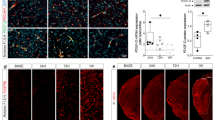
Abstract
miR-212-5p has been reported to be involved in many biological processes. However, the role of miR-212-5p in ischemic stroke remains unclear. This study explored the biological role and potential mechanism of miR-212-5p in ischemic stroke by investigating the lncfos/miR-212-5p/CASP7 axis. A total of 32 patients with ischemic stroke and 32 age- and sex-matched healthy controls (HCs) were enrolled in this study. In addition, 336 rats were used in this study. The rats were subjected to middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and intracerebroventricular injection of a microRNA (miRNA) agomir, a miRNA antagomir, a short hairpin RNA (shRNA) lentiviral vector, or a negative control. The neurological deficit score was calculated; the infarct volume was measured; histopathological assays were performed; the neuronal apoptosis rate was determined; and the lncfos, miR-212-5p, and CASP7 expression levels in the peri-infarct area were assessed. In this study, we found that the expression level of miR-212-5p was significantly downregulated in the peri-infarct area and blood of the MCAO model rats and the blood of patients with ischemic stroke. A double-luciferase experiment showed that CASP7 was a direct target gene of miR-212-5p and that miR-212-5p was a target miRNA of lncfos. Lateral ventricular injection of the miR-212-5p agomir effectively inhibited the apoptosis induced by ischemic brain damage, reduced the infarct volume, attenuated the neurological deficit symptoms, and downregulated the expression of CASP7 in the peri-infarct area of the MCAO model rats. Suppressing lncfos with sh-fos led to the upregulated expression of miR-212-5p and played a neuroprotective role in the rat MCAO models. We concluded that miR-212-5p plays a neuroprotective role in ischemic stroke and that its function is regulated by the lncfos/miR-212-5p/CASP7 axis. Moreover, miR-212-5p may be a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for ischemic stroke.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Change history
23 February 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03284-0
References
Chen Y, Wright N, Guo Y, Turnbull I, Kartsonaki C, Yang L et al (2020) Mortality and recurrent vascular events after first incident stroke: a 9-year community-based study of 0.5 million Chinese adults. Lancet Glob Health 8:e580–e590. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30069-3
Feigin VL, Krishnamurthi RV, Parmar P, Norrving B, Mensah GA, Bennett DA et al (2015) Update on the global burden of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke in 1990–2013: the GBD 2013 Study. Neuroepidemiology 45:161–176. https://doi.org/10.1159/000441085
Collaborators, GBDCoD (2017) Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 390:1151–1210. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32152-9
National Institute of Neurological, D & Stroke rt, PASSG (1995) Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 333:1581–1587. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199512143332401
Kaito M, Araya S, Gondo Y, Fujita M, Minato N, Nakanishi M et al (2013) Relevance of distinct monocyte subsets to clinical course of ischemic stroke patients. PLoS One 8:e69409. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0069409
Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, Brozman M, Davalos A, Guidetti D et al (2008) Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 359:1317–1329. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0804656
Juttler E, Kohrmann M, Schellinger PD (2006) Therapy for early reperfusion after stroke. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 3:656–663. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpcardio0721
Wang J, Han B, Zhao X, Sun Y, Liu Y, Hu F et al (2021) MicroRNA-532–5p upregulation protects neurological deficits after ischemic stroke through inhibition of BTB and CNC homology 1. Int Immunopharmacol 100:108003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108003
Rink C, Khanna S (2011) MicroRNA in ischemic stroke etiology and pathology. Physiol Genomics 43:521–528. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00158.2010
Ghafouri-Fard S, Shoorei H, Taheri M (2020) Non-coding RNAs participate in the ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biomed Pharmacother 129:110419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110419
Zhao F, Xing Y, Jiang P, Hu L, Deng S (2021) LncRNA MEG3 inhibits the proliferation of neural stem cells after ischemic stroke via the miR-493-5P/MIF axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 568:186–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.06.033
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00045-5
