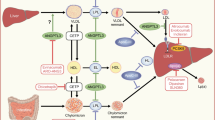
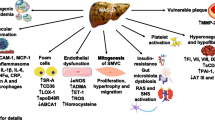
Abstract
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is one of the most common chronic liver diseases worldwide. In recent years, a new terminology and definition of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) has been proposed. Compared to the NAFLD definition, MAFLD better emphasizes the pathogenic role of metabolic dysfunction in the development and progression of this highly prevalent condition. Metabolic disorders, including overweight/obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), atherogenic dyslipidemia and hypertension, are often associated with systemic organ dysfunctions, thereby suggesting that multiple organ damage can occur in MAFLD. Substantial epidemiological evidence indicates that MAFLD is not only associated with an increased risk of liver-related complications, but also increases the risk of developing several extra-hepatic diseases, including new-onset T2DM, adverse cardiovascular and renal outcomes, and some common endocrine diseases. We have summarized the current literature on the adverse effect of MAFLD on the development of multiple extrahepatic (cardiometabolic and endocrine) complications and examined the role of different metabolic pathways and organ systems in the progression of MAFLD, thus providing new insights into the role of MAFLD as a multisystem metabolic disorder. Our narrative review aimed to provide insights into potential mechanisms underlying the known associations between MAFLD and extrahepatic diseases, as part of MAFLD as a multisystem disease, in order to help focus areas for future drug development targeting not only liver disease but also the risk of extrahepatic complications.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NAFLD:
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- MAFLD:
-
Metabolic dysfunctions associated fatty liver disease
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- HOMA:
-
Homeostasis model assessment
- NHANES:
-
National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- PPAR-α:
-
Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-alpha
- SREBP-1:
-
Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1
- MDM2:
-
Murine double minute 2
- TG-VLDL:
-
Triglyceride-very low-density lipoprotein
- apoB:
-
Apolipoprotein B
- CREBH:
-
CAMP response element-binding protein H
- SIRT3:
-
Sirtuin 3
- AdipoR2:
-
Adiponectin receptor 2
- FGF1-IGFBP2:
-
Fibroblast growth factor-insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2
- SGLT2:
-
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2
- GLP-1:
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1
- GLUT4:
-
Glucose transporter-4
- PI3K/AKT:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B
- AMPK:
-
AMP-activated protein kinase
- GPX4:
-
Glutathione peroxidase 4
- GCDCA:
-
Glycochenodeoxycholate
- TFR/ACSL4:
-
Transferrin receptor/acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family 4
- TGR5:
-
Takeda G protein-coupled receptor 5
- FXR:
-
Farnesoid X receptor
- mtDNA:
-
Mitochondrial genome
- IRX3:
-
Iroquois homeobox 3
- Grx2a:
-
Glutaredoxin 2a
- NLRP3:
-
NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing 3
- NKG2D:
-
Monokine induced by interferon-gamma natural killer cell group 2D
- CKD:
-
Chronic kidney disease
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular disease
- PSVT:
-
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia
- GGT:
-
Gamma-glutamyl transferase
- OSA:
-
Obstructive sleep apnea
- COPD:
-
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- FIB-4:
-
Fibrosis-4
- FVC:
-
Forced vital capacity
- FEV1:
-
Forced expiratory volume in 1 s
- BM:
-
Breast masses
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoprotein
- PCOS:
-
Polycystic ovary syndrome
References
Feng G, Valenti L, Wong VW, Fouad YM, Yilmaz Y, Kim W, et al. Recompensation in cirrhosis: unravelling the evolving natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;21:46–56
Wong VW, Ekstedt M, Wong GL, Hagström H. Changing epidemiology, global trends and implications for outcomes of NAFLD. J Hepatol. 2023;79:842–852
Saiman Y, Duarte-Rojo A, Rinella ME. Fatty liver disease: diagnosis and stratification. Annu Rev Med. 2022;73:529–544
Mendez-Sanchez N, Bugianesi E, Gish RG, Lammert F, Tilg H, Nguyen MH, et al. Global multi-stakeholder endorsement of the MAFLD definition. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;7:388–390
Eslam M, Newsome PN, Sarin SK, Anstee QM, Targher G, Romero-Gomez M, et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: an international expert consensus statement. J Hepatol. 2020;73:202–209
