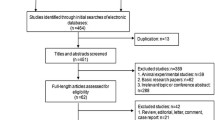
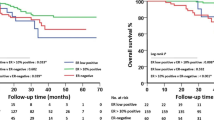
Abstract
Estrogen receptor (ER) is a molecular marker and target for diagnosing and treating breast cancer (BC). ER-α36, a novel estrogen receptor subtype, involved in the proliferation, differentiation, metastasis, and invasion of tumor cells. It is closely linked to the progression of various cancers. Therefore, studying ER is of high significance in treating BC. In this study, we will investigate the changes in the expression level of ER-α36 in patients with BC treated by chemotherapy through meta-analysis, so as to evaluate the clinical value of ER-α36 in the prognosis of BC treated by chemotherapy. English databases such as PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and The Cochrane Library were searched to retrieve the articles published from the establishment of the database to April 2023. The keywords included chemotherapy, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, breast cancer, estrogen receptor alpha, and ER-α36. Five suitable studies, encompassing 636 patients, were ultimately selected. The meta-analysis results revealed that, following the chemotherapy, the analysis of ER-α36 positive cases yielded an Odds Ratio (OR) of 0.42, a 95% confidence interval (CI) of 0.28–0.64 (Z = 4.00, P < 0.0001). Additionally, the analysis of cases exhibiting remission in BC demonstrated an OR of 2.22 (95% CI = 1.40–3.50, Z = 3.40, P = 0.0007). Compared to patients receiving single chemotherapy agents or those untreated with chemotherapy, the combined use of multiple chemotherapy drugs can significantly reduce the levels of ER-α36 in BC patients, enhancing the remission rate of BC. ER-α36 can serve as a critical indicator for assessing the prognosis of BC following chemotherapy.
Graphical Abstract
Estrogen receptor (ER) serves as a molecular marker and target for cancer diagnosis and treatment. The novel ER subtype, ER-α36, is involved in the proliferation, differentiation, migration, and invasion of tumor cells. It is closely associated with the development of endometrial cancer, as well as the progression of various cancers. This study, based on meta-analysis, evaluated the impact of chemotherapy on the expression of ER-α36 in breast cancer (BC) patients. The results indicated that chemotherapy treatment can decrease the levels of ER-α36 in BC patients, leading to an increased rate of BC remission. Therefore, the level of ER-α36 served as a crucial indicator for assessing the prognosis of BC under chemotherapy treatment.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data and Materials Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Gao, C. W., Wang, J. G., He, P. S., & Xiong, X. (2022). Metastatic pattern of breast cancer by histologic grade: A seer population-based study. Discovery Medicine, 34(173), 189–197.
Li, L., Zhu, X. H., & Wu, P. (2023). Correlation between the expression levels of c-erbb-2, pr and er and the characteristics of calcification foci in breast cancer. Acta Medica Mediterranea, 39(2), 435–439.
Yao, G. D., Niu, Y. Y., Chen, K. X., Meng, H. X., Song, H. T., Tian, Z. N., Geng, J. S., & Feng, M. Y. (2018). SOX2 gene expression and its role in triple negative breast cancer tissues. Journal of Biological Regulators and Homeostatic Agents, 32(6), 1399–1406.
Gotzos, V., Cappelli-Gotzos, B., & Conti, G. (1983). Study on the multiplication of cancer cells in a pleural effusion from a woman having a breast adenocarcinoma. Cellular and Molecular Biology, 29(5), 353–355.
Koual, M., Tomkiewicz, C., Cano-Sancho, G., Antignac, J. P., Bats, A. S., & Coumoul, X. (2020). Environmental chemicals, breast cancer progression and drug resistance. Environmental Health, 19(1), 117.
Yan, H. L., Luo, B., Wu, X. Y., Guan, F., Yu, X. X., Zhao, L. N., Ke, X. K., Wu, J., & Yuan, J. P. (2021). Cisplatin induces pyroptosis via activation of meg3/nlrp3/caspase-1/gsdmd pathway in triple-negative breast cancer. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 17(10), 2606–2621.
Iwamoto, T., Kajiwara, Y., Zhu, Y. D., & Iha, S. (2020). Biomarkers of neoadjuvant/adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. Chinese Clinical Oncology, 9(3), 27.
Orrantia-Borunda, E., Anchondo-Nuñez, P., Acuña-Aguilar, L. E., Gómez-Valles, F. O., Ramírez-Valdespino, C. A., & Mayrovitz, H. N. (Eds.). (2022). Subtypes of breast cancer. Exon Publications.
Li, Y., Kong, X. Y., Xuan, L. X., Wang, Z. Z., & Huang, Y. H. (2021). Prolactin and endocrine therapy resistance in breast cancer: The next potential hope for breast cancer treatment. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 25(22), 10327–10348.
