation by CaMKII promotes spontaneous Ca2+ release events in a rodent model of early stage diabetes: the arrhythmogenic substrate. Int J Cardiol 202:394–406
Speckmann T, Sabatini PV, Nian C et al (2016) Npas4 transcription factor expression is regulated by calcium signaling pathways and prevents tacrolimus-induced cytotoxicity in pancreatic beta cells. J Biol Chem 291:2682–2695
Sun EW, De Fontgalland D, Rabbitt P et al (2017) Mechanisms controlling glucose-induced GLP-1 secretion in human small intestine. Diabetes 66:2144–2149
Thapak P, Bishnoi M, Sharma SS (2020) Amelioration of diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 2 (TRPV2) channel inhibitor: behavioral and mechanistic study. Neurochem Int 139:104783
Verma MK, Sadasivuni MK, Yateesh AN et al (2014) Activation of GPR40 attenuates chronic inflammation induced impact on pancreatic β-cells health and function. BMC Cell Biol 15:1–12
Vieira E, Silveira LR (2014) Melatonin prevents mitochondrial dysfunction and insulin resistance in rat skeletal muscle. J Pineal Res 57:155–167
Wang H, Peng R-Y (2016) Basic roles of key molecules connected with NMDAR signaling pathway on regulating learning and memory and synaptic plasticity. Mil Med Res 3:1–7
Wang Y, Li G, Goode J et al (2012) Inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor regulates hepatic gluconeogenesis in fasting and diabetes. Nature 485:128–132
Witczak CA, Jessen N, Warro DM et al (2010) CaMKII regulates contraction-but not insulin-induced glucose uptake in mouse skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Metab 298:E1150–E1160
Wright DC, Hucker KA, Holloszy JO, Han DH (2004) Ca2+ and AMPK both mediate stimulation of glucose transport by muscle contractions. Diabetes 53:330–335
Wu X, Liang W, Guan H et al (2017) Exendin-4 promotes pancreatic β-cell proliferation via inhibiting the expression of Wnt5a. Endocrine 55:398–409
Xu Z, Huo J, Ding X et al (2017) Coenzyme Q10 improves lipid metabolism and ameliorates obesity by regulating CaMKII-mediated PDE4 inhibition. Sci Rep 7:1–12
Yang H, Gan S, Jiang Z et al (2020a) Protective effects of essential oil from Fructus Alpiniae zerumbet on retinal Müller gliosis via the PPAR-γ-p-CREB signaling pathway. Chin Med 15:4
Yang X, Zhang P, Zhang F et al (2020b) Protective effect of hypoglycemic granule against diabetes-induced liver injury by alleviating glycolipid metabolic disorder and oxidative stress. J Cell Biochem 121:3221–3234
Yang Y, He J, Yuan M et al (2020c) Xanthine oxidase inhibitor allopurinol improves atrial electrical remodeling in diabetic rats by inhibiting CaMKII/NCX signaling. Life Sci 259:118290
Zhang G, Fang H, Li Y et al (2019a) Neuroprotective effect of Astragalus polysacharin on streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats. Med Sci Monit 25:135–141
Zhang L, Chen Z, Yang S et al (2019b) Micro RNA-219 decreases hippocampal long-term potentiation inhibition and hippocampal neuronal cell apoptosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus mice by suppressing the NMDAR signaling pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther 25:69–77
Zhang X, Zhang M, Fang X et al (2019c) Mechanism of AMPK-mediated apoptosis of rat gastric smooth muscle cells under high glucose condition. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20192504
Zhang F, Ma D, Zhao W et al (2020) Obesity-induced overexpression of miR-802 impairs insulin transcription and secretion. Nat Commun 11:1–16
Zhong X, Wang Y, Wu J et al (2015) Calcium sensing receptor regulating smooth muscle cells proliferation through initiating cystathionine-gamma-lyase/hydrogen sulfide pathway in diabetic rat. Cell Physiol Biochem 35:1582–1598
Zhong Y, Jin J, Liu P et al (2020) Berberine attenuates hyperglycemia by inhibiting the hepatic glucagon pathway in diabetic mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6210526
Funding
This review is supported by Taylor’s University Flagship Research Grant—Scheme Project No. TUFR/2017/003/05.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to, wrote, read, and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benchoula, K., Mediani, A. & Hwa, W.E. The functions of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) in diabetes progression. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 17, 25–34 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-022-00680-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-022-00680-4