Zheng KI, Sun DQ, Jin Y, Zhu PW, Zheng MH. Clinical utility of the MAFLD definition. J Hepatol. 2021;74:989–991
Han HS, Kang G, Kim JS, Choi BH, Koo SH. Regulation of glucose metabolism from a liver-centric perspective. Exp Mol Med. 2016;48: e218
Tilg H, Adolph TE, Dudek M, Knolle P. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: the interplay between metabolism, microbes and immunity. Nat Metab. 2021;3:1596–1607
Byrne CD, Targher G. NAFLD: a multisystem disease. J Hepatol. 2015;62:S47-64
Pipitone RM, Ciccioli C, Infantino G, La Mantia C, Parisi S, Tulone A, et al. MAFLD: a multisystem disease. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2023;14:20420188221145548
Kaya E, Yilmaz Y. Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD): a multi-systemic disease beyond the liver. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2022;10:329–338
Sun DQ, Jin Y, Wang TY, Zheng KI, Rios RS, Zhang HY, et al. MAFLD and risk of CKD. Metabolism. 2021;115: 154433
Wang TY, Wang RF, Bu ZY, Targher G, Byrne CD, Sun DQ, et al. Association of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease with kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2022;18:259–268
Zhou XD, Cai J, Targher G, Byrne CD, Shapiro MD, Sung KC, et al. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and implications for cardiovascular risk and disease prevention. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022;21:270
Tanase DM, Gosav EM, Costea CF, Ciocoiu M, Lacatusu CM, Maranduca MA, et al. The intricate relationship between type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), insulin resistance (IR), and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). J Diabetes Res. 2020;2020:3920196
Jinjuvadia R, Antaki F, Lohia P, Liangpunsakul S. The association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic abnormalities in the United States population. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2017;51:160–166
Bril F, Barb D, Portillo-Sanchez P, Biernacki D, Lomonaco R, Suman A, et al. Metabolic and histological implications of intrahepatic triglyceride content in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2017;65:1132–1144
Sun DQ, Wu SJ, Liu WY, Wang LR, Chen YR, Zhang DC, et al. Association of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol within the normal range and NAFLD in the non-obese Chinese population: a cross-sectional and longitudinal study. BMJ Open. 2016;6: e013781
Heida A, Gruben N, Catrysse L, Koehorst M, Koster M, Kloosterhuis NJ, et al. The hepatocyte IKK:NF-κB axis promotes liver steatosis by stimulating de novo lipogenesis and cholesterol synthesis. Mol Metab. 2021;54: 101349
Hammoutene A, Laouirem S, Albuquerque M, Colnot N, Brzustowski A, Valla D, et al. A new NRF2 activator for the treatment of human metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. JHEP Rep. 2023;5: 100845
Teng F, Jiang J, Zhang J, Yuan Y, Li K, Zhou B, et al. The S100 calcium-binding protein A11 promotes hepatic steatosis through RAGE-mediated AKT-mTOR signaling. Metabolism. 2021;117: 154725
Gu Y, Duan S, Ding M, Zheng Q, Fan G, Li X, et al. Saikosaponin D attenuates metabolic associated fatty liver disease by coordinately tuning PPARα and INSIG/SREBP1c pathway. Phytomedicine. 2022;103: 154219
Yang B, Sun J, Liang S, Wu P, Lv R, He Y, et al. Prediction of Srebp-1 as a key target of Qing Gan San against MAFLD in rats via RNA-sequencing profile analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12: 680081
Lin H, Wang L, Liu Z, Long K, Kong M, Ye D, et al. Hepatic MDM2 causes metabolic associated fatty liver disease by blocking triglyceride-VLDL secretion via ApoB degradation. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9: e2200742
Junli Z, Shuhan W, Yajuan Z, Xiaoling D, Jiahuan L, Keshu X. The role and mechanism of CREBH regulating SIRT3 in metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Life Sci. 2022;306: 120838
Ma C, Wang Z, Xia R, Wei L, Zhang C, Zhang J, et al. Danthron ameliorates obesity and MAFLD through activating the interplay between PPARα/RXRα heterodimer and adiponectin receptor 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;137: 111344
Wang J, Zhang F, Yang W, Gao D, Yang L, Yu C, et al. FGF1 ameliorates obesity-associated hepatic steatosis by reversing IGFBP2 hypermethylation. Faseb J. 2023;37: e22881
Boutari C, Pappas PD, Anastasilakis D, Mantzoros CS. Statins’ efficacy in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Nutr. 2022;41:2195–2206
