Abstract
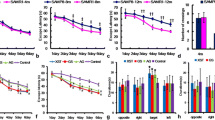
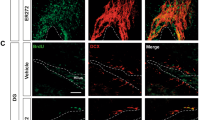
Cognition in all mammals including human beings declines during aging. The cellular events responsible for this decay involve a reduction of neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus. Here, we show that treatment with a nature product from a traditional Chinese medicine, namely salidroside restores the capacity of the dentate gyrus to generate new neurons and intercepts learning and memory decays in mice during aging. We uncover that new neurons in aging mice have functional features of an adult granule neuron by forming excitatory synapses with their putative targeting neurons. Genetic inhibition of synaptic transmission from new neurons abolishes the therapeutic effects of salidroside in behavioral tests. We also identify that salidroside targets CREB transcription for the survival of new neurons in the dentate gyrus of old mice. Thus, salidroside is therapeutically effective against learning and memory decays via stimulation of CREB-dependent functional neurogenesis in aging.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mattson MP, Chan SL, Duan W (2002) Modification of brain aging and neurodegenerative disorders by genes, diet, and behavior. Physiol Rev 82(3):637–672. doi:10.1152/physrev.00004.2002
Goldman SA (2004) Directed mobilization of endogenous neural progenitor cells: the intersection of stem cell biology and gene therapy. Curr Opin Mol Ther 6(5):466–472
Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Bjork-Eriksson T, Alborn AM, Nordborg C, Peterson DA, Gage FH (1998) Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med 4(11):1313–1317. doi:10.1038/3305
Zhao C, Deng W, Gage FH (2008) Mechanisms and functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell 132(4):645–660. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.01.033
Spalding KL, Bergmann O, Alkass K, Bernard S, Salehpour M, Huttner HB, Bostrom E, Westerlund I, Vial C, Buchholz BA, Possnert G, Mash DC, Druid H, Frisen J (2013) Dynamics of hippocampal neurogenesis in adult humans. Cell 153(6):1219–1227. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.002
van Praag H, Schinder AF, Christie BR, Toni N, Palmer TD, Gage FH (2002) Functional neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Nature 415(6875):1030–1034. doi:10.1038/4151030a
Toni N, Laplagne DA, Zhao C, Lombardi G, Ribak CE, Gage FH, Schinder AF (2008) Neurons born in the adult dentate gyrus form functional synapses with target cells. Nat Neurosci 11(8):901–907. doi:10.1038/nn.2156
Vivar C, Potter MC, Choi J, Lee JY, Stringer TP, Callaway EM, Gage FH, Suh H, van Praag H (2012) Monosynaptic inputs to new neurons in the dentate gyrus. Nat Commun 3:1107. doi:10.1038/ncomms2101
Deshpande A, Bergami M, Ghanem A, Conzelmann KK, Lepier A, Gotz M, Berninger B (2013) Retrograde monosynaptic tracing reveals the temporal evolution of inputs onto new neurons in the adult dentate gyrus and olfactory bulb. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(12):E1152–1161. doi:10.1073/pnas.1218991110
Kempermann G, Wiskott L, Gage FH (2004) Functional significance of adult neurogenesis. Curr Opin Neurobiol 14(2):186–191. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2004.03.001
Clelland CD, Choi M, Romberg C, Clemenson GD Jr, Fragniere A, Tyers P, Jessberger S, Saksida LM, Barker RA, Gage FH, Bussey TJ (2009) A functional role for adult hippocampal neurogenesis in spatial pattern separation. Science (New York) 325(5937):210–213. doi:10.1126/science.1173215
Sahay A, Scobie KN, Hill AS, O’Carroll CM, Kheirbek MA, Burghardt NS, Fenton AA, Dranovsky A, Hen R (2011) Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to improve pattern separation. Nature 472(7344):466–470. doi:10.1038/nature09817
Nakashiba T, Cushman JD, Pelkey KA, Renaudineau S, Buhl DL, McHugh TJ, Rodriguez Barrera V, Chittajallu R, Iwamoto KS, McBain CJ, Fanselow MS, Tonegawa S (2012) Young dentate granule cells mediate pattern separation, whereas old granule cells facilitate pattern completion. Cell 149(1):188–201. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.046
Alonso M, Lepousez G, Sebastien W, Bardy C, Gabellec MM, Torquet N, Lledo PM (2012) Activation of adult-born neurons facilitates learning and memory. Nat Neurosci 15(6):897–904. doi:10.1038/nn.3108
Gould E, Tanapat P, McEwen BS, Flugge G, Fuchs E (1998) Proliferation of granule cell precursors in the dentate gyrus of adult monkeys is diminished by stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(6):3168–3171
Snyder JS, Soumier A, Brewer M, Pickel J, Cameron HA (2011) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis buffers stress responses and depressive behaviour. Nature 476(7361):458–461. doi:10.1038/nature10287
Kheirbek MA, Klemenhagen KC, Sahay A, Hen R (2012) Neurogenesis and generalization: a new approach to stratify and treat anxiety disorders. Nat Neurosci 15(12):1613–1620. doi:10.1038/nn.3262