Kalani MYS, Alsop E, Meechoovet B, Beecroft T, Agrawal K, Whitsett TG et al (2020) Extracellular microRNAs in blood differentiate between ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke subtypes. J Extracell Vesicles 9:1713540. https://doi.org/10.1080/20013078.2020.1713540
Sorensen SS, Nygaard AB, Nielsen MY, Jensen K, Christensen T (2014) miRNA expression profiles in cerebrospinal fluid and blood of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Transl Stroke Res 5:711–718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-014-0364-8
Dewdney B, Trollope A, Moxon J, Thomas Manapurathe D, Biros E, Golledge J (2018) Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 27:522–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.09.058
Xie K, Cai Y, Yang P, Du F, Wu K (2020) Upregulating microRNA-874-3p inhibits CXCL12 expression to promote angiogenesis and suppress inflammatory response in ischemic stroke. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 319:C579–C588. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00001.2020
Zhang H, Chen G, Qiu W, Pan Q, Chen Y, Chen Y et al (2020) Plasma endothelial microvesicles and their carrying miRNA-155 serve as biomarkers for ischemic stroke. J Neurosci Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.24696
Liu X, Li F, Zhao S, Luo Y, Kang J, Zhao H et al (2013) MicroRNA-124-mediated regulation of inhibitory member of apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53 family in experimental stroke. Stroke 44:1973–1980. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.000613
Yang ZB, Zhang Z, Li TB, Lou Z, Li SY, Yang H et al (2014) Up-regulation of brain-enriched miR-107 promotes excitatory neurotoxicity through down-regulation of glutamate transporter-1 expression following ischaemic stroke. Clin Sci (Lond) 127:679–689. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20140084
Rom S, Dykstra H, Zuluaga-Ramirez V, Reichenbach NL, Persidsky Y (2015) miR-98 and let-7 g* protect the blood-brain barrier under neuroinflammatory conditions. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 35:1957–1965. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2015.154
Sun S, Han X, Li X, Song Q, Lu M, Jia M et al (2018) MicroRNA-212-5p prevents dopaminergic neuron death by inhibiting SIRT2 in MPTP-induced mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Front Mol Neurosci 11:381. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2018.00381
Gupta SK, Garg A, Avramopoulos P, Engelhardt S, Streckfuss-Bomeke K, Batkai S et al (2019) miR-212/132 cluster modulation prevents doxorubicin-mediated atrophy and cardiotoxicity. Mol Ther 27:17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.11.004
McIlwain DR, Berger T, Mak TW (2013) Caspase functions in cell death and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5:a008656. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a008656
Twiddy D, Cohen GM, Macfarlane M, Cain K (2006) Caspase-7 is directly activated by the approximately 700-kDa apoptosome complex and is released as a stable XIAP-caspase-7 approximately 200-kDa complex. J Biol Chem 281:3876–3888. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M507393200
Wang Y, Jasper H, Toan S, Muid D, Chang X, Zhou H (2021) Mitophagy coordinates the mitochondrial unfolded protein response to attenuate inflammation-mediated myocardial injury. Redox Biol 45:102049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2021.102049
Chang X, Lochner A, Wang HH, Wang S, Zhu H, Ren J et al (2021) Coronary microvascular injury in myocardial infarction: perception and knowledge for mitochondrial quality control. Theranostics 11:6766–6785. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.60143
Zhou H, Ren J, Toan S, Mui D (2021) Role of mitochondrial quality surveillance in myocardial infarction: from bench to bedside. Ageing Res Rev 66:101250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2020.101250
Vahidinia Z, Karimian M, Joghataei MT (2020) Neurosteroids and their receptors in ischemic stroke: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Pharmacol Res 160:105163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105163
Jurcau A, Ardelean IA (2021) Molecular pathophysiological mechanisms of ischemia/reperfusion injuries after recanalization therapy for acute ischemic stroke. J Integr Neurosci 20:727–744. https://doi.org/10.31083/j.jin2003078
Wang Z, Zhou Z, Wei X, Wang M, Wang BO, Zhang Y et al (2017) Therapeutic potential of novel twin compounds containing tetramethylpyrazine and carnitine substructures in experimental ischemic stroke. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:7191856. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7191856
Nicholson DW, Thornberry NA (1997) Caspases: killer proteases. Trends Biochem Sci 22:299–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0968-0004(97)01085-2