Ayada I, van Kleef LA, Zhang H, Liu K, Li P, Abozaid YJ, et al. Dissecting the multifaceted impact of statin use on fatty liver disease: a multidimensional study. EBioMedicine. 2023;87: 104392
Zhang D, Ma Y, Liu J, Wang D, Geng Z, Wen D, et al. Fenofibrate improves hepatic steatosis, insulin resistance, and shapes the gut microbiome via TFEB-autophagy in NAFLD mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023;960: 176159
Lawitz EJ, Bhandari BR, Ruane PJ, Kohli A, Harting E, Ding D, et al. Fenofibrate mitigates hypertriglyceridemia in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis patients treated with cilofexor/firsocostat. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;21:143-152.e143
Moon JS, Hong JH, Jung YJ, Ferrannini E, Nauck MA, Lim S. SGLT-2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists in metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2022;33:424–442
Mantovani A, Byrne CD, Targher G. Efficacy of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonists, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, or sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors for treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;7:367–378
Liang Y, Chen H, Liu Y, Hou X, Wei L, Bao Y, et al. Association of MAFLD with diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease: a 46-year cohort study in China. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;107:88–97
Mantovani A, Petracca G, Beatrice G, Tilg H, Byrne CD, Targher G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident diabetes mellitus: an updated meta-analysis of 501,022 adult individuals. Gut. 2021;70:962–969
Fan X, Jiao G, Pang T, Wen T, He Z, Han J, et al. Ameliorative effects of mangiferin derivative TPX on insulin resistance via PI3K/AKT and AMPK signaling pathways in human HepG2 and HL-7702 hepatocytes. Phytomedicine. 2023;114: 154740
Liu T, Li R, Sun L, Xu Z, Wang S, Zhou J, et al. Menin orchestrates hepatic glucose and fatty acid uptake via deploying the cellular translocation of SIRT1 and PPARγ. Cell Biosci. 2023;13:175
Karpale M, Kummu O, Kärkkäinen O, Lehtonen M, Näpänkangas J, Herfurth UM, et al. Pregnane X receptor activation remodels glucose metabolism to promote NAFLD development in obese mice. Mol Metab. 2023;76: 101779
Fan Y, Zhang Y, Chen C, Ying Z, Su Q, Li X, et al. Fasting serum fructose is associated with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: a prospective study. Hepatol Res. 2023;53:479–488
Lefebvre P, Cariou B, Lien F, Kuipers F, Staels B. Role of bile acids and bile acid receptors in metabolic regulation. Physiol Rev. 2009;89:147–191
Hofmann AF. Chemistry and enterohepatic circulation of bile acids. Hepatology. 1984;4:4s–14s
Liu AN, Xu CF, Liu YR, Sun DQ, Jiang L, Tang LJ, et al. Secondary bile acids improve risk prediction for non-invasive identification of mild liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2023;57:872–885
Wu W, Kaicen W, Bian X, Yang L, Ding S, Li Y, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila alleviates high-fat-diet-related metabolic-associated fatty liver disease by modulating gut microbiota and bile acids. Microb Biotechnol. 2023;16:1924–1939
Castellanos-Jankiewicz A, Guzmán-Quevedo O, Fénelon VS, Zizzari P, Quarta C, Bellocchio L, et al. Hypothalamic bile acid-TGR5 signaling protects from obesity. Cell Metab. 2021;33:1483-1492.e1410
He J, Yang Y, Zhang F, Li Y, Li X, Pu X, et al. Effects of Poria cocos extract on metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease via the FXR/PPARα-SREBPs pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1007274
Gillard J, Picalausa C, Ullmer C, Adorini L, Staels B, Tailleux A, et al. Enterohepatic takeda g-protein coupled receptor 5 agonism in metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and related glucose dysmetabolism. Nutrients. 2022;14:2707
Sun DQ, Yuan F, Fu MZ, Zhong MY, Zhang SL, Lu Y, et al. Farnesoid X receptor activation protects against renal fibrosis via modulation of β-catenin signaling. Mol Metab. 2023;79: 101841
He H, Liao S, Zeng Y, Liang L, Chen J, Tao C. Causal relationships between metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and iron status: Two-sample Mendelian randomization. Liver Int. 2022;42:2759–2768
Feng G, Byrne CD, Targher G, Wang F, Zheng MH. Ferroptosis and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: is there a link? Liver Int. 2022;42:1496–1502
Tong J, Li D, Meng H, Sun D, Lan X, Ni M, et al. Targeting a novel inducible GPX4 alternative isoform to alleviate ferroptosis and treat metabolic-associated fatty liver disease. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022;12:3650–3666
