Abstract
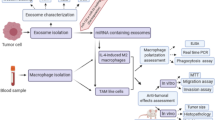
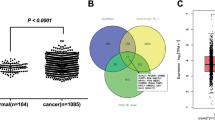
Differential activation of macrophages is associated with poor progression of breast cancer (BC). Many reports have elucidated the important involvement of exosomes produced by cancer cells in remodeling the macrophage activation phenotype to promote tumor expansion and invasion. However, the underlying mechanisms by which exosomes secreted by BC cells facilitate macrophage M2 polarization remain enigmatic and worth exploring. In this study, quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) was used to investigate miR-191-5p expression in BC tumor tissues and cells. Cell counting kit 8 (CCK-8), transwell, and flow cytometry were applied to assess the functional role of miR-191-5p in BC. Isolated nano-vesicles were identified using transmission electron microscopy and western blotting. We also observed that miR-191-5p was significantly elevated in BC clinical samples and that inhibition of miR-191-5p hindered the growth and metastasis of BC cells. Importantly, BC cells successfully accelerated macrophage M2-like polarization by directly transferring exosomes to macrophages, resulting in increased miR-191-5p levels in macrophages. Mechanistically, exosomal miR-191-5p directly inhibited the suppressors of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) expression in macrophages and aggravated macrophage M2 polarization. Similarly, si-SOCS3 transfected macrophages boosted BC cell migration and invasion in a positive feedback manner. Overall, our results manifested a pro-growth and pro-metastatic role between the two cells by elucidating the crucial role of exosomal miR-191-5p in stimulating M2 macrophage polarization and mediating communication between BC cells and macrophages. These findings opened up new horizons for the development of BC therapeutic strategies.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Lei, S., Zheng, R., Zhang, S., Wang, S., Chen, R., Sun, K., Zeng, H., Zhou, J., & Wei, W. (2021). Global patterns of breast cancer incidence and mortality: A population-based cancer registry data analysis from 2000 to 2020. Cancer Communications, 41, 1183–1194.
Lei, S., Zheng, R., Zhang, S., Chen, R., Wang, S., Sun, K., Zeng, H., Wei, W., & He, J. (2021). Breast cancer incidence and mortality in women in China: Temporal trends and projections to 2030. Cancer Biology and Medicine, 18, 900–909.
Ngamcherdtrakul, W., & Yantasee, W. (2019). siRNA therapeutics for breast cancer: Recent efforts in targeting metastasis, drug resistance, and immune evasion. Translational Research, 214, 105–120.
Arneth, B. (2019). Tumor microenvironment. Medicina (Kaunas, Lithuania), 56, 15.
Boutilier, A. J., & Elsawa, S. F. (2021). Macrophage polarization states in the tumor microenvironment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22, 6995.
Qiu, S. Q., Waaijer, S. J. H., Zwager, M. C., de Vries, E. G. E., van der Vegt, B., & Schröder, C. P. (2018). Tumor-associated macrophages in breast cancer: Innocent bystander or important player? Cancer Treatment Reviews, 70, 178–189.
Tang, Z., Li, D., Hou, S., & Zhu, X. (2020). The cancer exosomes: Clinical implications, applications and challenges. International Journal of Cancer, 146, 2946–2959.
Rao, X., Zhou, X., Wang, G., Jie, X., Xing, B., Xu, Y., Chen, Y., Li, J., Zhu, K., Wu, Z., Wu, G., Wu, C., & Zhou, R. (2022). NLRP6 is required for cancer-derived exosome-modified macrophage M2 polarization and promotes metastasis in small cell lung cancer. Cell Death & Disease, 13, 891.
Kok, V. C., & Yu, C. C. (2020). Cancer-derived exosomes: Their role in cancer biology and biomarker development. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 15, 8019–8036.
Sun, Z., Shi, K., Yang, S., Liu, J., Zhou, Q., Wang, G., Song, J., Li, Z., Zhang, Z., & Yuan, W. (2018). Effect of exosomal miRNA on cancer biology and clinical applications. Molecular Cancer, 17, 147.
Mahdi, M. A., Yousefi, S. R., Jasim, L. S., & Salavati-Niasari, M. (2022). Green synthesis of DyBa2Fe3O7. 988/DyFeO3 nanocomposites using almond extract with dual eco-friendly applications: photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 47, 14319–14330.
Yousefi, S. R., Amiri, O., & Salavati-Niasari, M. (2019). Control sonochemical parameter to prepare pure Zn0.35Fe2.65O4 nanostructures and study their photocatalytic activity. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 58, 104619.
Yousefi, S. R., Alshamsi, H. A., Amiri, O., & Salavati-Niasari, M. (2021). Synthesis, characterization and application of Co/Co3O4 nanocomposites as an effective photocatalyst for discoloration of organic dye contaminants in wastewater and antibacterial properties. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 337, 116405.