Santarelli L, Saxe M, Gross C, Surget A, Battaglia F, Dulawa S, Weisstaub N, Lee J, Duman R, Arancio O, Belzung C, Hen R (2003) Requirement of hippocampal neurogenesis for the behavioral effects of antidepressants. Science (New York) 301(5634):805–809. doi:10.1126/science.1083328
Eisch AJ, Petrik D (2012) Depression and hippocampal neurogenesis: a road to remission? Science (New York) 338(6103):72–75. doi:10.1126/science.1222941
Duan X, Chang JH, Ge S, Faulkner RL, Kim JY, Kitabatake Y, Liu XB, Yang CH, Jordan JD, Ma DK, Liu CY, Ganesan S, Cheng HJ, Ming GL, Lu B, Song H (2007) Disrupted-In-Schizophrenia 1 regulates integration of newly generated neurons in the adult brain. Cell 130(6):1146–1158. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.07.010
Kim JY, Liu CY, Zhang F, Duan X, Wen Z, Song J, Feighery E, Lu B, Rujescu D, St Clair D, Christian K, Callicott JH, Weinberger DR, Song H, Ming GL (2012) Interplay between DISC1 and GABA signaling regulates neurogenesis in mice and risk for schizophrenia. Cell 148(5):1051–1064. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.12.037
Lee SW, Clemenson GD, Gage FH (2012) New neurons in an aged brain. Behav Brain Res 227(2):497–507. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2011.10.009
Cameron HA, McKay RD (1999) Restoring production of hippocampal neurons in old age. Nat Neurosci 2(10):894–897. doi:10.1038/13197
Drapeau E, Mayo W, Aurousseau C, Le Moal M, Piazza PV, Abrous DN (2003) Spatial memory performances of aged rats in the water maze predict levels of hippocampal neurogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(24):14385–14390. doi:10.1073/pnas.2334169100
Bizon JL, Lee HJ, Gallagher M (2004) Neurogenesis in a rat model of age-related cognitive decline. Aging Cell 3(4):227–234. doi:10.1111/j.1474-9728.2004.00099.x
van Praag H, Shubert T, Zhao C, Gage FH (2005) Exercise enhances learning and hippocampal neurogenesis in aged mice. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neuroscie 25(38):8680–8685. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI. 1731-05.2005
Nilsson M, Perfilieva E, Johansson U, Orwar O, Eriksson PS (1999) Enriched environment increases neurogenesis in the adult rat dentate gyrus and improves spatial memory. J Neurobiol 39(4):569–578
Tang Y, Vater C, Jacobi A, Liebers C, Zou X, Stiehler M (2014) Salidroside exerts angiogenic and cytoprotective effects on human bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells via Akt/mTOR/p70S6K and MAPK signalling pathways. Br J Pharmacol 171(9):2440–2456. doi:10.1111/bph.12611
Zhang JK, Yang L, Meng GL, Yuan Z, Fan J, Li D, Chen JZ, Shi TY, Hu HM, Wei BY, Luo ZJ, Liu J (2013) Protection by salidroside against bone loss via inhibition of oxidative stress and bone-resorbing mediators. PLoS One 8(2):e57251. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0057251
Chen SF, Tsai HJ, Hung TH, Chen CC, Lee CY, Wu CH, Wang PY, Liao NC (2012) Salidroside improves behavioral and histological outcomes and reduces apoptosis via PI3K/Akt signaling after experimental traumatic brain injury. PLoS One 7(9):e45763. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0045763
Sheng QS, Wang ZJ, Zhang J, Zhang YG (2013) Salidroside promotes peripheral nerve regeneration following crush injury to the sciatic nerve in rats. Neuroreport 24(5):217–223. doi:10.1097/WNR.0b013e32835eb867
Qu ZQ, Zhou Y, Zeng YS, Lin YK, Li Y, Zhong ZQ, Chan WY (2012) Protective effects of a Rhodiola crenulata extract and salidroside on hippocampal neurogenesis against streptozotocin-induced neural injury in the rat. PLoS One 7(1):e29641. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0029641
Brown JP, Couillard-Despres S, Cooper-Kuhn CM, Winkler J, Aigner L, Kuhn HG (2003) Transient expression of doublecortin during adult neurogenesis. J Comp Neurol 467(1):1–10. doi:10.1002/cne.10874
Zhang J, Zhen YF, Pu Bu Ci R, Song LG, Kong WN, Shao TM, Li X, Chai XQ (2013) Salidroside attenuates beta amyloid-induced cognitive deficits via modulating oxidative stress and inflammatory mediators in rat hippocampus. Behav Brain Res 244:70–81. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2013.01.037
Creer DJ, Romberg C, Saksida LM, van Praag H, Bussey TJ (2010) Running enhances spatial pattern separation in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(5):2367–2372. doi:10.1073/pnas.0911725107
Malenka RC (2003) The long-term potential of LTP. Nat Rev Neurosci 4(11):923–926. doi:10.1038/nrn1258
Yamamoto M, Wada N, Kitabatake Y, Watanabe D, Anzai M, Yokoyama M, Teranishi Y, Nakanishi S (2003) Reversible suppression of glutamatergic neurotransmission of cerebellar granule cells in vivo by genetically manipulated expression of tetanus neurotoxin light chain. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neuroscie 23(17):6759–6767