Tong J, Lan XT, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Sun DY, Wang XJ, et al. Ferroptosis inhibitor liproxstatin-1 alleviates metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in mice: potential involvement of PANoptosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023;44:1014–1028
Jiang X, Stockwell BR, Conrad M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22:266–282
Liu S, Gao Z, He W, Wu Y, Liu J, Zhang S, et al. The gut microbiota metabolite glycochenodeoxycholate activates TFR-ACSL4-mediated ferroptosis to promote the development of environmental toxin-linked MAFLD. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022;193:213–226
Członkowska A, Litwin T, Dusek P, Ferenci P, Lutsenko S, Medici V, et al. Wilson disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:21
Koizumi M, Fujii J, Suzuki K, Inoue T, Inoue T, Gutteridge JM, et al. A marked increase in free copper levels in the plasma and liver of LEC rats: an animal model for Wilson disease and liver cancer. Free Radic Res. 1998;28:441–450
Lan Y, Wu S, Wang Y, Chen S, Liao W, Zhang X, et al. Association between blood copper and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease according to sex. Clin Nutr. 2021;40:2045–2052
Lee SH, Kim MJ, Kim YS, Chun H, Won BY, Lee JH, et al. Low hair copper concentration is related to a high risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in adults. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2018;50:28–33
Ramanathan R, Ali AH, Ibdah JA. Mitochondrial dysfunction plays central role in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:7280
Fahlbusch P, Nikolic A, Hartwig S, Jacob S, Kettel U, Köllmer C, et al. Adaptation of oxidative phosphorylation machinery compensates for hepatic lipotoxicity in early stages of MAFLD. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:6873
Cioffi F, Giacco A, Petito G, de Matteis R, Senese R, Lombardi A, et al. Altered mitochondrial quality control in rats with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) induced by high-fat feeding. Genes (Basel). 2022;13:315
San J, Hu J, Pang H, Zuo W, Su N, Guo Z, et al. Taurine protects against the fatty liver hemorrhagic syndrome in laying hens through the regulation of mitochondrial homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24: 10360
Ma Y, Chen G, Yi J, Li Q, Tan Z, Fan W, et al. IRX3 plays an important role in the pathogenesis of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease by regulating hepatic lipid metabolism. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13: 895593
Scalcon V, Folda A, Lupo MG, Tonolo F, Pei N, Battisti I, et al. Mitochondrial depletion of glutaredoxin 2 induces metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in mice. Redox Biol. 2022;51: 102277
Kazankov K, Jørgensen SMD, Thomsen KL, Møller HJ, Vilstrup H, George J, et al. The role of macrophages in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16:145–159
Lu B, Wang D, Xie D, Wu C, Sun M. 20(S)-Protopanaxatriol ameliorates MAFLD by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023;940: 175468
Alharthi J, Bayoumi A, Thabet K, Pan Z, Gloss BS, Latchoumanin O, et al. A metabolic associated fatty liver disease risk variant in MBOAT7 regulates toll like receptor induced outcomes. Nat Commun. 2022;13:7430
Remmerie A, Martens L, Thoné T, Castoldi A, Seurinck R, Pavie B, et al. Osteopontin expression identifies a subset of recruited macrophages distinct from Kupffer cells in the fatty liver. Immunity. 2020;53:641-657.e614
Laursen TL, Mellemkjær A, Møller HJ, Grønbæk H, Kazankov K. Spotlight on liver macrophages for halting injury and progression in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2022;26:697–705
Li L, Xia Y, Ji X, Wang H, Zhang Z, Lu P, et al. MIG/CXCL9 exacerbates the progression of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease by disrupting Treg/Th17 balance. Exp Cell Res. 2021;407: 112801
Marinović S, Lenartić M, Mladenić K, Šestan M, Kavazović I, Benić A, et al. NKG2D-mediated detection of metabolically stressed hepatocytes by innate-like T cells is essential for initiation of NASH and fibrosis. Sci Immunol. 2023;8: eadd1599
Duell PB, Welty FK, Miller M, Chait A, Hammond G, Ahmad Z, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular risk: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2022;42:e168–e185
Mantovani A, Csermely A, Petracca G, Beatrice G, Corey KE, Simon TG, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;6:903–913
Lee H, Lee YH, Kim SU, Kim HC. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and incident cardiovascular disease risk: a nationwide cohort study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19:2138-2147.e2110