Lev, S. (2020). Targeted therapy and drug resistance in triple-negative breast cancer: The EGFR axis. Biochemical Society Transactions, 48(2), 657–665.
Singh, D., Assaraf, Y. G., & Gacche, R. N. (2022). Long non-coding RNA mediated drug resistance in breast cancer. Drug Resist Updat, 63, 100851.
Kaboli, J. P., Salimian, F., Aghapour, S., Xiang, S. X., Zhao, Q. J., Li, M. X., Wu, X., Du, F. K., Zhao, Y. S., Shen, J., Cho, C. H., & Xiao, Z. G. (2020). Akt-targeted therapy as a promising strategy to overcome drug resistance in breast cancer—A comprehensive review from chemotherapy to immunotherapy. Pharmacological Research, 156, 104806.
Pan, X. H., Song, Z., Cui, Y., Qi, M., Wu, G. J., & Wang, M. (2022). Enhancement of sensitivity to tamoxifen by berberine in breast cancer cells by inhibiting er-α36 expression. Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 21(1), e126919.
Juliansyah, A., Rahman, S., Indra, I., Nelwan, B., & Prihantono, P. (2021). Association of ERα-36 expression with the de novo resistance of tamoxifen in ER-positive breast cancer. Breast Disease, 40(S1), S123–S127.
Wang, Y. X., Pan, X. H., Li, Y. J., Wang, R., Yang, Y. Y., Jiang, B. C., Sun, G. P., Shao, C. S. H., Wang, M., & Gong, Y. Q. (2021). CUL4B renders breast cancer cells tamoxifen-resistant via miR-32-5p/ER-α36 axis. The Journal of Pathology, 254(2), 185–198.
Yu, L. F., Ke, W., Wang, Y. L., Ding, W., Wang, B., Huang, S., Chen, J., Wang, X. T., Wang, Z. Y., & Shen, P. (2014). Predictive and prognostic value of ER-α36 expression in breast cancer patients treated with chemotherapy. Steroids, 84, 11–16.
Zhu, S. G., Li, Y., Wang, Y. D., Cao, J. Q., Li, X. H., Wang, J., & Wang, X. M. (2019). Efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and Annexin A3 expression in breast cancer. Journal of B.U.ON., 24(2), 522–528.
Qin, Q. H., Gao, F. F., Jiang, W., Tan, Q. X., Mo, Q. G., & Wei, C. Y. (2014). Effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on expressions of estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, and Ki-67 in breast cancer. Chinese Medical Journal (England), 127(18), 3272–3277.
Vranic, S., Gatalica, Z., Deng, H., Frkovic-Grazio, S., Lee, L. M., Gurjeva, O., & Wang, Z. Y. (2011). ER-α36, a novel isoform of ER-α66, is commonly over-expressed in apocrine and adenoid cystic carcinomas of the breast. Journal of Clinical Pathology, 64(1), 54–57.
Konan, H. P., Kassem, L., Omarjee, S., Surmieliova-Garnès, A., Jacquemetton, J., Cascales, E., Rezza, A., Trédan, O., Treilleux, I., Poulard, C., & Le Romancer, M. (2020). ERα-36 regulates progesterone receptor activity in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Research, 22(1), 50.
Kerr, A. J., Dodwell, D., McGale, P., Holt, F., Duane, F., Mannu, G., Darby, S. C., & Taylor, C. W. (2022). Adjuvant and neoadjuvant breast cancer treatments: A systematic review of their effects on mortality. Cancer Treatment Reviews, 105, 102375.
Yin, L., Qi, X. W., Liu, X. Z., Yang, Z. Y., Cai, R. L., Cui, H. J., Chen, L., & Yu, S. C. (2020). Icaritin enhances the efficacy of cetuximab against triple-negative breast cancer cells. Oncology Letters, 19(6), 3950–3958.
Mahboobifard, F., Dargahi, L., Jorjani, M., Ramezani Tehrani, F., & Pourgholami, M. H. (2021). The role of ERα36 in cell type-specific functions of estrogen and cancer development. Pharmacological Research, 163, 105307.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The research is supported by: 2019 Bidding Project of Sichuan Elderly Care and Elderly Health Collaborative Innovation Center, Ping Leng, ER α Study on the expression of 36 in elderly breast cancer and its relationship with clinicopathological characteristics (No. 19Z15).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EH, XX, HQ, and PL conceived and designed the study, wrote the original, and performed experimental work and data analysis and review of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, E., Xia, X., Quan, H. et al. Expression Significance of Estrogen Receptor ER-α36 in Breast Cancer Treated by Chemotherapy: A Meta-Analysis. Mol Biotechnol 66, 991–999 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-01029-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-01029-x