Abstract
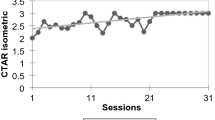
Introduction: Effortful swallow with progressive resistance has a potential clinical implication in improving the oro-muscular strength, swallow safety, and efficiency in elderly individuals. But to date, no studies have explored its benefits in training individuals with post-stroke dysphagia. Aim: The present study investigated the long- term effect of effortful swallow with progressive resistance on swallow safety, efficiency and quality of life in persons with dysphagia following stroke. Method: The study consisted of 5 males (mean age: 41.80yrs ± 9.6yrs) diagnosed with dysphagia post-stroke. The participants underwent 20 sessions (5 days/week) of intensive effortful swallow with progressive training spread across four weeks. In the first two weeks, the participants performed 10 × 3 sets of effortful swallows with a 50% of resistance load, which was further increased to 15 × 3 sets with a 70% resistance load. Results: DIGEST-FEES safety and overall swallow quality of life significantly improved post-therapy, whereas DIGEST-FEES efficiency and overall swallow grades showed no significant changes. Inter-rater reliability of DIGEST-FEES revealed substantial agreement between judges. Conclusion: The results are promising as the technique improved swallow safety, and swallow quality of life in persons with dysphagia following stroke.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in the article. Further enquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
References
Rofes L, Arreola V, Almirall J, Cabré M, Campins L, García-Peris P et al (2011) Diagnosis and management of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia and its nutritional and respiratory complications in the Elderly. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 1–13
Abdel Jalil AA, Katzka DA, Castell DO (2015) Approach to the Patient with Dysphagia. Am J Med. Oct 1;128(10)
Broniatowski M, Sonies BC, Rubin JS, Bradshaw CR, Spiegel JR, Bastian RW et al (1999 Apr) Current evaluation and treatment of patients with swallowing Disorders. Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery 17(4):464–473
González-Fernández M, Ottenstein L, Atanelov L, Christian AB (2013 Sep) Dysphagia after stroke: an overview. Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep 3(3):187–196
Crary M, Dysphagia GM (2016) : Clinical Management in Adults and Children. In: Dysphagia. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Altman KW (2012) Stepping Stones to Living Well with Dysphagia. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 72. Nestec Ltd., Vevey/S. Karger AG
Molfenter SM, Hsu CY, Lu Y, Lazarus CL Alterations to swallowing physiology as the result of Effortful swallowing in healthy seniors. Dysphagia. 2018 Jun 17;33(3):380–8
Nekl CG, Lintzenich CR, Leng X, Lever T, Butler SG (2012 Mar) Effects of effortful swallow on esophageal function in healthy adults. Neurogastroentereology & Motility 24(3):252–e108
Park H, Oh D, Yoon T, Park J Effect of effortful swallowing training on tongue strength and oropharyngeal swallowing function in stroke patients with dysphagia: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2019 May 28;54(3):479–84
Oh JC Effects of Effortful Swallowing Exercise with Progressive Anterior Tongue Press using Iowa oral performance instrument (IOPI) on the strength of swallowing-related muscles in the Elderly: a preliminary study.Dysphagia. 2021 Feb 10; 37(1):158–67
Trapl M, Enderle P, Nowotny M, Teuschl Y, Matz K, Dachenhausen A et al (2007 Nov) Dysphagia Bedside Screening for Acute-Stroke Patients. Stroke 38(11):2948–2952
Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bédirian V, Charbonneau S, Whitehead V, Collin I et al (1995) The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A Brief Screening Tool for Mild Cognitive Impairment.
Chengappa & Kumar (2008) Normative & Clinical Data on the Kannada Version of Western Aphasia Battery (WAB-K). Language in India. 2008;8(6)
Basavaraj V, Venkatesan S (2009) Ethical guidelines for Bio-Behavioural Research Involving human subjects. All India Institute of Speech and Hearing, Mysuru
Langmore SE (1998 Dec) State of the Science. Perspectives on swallowing and swallowing Disorders. Dysphagia 7(4):8–10
Rosenbek JC, Robbins JA, Roecker EB, Coyle JL, Wood JL (1996) A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia 11(2):93–98
Starmer HM, Arrese L, Langmore S, Ma Y, Murray J, Patterson J et al (2021) Adaptation and validation of the dynamic imaging Grade of swallowing toxicity for flexible endoscopic evaluation of swallowing: DIGEST-FEES. Journal of Speech, Language, and hearing Research. 4(6):1802–1810
McHorney CA, Martin-Harris B, Robbins J, Rosenbek J Clinical validity of the SWAL-QOL and SWAL-CARE outcome tools with respect to Bolus Flow Measures.Dysphagia. 2006 Jul 17;21(3):141–8
Bülow M, Olsson R, Ekberg O (1999 Spring) Videomanometric analysis of Supraglottic Swallow, Effortful Swallow, and Chin Tuck in healthy volunteers. Dysphagia 14(2):67–72
Oh JC Effects of Tongue Strength Training and Detraining on Tongue Pressures in healthy adults. Dysphagia. 2015 Jun 17;30(3):315–20
Robbins J, Kays SA, Gangnon RE, Hind JA, Hewitt AL, Gentry LR et al The Effects of Lingual Exercise in Stroke patients with Dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2007 Feb 1; 88(2):150–8
Steele CM, Bailey GL, Polacco REC, Hori SF, Molfenter SM, Oshalla M et al (2013) Outcomes of tongue-pressure strength and accuracy training for dysphagia following acquired brain injury. Int J Speech Lang Pathol. Oct 22;15(5):492–502
Kim HD, Choi JB, Yoo SJ, Chang MY, Lee SW, Park JS Tongue-to-palate resistance training improves tongue strength and oropharyngeal swallowing function in subacute stroke survivors with dysphagia.J Oral Rehabil. 2017 Jan 1; 44(1):59–64
Ayres A, Jotz G, Rieder C, Schuh A, Olchik M (2016 Apr) The impact of Dysphagia Therapy on Quality of Life in patients with Parkinson’s Disease as measured by the swallowing quality of Life Questionnaire (SWALQOL). Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 19(03):202–206
Zhang M, Tao T, Zhang ZB, Zhu X, Fan WG, Pu LJ et al (2016) Effectiveness of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on Patients with Dysphagia with Medullary Infarction. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. Mar 1;97(3):355–62
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. M. Pushpavathi, Director, AIISH for granting permission to carry out the study and providing the necessary resources and infrastructure. We would also like to thank the University of Mysuru (UOM) for the constant support. The authors also thank the participants of the current study.
Funding
There are no funding sources to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BC and SN: conceptualizing and designing of the research study, seeking ethical approval, drafting the manuscript in whole or in part. BC and PTK: data collection; BC: analyzing the data: All the authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Statement of Ethics
Participant/guardians had given their written informed consent. The ethical clearance according to the Declaration of Helsinki was obtained from the Institutional Review Board, AIISH Ethics committee (AEC), Approval number: No.DOR.9.1/Ph. D/BC/920/2021–2022 dt 10th February, 2023.
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chandrashekaraiah, B., N, S. & K, P.T. Impact of Effortful Swallow with Progressive Resistance on Swallow Safety, Efficiency and Quality of Life in Individuals with Post-Stroke Dysphagia: Analysis Using DIGEST- FEES and SWAL-QOL. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 75, 2836–2841 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03846-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03846-7