Sung KC, Yoo TK, Lee MY, Byrne CD, Zheng MH, Targher G. Comparative associations of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease with coronary artery calcification: a cross-sectional and longitudinal cohort study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2023;43:482–491
Mantovani A, Csermely A, Tilg H, Byrne CD, Targher G. Comparative effects of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease on risk of incident cardiovascular events: a meta-analysis of about 13 million individuals. Gut. 2023;72:1433–1436
Zhou XD, Targher G, Byrne CD, Somers V, Kim SU, Chahal CAA, et al. An international multidisciplinary consensus statement on MAFLD and the risk of CVD. Hepatol Int. 2023;17:773–791
Ismaiel A, Spinu M, Socaciu C, Budisan L, Leucuta DC, Popa SL, et al. Metabolic biomarkers related to cardiac dysfunction in metabolic-dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: a cross-sectional analysis. Nutr Diabetes. 2022;12:4
Lei F, Qin JJ, Song X, Liu YM, Chen MM, Sun T, et al. The prevalence of MAFLD and its association with atrial fibrillation in a nationwide health check-up population in China. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:1007171
Decoin R, Butruille L, Defrancq T, Robert J, Destrait N, Coisne A, et al. High liver fibrosis scores in metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease patients are associated with adverse atrial remodeling and atrial fibrillation recurrence following catheter ablation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13: 957245
Mantovani A, Csermely A, Taverna A, Cappelli D, Benfari G, Bonapace S, et al. Association between metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and supraventricular and ventricular tachyarrhythmias in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2023;49: 101416
Lei F, Wang XM, Wang C, Huang X, Liu YM, Qin JJ, et al. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease increased the risk of subclinical carotid atherosclerosis in China. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1109673
Mantovani A, Petracca G, Beatrice G, Csermely A, Lonardo A, Schattenberg JM, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident chronic kidney disease: an updated meta-analysis. Gut. 2022;71:156–162
Sun DQ, Ye FZ, Kani HT, Yang JR, Zheng KI, Zhang HY, et al. Higher liver stiffness scores are associated with early kidney dysfunction in patients with histologically proven non-cirrhotic NAFLD. Diabetes Metab. 2020;46:288–295
Jung CY, Koh HB, Park KH, Joo YS, Kim HW, Ahn SH, et al. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and risk of incident chronic kidney disease: a nationwide cohort study. Diabetes Metab. 2022;48: 101344
Chen S, Pang J, Huang R, Xue H, Chen X. Association of MAFLD with end-stage kidney disease: a prospective study of 337,783 UK Biobank participants. Hepatol Int. 2023;17:595–605
Sun DQ, Targher G, Byrne CD, Wheeler DC, Wong VW, Fan JG, et al. An international Delphi consensus statement on metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and risk of chronic kidney disease. HepatoBiliary Surg Nutr. 2023;12:386
Sun DQ, Wang TY, Zheng KI, Zhang HY, Wang XD, Targher G, et al. The HSD17B13 rs72613567 variant is associated with lower levels of albuminuria in patients with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2021;31:1822–1831
Sun DQ, Zheng KI, Xu G, Ma HL, Zhang HY, Pan XY, et al. PNPLA3 rs738409 is associated with renal glomerular and tubular injury in NAFLD patients with persistently normal ALT levels. Liver Int. 2020;40:107–119
Zelniker TA, Wiviott SD, Raz I, Im K, Goodrich EL, Furtado RHM, et al. Comparison of the effects of glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for prevention of major adverse cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 2019;139:2022–2031
Liao Y, Wang L, Liu F, Zhou Y, Lin X, Zhao Z, et al. Emerging trends and hotspots in metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) research from 2012 to 2021: a bibliometric analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1078149
Yang K, Song M. New insights into the pathogenesis of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD): gut-liver-heart crosstalk. Nutrients. 2023;15:3970
Zhang Y, Yan S, Sheng S, Qin Q, Chen J, Li W, et al. Comparison of gut microbiota in male MAFLD patients with varying liver stiffness. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022;12: 873048