Creagh EM, Conroy H, Martin SJ (2003) Caspase-activation pathways in apoptosis and immunity. Immunol Rev 193:10–21. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-065x.2003.00048.x
Lamkanfi M, Kanneganti TD (2010) Caspase-7: a protease involved in apoptosis and inflammation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42:21–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2009.09.013
Luo R, Xiao F, Wang P, Hu YX (2020) lncRNA H19 sponging miR-93 to regulate inflammation in retinal epithelial cells under hyperglycemia via XBP1s. Inflamm Res 69:255–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-019-01312-1
Xu Y, Niu Y, Li H, Pan G (2020) Downregulation of lncRNA TUG1 attenuates inflammation and apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cell induced by ischemia-reperfusion by sponging miR-449b-5p via targeting HMGB1 and MMP2. Inflammation 43:1362–1374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01214-z
Wang CJ, Zhu CC, Xu J, Wang M, Zhao WY, Liu Q et al (2019) The lncRNA UCA1 promotes proliferation, migration, immune escape and inhibits apoptosis in gastric cancer by sponging anti-tumor miRNAs. Mol Cancer 18:115. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1032-0
Zhang L, Wang Y, Zhang L, Xia X, Chao Y, He R et al (2019) ZBTB7A, a miR-663a target gene, protects osteosarcoma from endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis by suppressing LncRNA GAS5 expression. Cancer Lett 448:105–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2019.01.046
Qi X, Hu M, Xiang Y, Wang D, Xu Y, Hou Y et al (2020) LncRNAs are regulated by chromatin states and affect the skeletal muscle cell differentiation. Cell Prolif e12879. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12879
Sui S, Sun L, Zhang W, Li J, Han J, Zheng J et al (2020) LncRNA MEG8 attenuates cerebral ischemia after ischemic stroke through targeting miR-130a-5p/VEGFA signaling. Cell Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00904-4
Wu Z, Wu P, Zuo X, Yu N, Qin Y, Xu Q et al (2017) LncRNA-N1LR enhances neuroprotection against ischemic stroke probably by inhibiting p53 phosphorylation. Mol Neurobiol 54:7670–7685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0246-z
Wang Y, Luo Y, Yao Y, Ji Y, Feng L, Du F et al (2020) Silencing the lncRNA Maclpil in pro-inflammatory macrophages attenuates acute experimental ischemic stroke via LCP1 in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 40:747–759. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X19836118
Xu X, Jiang R, Gong P, Liu Q, Chen Y, Hou S et al (2018) Up-regulation of FOS-like antigen 1 contributes to neuronal apoptosis in the cortex of rat following traumatic brain injury. Metab Brain Dis 33:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0129-7
Lu J, Moochhala S, Kaur C, Ling E (2000) Changes in apoptosis-related protein (p53, Bax, Bcl-2 and Fos) expression with DNA fragmentation in the central nervous system in rats after closed head injury. Neurosci Lett 290:89–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3940(00)01307-0
Thangaleela S, Shanmugapriya V, Mukilan M, Radhakrishnan K, Rajan KE (2018) Alterations in microRNA-132/212 expression impairs fear memory in goldfish Carassius auratus. Ann Neurosci 25:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1159/000486842
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.20.1.84
Chen J, Sanberg PR, Li Y, Wang L, Lu M, Willing AE et al (2001) Intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood reduces behavioral deficits after stroke in rats. Stroke 32:2682–2688. https://doi.org/10.1161/hs1101.098367
Slee EA, Harte MT, Kluck RM, Wolf BB, Casiano CA, Newmeyer DD et al (1999) Ordering the cytochrome c-initiated caspase cascade: hierarchical activation of caspases-2, -3, -6, -7, -8, and -10 in a caspase-9-dependent manner. J Cell Biol 144:281–292. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.144.2.281
Qi Z, Dong W, Shi W, Wang R, Zhang C, Zhao Y et al (2015) Bcl-2 phosphorylation triggers autophagy switch and reduces mitochondrial damage in limb remote ischemic conditioned rats after ischemic stroke. Transl Stroke Res 6:198–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-015-0393-y
An H, Zhou B, Ji X (2021) Mitochondrial quality control in acute ischemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 41:3157–3170. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X211046992
Wang J, Zhou H (2020) Mitochondrial quality control mechanisms as molecular targets in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury. Acta Pharm Sin B 10:1866–1879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2020.03.004
Wang J, Toan S, Zhou H (2020) New insights into the role of mitochondria in cardiac microvascular ischemia/reperfusion injury. Angiogenesis 23:299–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-020-09720-2