Zhao, S., Mi, Y., Guan, B., Zheng, B., Wei, P., Gu, Y., & Li, D. (2020). Tumor-derived exosomal miR-934 induces macrophage M2 polarization to promote liver metastasis of colorectal cancer. Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 13, 1–19.
Chen, X., Ying, X., Wang, X., Wu, X., Zhu, Q., & Wang, X. (2017). Exosomes derived from hypoxic epithelial ovarian cancer deliver microRNA-940 to induce macrophage M2 polarization. Oncology Reports, 38, 522–528.
Cai, J., Qiao, B., Gao, N., Lin, N., & He, W. (2019). Oral squamous cell carcinoma-derived exosomes promote M2 subtype macrophage polarization mediated by exosome-enclosed miR-29a-3p. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology, 316, C731–C740.
Fong, M. Y., Zhou, W., Liu, L., Alontaga, A. Y., Chandra, M., Ashby, J., Chow, A., O’Connor, S. T., Li, S., Chin, A. R., Somlo, G., Palomares, M., Li, Z., Tremblay, J. R., Tsuyada, A., Sun, G., Reid, M. A., Wu, X., Swiderski, P., … Wang, S. E. (2015). Breast-cancer-secreted miR-122 reprograms glucose metabolism in premetastatic niche to promote metastasis. Nature Cell Biology, 17, 183–194.
He, L., Zhu, W., Chen, Q., Yuan, Y., Wang, Y., Wang, J., & Wu, X. (2019). Ovarian cancer cell-secreted exosomal miR-205 promotes metastasis by inducing angiogenesis. Theranostics, 9, 8206–8220.
Shen, S., Song, Y., Zhao, B., Xu, Y., Ren, X., Zhou, Y., & Sun, Q. (2021). Cancer-derived exosomal miR-7641 promotes breast cancer progression and metastasis. Cell Communication and Signaling, 19, 20.
Yang, Q., Zhao, S., Shi, Z., Cao, L., Liu, J., Pan, T., Zhou, D., & Zhang, J. (2021). Chemotherapy-elicited exosomal miR-378a-3p and miR-378d promote breast cancer stemness and chemoresistance via the activation of EZH2/STAT3 signaling. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 40, 120.
Xun, J., Du, L., Gao, R., Shen, L., Wang, D., Kang, L., Chen, C., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Y., Yue, S., Feng, S., Xiang, R., Mi, X., & Tan, X. (2021). Cancer-derived exosomal miR-138-5p modulates polarization of tumor-associated macrophages through inhibition of KDM6B. Theranostics, 11, 6847–6859.
Ashirbekov, Y., Abaildayev, A., Omarbayeva, N., Botbayev, D., Belkozhayev, A., Askandirova, A., Neupokoyeva, A., Utegenova, G., Sharipov, K., & Aitkhozhina, N. (2020). Combination of circulating miR-145-5p/miR-191-5p as biomarker for breast cancer detection. PeerJ, 8, e10494.
Zhang, X. F., Li, K. K., Gao, L., Li, S. Z., Chen, K., Zhang, J. B., Wang, D., Tu, R. F., Zhang, J. X., Tao, K. X., Wang, G., & Zhang, X. D. (2015). miR-191 promotes tumorigenesis of human colorectal cancer through targeting C/EBPβ. Oncotarget, 6, 4144–4158.
Li, H., Zhou, Z. Q., Yang, Z. R., Tong, D. N., Guan, J., Shi, B. J., Nie, J., Ding, X. T., Li, B., Zhou, G. W., & Zhang, Z. Y. (2017). MicroRNA-191 acts as a tumor promoter by modulating the TET1-p53 pathway in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology, 66, 136–151.
Mar-Aguilar, F., Luna-Aguirre, C. M., Moreno-Rocha, J. C., Araiza-Chávez, J., Trevino, V., Rodríguez-Padilla, C., & Reséndez-Pérez, D. (2013). Differential expression of miR-21, miR-125b and miR-191 in breast cancer tissue. Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology, 9, 53–59.
Chen, X., Ren, X., & E, J., Zhou, Y., & Bian, R. (2023). Exosome-transmitted circIFNGR2 modulates ovarian cancer metastasis via miR-378/ST5 axis. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 43, 22–42.
Xu, T., Yu, S., Zhang, J., & Wu, S. (2021). Dysregulated tumor-associated macrophages in carcinogenesis, progression and targeted therapy of gynecological and breast cancers. Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 14, 181.
Ding, H., Wen, W., Ding, Q., & Zhao, X. (2020). Diagnostic valuation of serum miR-184 and miR-191 in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Control, 27, 1073274820964783.
Gao, X., Xie, Z., Wang, Z., Cheng, K., Liang, K., & Song, Z. (2017). Overexpression of miR-191 predicts poor prognosis and promotes proliferation and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Yonsei Medical Journal, 58, 1101–1110.