Zeybel M, Arif M, Li X, Altay O, Yang H, Shi M, et al. Multiomics analysis reveals the impact of microbiota on host metabolism in hepatic steatosis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9: e2104373
Tan J, Hu R, Gong J, Fang C, Li Y, Liu M, et al. Protection against metabolic associated fatty liver disease by protocatechuic acid. Gut Microbes. 2023;15:2238959
Fukunaga S, Nakano D, Tsutsumi T, Kawaguchi T, Eslam M, Yoshinaga S, et al. Lean/normal-weight metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease is a risk factor for reflux esophagitis. Hepatol Res. 2022;52:699–711
Váncsa S, Sipos Z, Váradi A, Nagy R, Ocskay K, Juhász FM, et al. Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease is associated with acute pancreatitis with more severe course: post hoc analysis of a prospectively collected international registry. United Eur Gastroenterol J. 2023;11:371–382
Yilmaz Y, Yilmaz N, Ates F, Karakaya F, Gokcan H, Kaya E, et al. The prevalence of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease in the Turkish population: a multicenter study. Hepatol Forum. 2021;2:37–42
Rodriguez-Duque JC, Calleja JL, Iruzubieta P, Hernández-Conde M, Rivas-Rivas C, Vera MI, et al. Increased risk of MAFLD and liver fibrosis in inflammatory bowel disease independent of classic metabolic risk factors. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;21:406-414.e407
Chen J, Dan L, Tu X, Sun Y, Deng M, Chen X, et al. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and liver function markers are associated with Crohn’s disease but not Ulcerative Colitis: a prospective cohort study. Hepatol Int. 2023;17:202–214
Seo JY, Cho EJ, Kim MJ, Kwak MS, Yang JI, Chung SJ, et al. The relationship between metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and low muscle mass in an asymptomatic Korean population. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13:2953–2960
Chun HS, Kim MN, Lee JS, Lee HW, Kim BK, Park JY, et al. Risk stratification using sarcopenia status among subjects with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021;12:1168–1178
Nachit M, Lanthier N, Rodriguez J, Neyrinck AM, Cani PD, Bindels LB, et al. A dynamic association between myosteatosis and liver stiffness: results from a prospective interventional study in obese patients. JHEP Rep. 2021;3: 100323
Han AL. Association between metabolic associated fatty liver disease and osteoarthritis using data from the Korean national health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES). Inflammopharmacology. 2021;29:1111–1118
Yilmaz P, Alferink LJM, Cremers LGM, Murad SD, Niessen WJ, Ikram MA, et al. Subclinical liver traits are associated with structural and hemodynamic brain imaging markers. Liver Int. 2023;43:1256–1268
Nucera S, Ruga S, Cardamone A, Coppoletta AR, Guarnieri L, Zito MC, et al. MAFLD progression contributes to altered thalamus metabolism and brain structure. Sci Rep. 2022;12:1207
Airaghi L, Rango M, Maira D, Barbieri V, Valenti L, Lombardi R, et al. Subclinical cerebrovascular disease in NAFLD without overt risk factors for atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2018;268:27–31
Hu J, Xu Y, He Z, Zhang H, Lian X, Zhu T, et al. Increased risk of cerebrovascular accident related to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2018;9:2752–2760
Kim D, Dennis BB, Cholankeril G, Ahmed A. Association between depression and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease/significant fibrosis. J Affect Disord. 2023;329:184–191
Yu Q, He R, Jiang H, Wu J, Xi Z, He K, et al. Association between metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and cognitive impairment. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2022;10:1034–1041
Shang Y, Widman L, Hagström H. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of dementia: a population-based cohort study. Neurology. 2022;99:e574–e582
Kim GA, Oh CH, Kim JW, Jeong SJ, Oh IH, Lee JS, et al. Association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and the risk of dementia: a nationwide cohort study. Liver Int. 2022;42:1027–1036
Basu E, Mehta M, Zhang C, Zhao C, Rosenblatt R, Tapper EB, et al. Association of chronic liver disease with cognition and brain volumes in two randomized controlled trial populations. J Neurol Sci. 2022;434: 120117
Tuttolomondo A, Petta S, Casuccio A, Maida C, Corte VD, Daidone M, et al. Reactive hyperemia index (RHI) and cognitive performance indexes are associated with histologic markers of liver disease in subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a case control study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018;17:28