Shah MA, Kang JB, Park DJ, Kim MO, Koh PO (2021) Chlorogenic acid alleviates neurobehavioral disorders and brain damage in focal ischemia animal models. Neurosci Lett 760:136085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2021.136085
Zhu XY, Xia B, Ye T, Dai MZ, Yang H, Li CQ et al (2020) Ponatinib-induced ischemic stroke in larval zebrafish for drug screening. Eur J Pharmacol 889:173292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173292
Dojo Soeandy C, Elia AJ, Cao Y, Rodgers C, Huang S, Elia AC et al (2021) Necroptotic-apoptotic eegulation in an endothelin-1 model of cerebral ischemia. Cell Mol Neurobiol 41:1727–1742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00942-y
Yang B, Harris KP, Jain S, Nicholson ML (2007) Caspase-7, Fas and FasL in long-term renal ischaemia/reperfusion and immunosuppressive injuries in rats. Am J Nephrol 27:397–408. https://doi.org/10.1159/000104741
Xia GN, Zou Y, Wang YC, Xia QJ, Lu BT, Wang TH et al (2013) Neural stem cells grafts decrease neural apoptosis associated with caspase-7 downregulation and BDNF upregulation in rats following spinal cord hemisection. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33:1013–1022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9969-9
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, Pandolfi PP (2011) A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 146:353–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.014
Cesana M, Cacchiarelli D, Legnini I, Santini T, Sthandier O, Chinappi M et al (2011) A long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell 147:358–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.028
Thomson DW, Dinger ME (2016) Endogenous microRNA sponges: evidence and controversy. Nat Rev Genet 17:272–283. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2016.20
Yu C, Li L, Xie F, Guo S, Liu F, Dong N et al (2018) LncRNA TUG1 sponges miR-204-5p to promote osteoblast differentiation through upregulating Runx2 in aortic valve calcification. Cardiovasc Res 114:168–179. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvx180
Zheng ZQ, Li ZX, Zhou GQ, Lin L, Zhang LL, Lv JW et al (2019) Long noncoding RNA FAM225A promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumorigenesis and metastasis by acting as ceRNA to sponge miR-590-3p/miR-1275 and upregulate ITGB3. Cancer Res 79:4612–4626. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-0799
Liang J, Wang Q, Li JQ, Guo T, Yu D (2020) Long non-coding RNA MEG3 promotes cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through increasing pyroptosis by targeting miR-485/AIM2 axis. Exp Neurol 325:113139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.113139
Bao MH, Szeto V, Yang BB, Zhu SZ, Sun HS, Feng ZP (2018) Long non-coding RNAs in ischemic stroke. Cell Death Dis 9:281. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0282-x
Chen Y, Liu W, Chen M, Sun Q, Chen H, Li Y (2021) Up-regulating lncRNA OIP5-AS1 protects neuron injury against cerebral hypoxia-ischemia induced inflammation and oxidative stress in microglia/macrophage through activating CTRP3 via sponging miR-186–5p. Int Immunopharmacol 92:107339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107339
Wei R, Zhang L, Hu W, Wu J, Zhang W (2019) Long non-coding RNA AK038897 aggravates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via acting as a ceRNA for miR-26a-5p to target DAPK1. Exp Neurol 314:100–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.01.009
Xiang Y, Zhang Y, Xia Y, Zhao H, Liu A, Chen Y (2020) LncRNA MEG3 targeting miR-424–5p via MAPK signaling pathway mediates neuronal apoptosis in ischemic stroke. Aging (Albany NY) 12:3156–3174. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102790
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the patients and their family members for their participation.
Funding
The present study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFC1307500, 2017YFC1307503) and by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81160168, 81460321, and 81660354).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL-L and SH-L designed the study. SH-L, XQ, ZX-Q, and JG-G performed the experiments. SH-L, JL-L, and JP-L analyzed the results together. SH-L wrote the article. All authors have approved the final submitted manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University (NO.2018-KY-E-063) and the Animal Care and Use Committee of Guangxi Medical University (No. 201801070).
Consent to Participate
All participants included in this study provided written informed consent.
Consent for Publication
This is not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Qu, X., Qin, Z. et al. lncfos/miR-212-5p/CASP7 Axis-Regulated miR-212-5p Protects the Brain Against Ischemic Damage. Mol Neurobiol 60, 2767–2785 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03216-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03216-y