Qiu, S., Xie, L., Lu, C., Gu, C., Xia, Y., Lv, J., Xuan, Z., Fang, L., Yang, J., Zhang, L., Li, Z., Wang, W., Xu, H., Li, B., & Xu, Z. (2022). Gastric cancer-derived exosomal miR-519a-3p promotes liver metastasis by inducing intrahepatic M2-like macrophage-mediated angiogenesis. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 41, 296.
Wang, D., Wang, X., Si, M., Yang, J., Sun, S., Wu, H., Cui, S., Qu, X., & Yu, X. (2020). Exosome-encapsulated miRNAs contribute to CXCL12/CXCR4-induced liver metastasis of colorectal cancer by enhancing M2 polarization of macrophages. Cancer Letters, 474, 36–52.
Chen, J., Zhang, K., Zhi, Y., Wu, Y., Chen, B., Bai, J., & Wang, X. (2021). Tumor-derived exosomal miR-19b-3p facilitates M2 macrophage polarization and exosomal LINC00273 secretion to promote lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via Hippo pathway. Clinical and Translational Medicine, 11, e478.
Linde, N., Casanova-Acebes, M., Sosa, M. S., Mortha, A., Rahman, A., Farias, E., Harper, K., Tardio, E., Reyes Torres, I., Jones, J., Condeelis, J., Merad, M., & Aguirre-Ghiso, J. A. (2018). Macrophages orchestrate breast cancer early dissemination and metastasis. Nature Communications, 9, 21.
Ji, X. C., Shi, Y. J., Zhang, Y., Chang, M. Z., & Zhao, G. (2020). Reducing suppressors of cytokine signaling-3 (SOCS3) expression promotes M2 macrophage polarization and functional recovery after intracerebral hemorrhage. Frontiers in Neurology, 11, 586905.
Liu, W., Long, Q., Zhang, W., Zeng, D., Hu, B., Liu, S., & Chen, L. (2021). miRNA-221-3p derived from M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophage exosomes aggravates the growth and metastasis of osteosarcoma through SOCS3/JAK2/STAT3 axis. Aging (Albany New York), 13, 19760–19775.
Ren, D., Lin, B., Zhang, X., Peng, Y., Ye, Z., Ma, Y., Liang, Y., Cao, L., Li, X., Li, R., Sun, L., Liu, Q., Wu, J., Zhou, K., & Zeng, J. (2017). Maintenance of cancer stemness by miR-196b-5p contributes to chemoresistance of colorectal cancer cells via activating STAT3 signaling pathway. Oncotarget, 8, 49807.
Shang, A. Q., Wu, J., Bi, F., Zhang, Y. J., Xu, L. R., Li, L. L., Chen, F. F., Wang, W. W., Zhu, J. J., & Liu, Y. Y. (2017). Relationship between HER2 and JAK/STAT-SOCS3 signaling pathway and clinicopathological features and prognosis of ovarian cancer. Cancer Biology & Therapy, 18, 314–322.
Ying, X., Wu, Q., Wu, X., Zhu, Q., Wang, X., Jiang, L., Chen, X., & Wang, X. (2016). Epithelial ovarian cancer-secreted exosomal miR-222-3p induces polarization of tumor-associated macrophages. Oncotarget, 7, 43076.
Shi, J., Li, X., Hu, Y., Zhang, F., Lv, X., Zhang, X., Chen, Q., & Hu, S. (2020). MiR-1203 is involved in hepatocellular carcinoma metastases and indicates a poor prognosis. Neoplasma, 67, 267–276.
Dai, L., Li, Z., Tao, Y., Liang, W., Hu, W., Zhou, S., Fu, X., & Wang, X. (2021). Emerging roles of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 in human cancers. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 144, 112262.
Li, Z., Zheng, J., Lin, W., Weng, J., Hong, W., Zou, J., Ye, C., & Chen, Y. (2020). Circular RNA hsa_circ_0001785 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo by sponging miR-942 to upregulate SOCS3. Cell Cycle, 19, 2811–2825.
Yang, C., Dou, R., Wei, C., Liu, K., Shi, D., Zhang, C., Liu, Q., Wang, S., & Xiong, B. (2021). Tumor-derived exosomal microRNA-106b-5p activates EMT-cancer cell and M2-subtype TAM interaction to facilitate CRC metastasis. Molecular Therapy, 29, 2088–2107.
Funding
The authors reported that there is no funding associated with the work featured in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JN designed the study and draft the manuscript. XX acquired and processed the data. SX partly contributed to the experiment. XX wrote, reviewed, and revised the paper. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
Ethical Approval
All participants were provided with written informed consent at the time of recruitment. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of People’s Hospital of Ganzhou City, and all experiments involving human tissue specimens comply with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, J., Xi, X., Xiao, S. et al. Tumor Cell-Derived Exosomal miR-191-5p Activates M2-Subtype Macrophages Through SOCS3 to Facilitate Breast Cancer. Mol Biotechnol 66, 1314–1325 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-01034-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-01034-0