Wang L, Sang B, Zheng Z. Risk of dementia or cognitive impairment in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14: 985109
Xiao T, van Kleef LA, Ikram MK, de Knegt RJ, Ikram MA. Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and fibrosis with incident dementia and cognition: the Rotterdam study. Neurology. 2022;99:e565–e573
Lonardo A, Mantovani A, Lugari S, Targher G. NAFLD in some common endocrine diseases: prevalence, pathophysiology, and principles of diagnosis and management. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:2841
Targher G, Rossini M, Lonardo A. Evidence that non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and polycystic ovary syndrome are associated by necessity rather than chance: a novel hepato-ovarian axis? Endocrine. 2016;51:211–221
Mantovani A, Nascimbeni F, Lonardo A, Zoppini G, Bonora E, Mantzoros CS, et al. Association between primary hypothyroidism and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Thyroid. 2018;28:1270–1284
Liu D, Gao X, Pan XF, Zhou T, Zhu C, Li F, et al. The hepato-ovarian axis: genetic evidence for a causal association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and polycystic ovary syndrome. BMC Med. 2023;21:62
Zeng X, Li B, Zou Y. The relationship between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hypothyroidism: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100: e25738
Chen YL, Tian S, Wu J, Li H, Li S, Xu Z, et al. Impact of thyroid function on the prevalence and mortality of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023;108:e434–e443
Hu Y, Zhou F, Lei F, Lin L, Huang X, Sun T, et al. The nonlinear relationship between thyroid function parameters and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1115354
Fan H, Li L, Liu Z, Cao L, Chen X, Suo C, et al. The association between thyroid hormones and MAFLD is mediated by obesity and metabolic disorders and varies among MAFLD subtypes. Dig Liver Dis. 2023;55:785–790
Zhang X, Li R, Chen Y, Dai Y, Chen L, Qin L, et al. The role of thyroid hormones and autoantibodies in metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease: TgAb may be a potential protective factor. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11: 598836
Byrne CD, Targher G, Tilg H. Thyroid hormone receptor-beta agonists: new MASLD therapies on the horizon. Gut. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330596
Sharma P, Kumar A. Metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease increases risk of severe COVID-19. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020;14:825–827
Marjot T, Moon AM, Cook JA, Abd-Elsalam S, Aloman C, Armstrong MJ, et al. Outcomes following SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with chronic liver disease: an international registry study. J Hepatol. 2021;74:567–577
Zhou YJ, Zheng KI, Wang XB, Sun QF, Pan KH, Wang TY, et al. Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease is associated with severity of COVID-19. Liver Int. 2020;40:2160–2163
Pan L, Huang P, Xie X, Xu J, Guo D, Jiang Y. Metabolic associated fatty liver disease increases the severity of COVID-19: a meta-analysis. Dig Liver Dis. 2021;53:153–157
Targher G, Mantovani A, Byrne CD, Wang XB, Yan HD, Sun QF, et al. Risk of severe illness from COVID-19 in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and increased fibrosis scores. Gut. 2020;69:1545–1547
Mantovani A, Lonardo A, Vinco G, Zoppini G, Lippi G, Bonora E, et al. Association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and decreased lung function in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. 2019;45:536–544
Tsutsumi T, Nakano D, Kawaguchi M, Hashida R, Yoshinaga S, Takahashi H, et al. MAFLD associated with COPD via systemic inflammation independent of aging and smoking in men. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2022;14:115
Huang J, Chen L, Li X, Chen M, Lin T, Chen G. Association between metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and obstructive sleep apnea: a cross-sectional study. Nat Sci Sleep. 2023;15:49–57
Miao L, Yang L, Guo LS, Shi QQ, Zhou TF, Chen Y, et al. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease is associated with greater impairment of lung function than nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2022;10:230–237
Ruan Z, Lu T, Chen Y, Yuan M, Yu H, Liu R, et al. Association between psoriasis and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease among outpatient US adults. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:745–753
Bellinato F, Gisondi P, Mantovani A, Girolomoni G, Targher G. Risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with chronic plaque psoriasis: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J Endocrinol Invest. 2022;45:1277–1288