Schoch S, Deak F, Konigstorfer A, Mozhayeva M, Sara Y, Sudhof TC, Kavalali ET (2001) SNARE function analyzed in synaptobrevin/VAMP knockout mice. Science (New York) 294(5544):1117–1122. doi:10.1126/science.1064335
Yang EJ, Ahn YS, Chung KC (2001) Protein kinase Dyrk1 activates cAMP response element-binding protein during neuronal differentiation in hippocampal progenitor cells. J Biol Chem 276(43):39819–39824. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104091200
Ming GL, Song H (2005) Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci 28:223–250. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.28.051804.101459
Hattiangady B, Rao MS, Shetty GA, Shetty AK (2005) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, phosphorylated cyclic AMP response element binding protein and neuropeptide Y decline as early as middle age in the dentate gyrus and CA1 and CA3 subfields of the hippocampus. Exp Neurol 195(2):353–371. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2005.05.014
Zhu DY, Lau L, Liu SH, Wei JS, Lu YM (2004) Activation of cAMP-response-element-binding protein (CREB) after focal cerebral ischemia stimulates neurogenesis in the adult dentate gyrus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(25):9453–9457. doi:10.1073/pnas.0401063101
Nakagawa S, Kim JE, Lee R, Chen J, Fujioka T, Malberg J, Tsuji S, Duman RS (2002) Localization of phosphorylated cAMP response element-binding protein in immature neurons of adult hippocampus. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neuroscie 22(22):9868–9876
Shors TJ, Townsend DA, Zhao M, Kozorovitskiy Y, Gould E (2002) Neurogenesis may relate to some but not all types of hippocampal-dependent learning. Hippocampus 12(5):578–584. doi:10.1002/hipo.10103
Merrill DA, Karim R, Darraq M, Chiba AA, Tuszynski MH (2003) Hippocampal cell genesis does not correlate with spatial learning ability in aged rats. J Comp Neurol 459(2):201–207. doi:10.1002/cne.10616
Kempermann G, Kuhn HG, Gage FH (1997) Genetic influence on neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94(19):10409–10414
Tashiro A, Makino H, Gage FH (2007) Experience-specific functional modification of the dentate gyrus through adult neurogenesis: a critical period during an immature stage. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neuroscie 27(12):3252–3259. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI. 4941-06.2007
Kuhn HG, Dickinson-Anson H, Gage FH (1996) Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat: age-related decrease of neuronal progenitor proliferation. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neuroscie 16(6):2027–2033
Kempermann G, Gast D, Gage FH (2002) Neuroplasticity in old age: sustained fivefold induction of hippocampal neurogenesis by long-term environmental enrichment. Ann Neurol 52(2):135–143. doi:10.1002/ana.10262
Wang J, Liu S, Fu Y, Wang JH, Lu Y (2003) Cdk5 activation induces hippocampal CA1 cell death by directly phosphorylating NMDA receptors. Nat Neurosci 6(10):1039–1047. doi:10.1038/nn1119
Liu S, Lau L, Wei J, Zhu D, Zou S, Sun HS, Fu Y, Liu F, Lu Y (2004) Expression of Ca(2+)-permeable AMPA receptor channels primes cell death in transient forebrain ischemia. Neuron 43(1):43–55. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2004.06.017
Tu W, Xu X, Peng L, Zhong X, Zhang W, Soundarapandian MM, Balel C, Wang M, Jia N, Lew F, Chan SL, Chen Y, Lu Y (2010) DAPK1 interaction with NMDA receptor NR2B subunits mediates brain damage in stroke. Cell 140(2):222–234. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.12.055
Yang Y, Shu X, Liu D, Shang Y, Wu Y, Pei L, Xu X, Tian Q, Zhang J, Qian K, Wang YX, Petralia RS, Tu W, Zhu LQ, Wang JZ, Lu Y (2012) EPAC null mutation impairs learning and social interactions via aberrant regulation of miR-124 and Zif268 translation. Neuron 73(4):774–788. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2012.02.003
Guo W, Allan AM, Zong R, Zhang L, Johnson EB, Schaller EG, Murthy AC, Goggin SL, Eisch AJ, Oostra BA, Nelson DL, Jin P, Zhao X (2011) Ablation of Fmrp in adult neural stem cells disrupts hippocampus-dependent learning. Nat Med 17(5):559–565. doi:10.1038/nm.2336
Acknowledgments
The authors greatly thank Ping Zhang (HUST) for drug treatments and Ling-Qiang Zhu (HUST) for the comments on this manuscript. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81130079 YL, 91232302 YL, 81301165 HJ) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2014M552047 HJ).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Huijuan Jin, Lei Pei, and Xiaogang Shu contributed equally to this work.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 155 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, H., Pei, L., Shu, X. et al. Therapeutic Intervention of Learning and Memory Decays by Salidroside Stimulation of Neurogenesis in Aging. Mol Neurobiol 53, 851–866 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-9045-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-9045-6