Näslund-Koch C, Bojesen SE, Gluud LL, Skov L, Vedel-Krogh S. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is not a causal risk factor for psoriasis: a Mendelian randomization study of 108,835 individuals. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1022460
Heitmann J, Frings VG, Geier A, Goebeler M, Kerstan A. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and psoriasis - is there a shared proinflammatory network? J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2021;19:517–528
Gau SY, Hsiao YP, Liao WC, Ma KS, Wu MC. Risk of liver dysfunction and non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases in people with hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review and meta-analysis of real-world evidences. Front Immunol. 2022;13: 959691
González-Villanueva I, DeGracia C, Planells M, Poveda I, Álvarez P, Schneller-Pavalescu L, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a cross-sectional study. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100: a00239
Durán-Vian C, Arias-Loste MT, Hernández JL, Fernández V, González M, Iruzubieta P, et al. High prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among hidradenitis suppurativa patients independent of classic metabolic risk factors. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:2131–2136
Lee SM, Cho GJ, Wi WY, Norwitz ER, Koo BK, Lee J, et al. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease as a risk factor for adverse outcomes in subsequent pregnancy: a nationwide cohort study. Hepatol Int. 2023;17:367–376
Lee SM, Jung YM, Choi ES, Kwak SH, Koo JN, Oh IH, et al. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and subsequent development of adverse pregnancy outcomes. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20:2542-2550.e2548
Chai TY, Deng D, Byth K, George J, Pasupathy D, Cheung NW. The prevalence of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and its association on adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;191: 110038
Li S, Xu Z, Li H, Tang J, Liang XY, Tian S, et al. An observational and cross-sectional study of the prevalence of breast lesions and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and their relationship in China. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2022;31:31–39
Giannouli A, Efthymiou V, Konidari M, Mani I, Aravantinos L, Dourakis SP, et al. The burden of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adolescents with polycystic ovary syndrome: a case-control study. J Clin Med. 2023;12:557
Hong X, Guo Z, Yu Q. Hepatic steatosis in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. BMC Endocr Disord. 2023;23:207
Faggion CM Jr, Bakas NP, Wasiak J. A survey of prevalence of narrative and systematic reviews in five major medical journals. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2017;17:176
Funding
This work is supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82370577, 82070588, 82000690), National Key R&D Program of China (2023YFA1800801) and supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2023M732681). Jing Zhao is supported in part by grants from Youth Research Project Fund from Wuxi Municipal Health Commission (Q202212). Dan-Qin Sun is supported in part by grants from Top Talent Support Program for young and middle-aged people of Wuxi Health Committee and scientific technological innovation and venture capital fund in Wuxi (BJ2023023), scientific technological innovation and venture capital fund in Wuxi (Y20232011). GT is supported in part by grants from the School of Medicine, University of Verona, Italy. CDB is supported in part by the Southampton NIHR Biomedical Research Centre (NIHR 203319), UK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MHZ, DQS and JZ researched data for the article. JZ wrote the manuscript. LL and YYC drew the schematic map for the manuscript. XG, GT and CDB conducted critical revision and writing of the manuscript. All authors reviewed and commented on the manuscript and approved the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors (Jing Zhao, Lu Liu, Ying-Ying Cao, Xin Gao, Giovanni Targher, Christopher D. Byrne, Dan-Qin Sun, Ming-Hua Zheng) have confirmed that there are no conflicts of interest.
Data availiability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, J., Liu, L., Cao, YY. et al. MAFLD as part of systemic metabolic dysregulation. Hepatol Int (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-024-10660-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-024-10660-y