Abstract
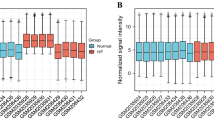
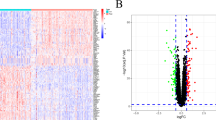
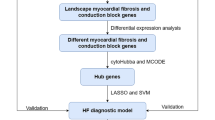
This research delves into the intricate relationship between hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and heart failure (HF) by exploring shared genetic characteristics and molecular processes. Employing advanced methodologies such as differential analysis, weighted correlation network analysis (WGCNA), and algorithms like Random Forest (RF), Least Absolute Shrinkage Selection (LASSO), and XGBoost, we meticulously identified modular differential genes (DEGs) associated with both HF and HCC. Gene Set Variation Analysis (GSVA) and single sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA) were employed to unveil underlying biological mechanisms. The study revealed 88 core genes shared between HF and HCC, indicating a common mechanism. Enrichment analysis emphasized the roles of immune responses and inflammation in both diseases. Leveraging XGBoost, we crafted a robust multigene diagnostic model (including FCN3, MAP2K1, AP3M2, CDH19) with an area under the curve (AUC) > 0.9, showcasing exceptional predictive accuracy. GSVA and ssGSEA analyses unveiled the involvement of immune cells and metabolic pathways in the pathogenesis of HF and HCC. This research uncovers a pivotal interplay between HF and HCC, highlighting shared pathways and key genes, offering promising insights for future clinical treatments and experimental research endeavors.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets for this study can be found in the GEO (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/) and TCGA (https://www.cancer.gov/ccg/research/genome-sequencing/tcga). The core code of this study has been uploaded to GitHub: https://github.com/Lizhiyongjuan/Code.git
References
Kirk, R., Dipchand, A. I., Rosenthal, D. N., et al. (2014). The International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation Guidelines for the management of pediatric heart failure: Executive summary. Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation, 33(9), 888–909.
Virani, S. S., Alonso, A., Benjamin, E. J., et al. (2020). Heart disease and stroke statistics-2020 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation, 141(9), E139–E596.
McGlynn, K. A., Petrick, J. L., & El-Serag, H. B. (2021). Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology, 73, 4–13.
Wang, J. Q., Liu, X. L., Jin, T. Q., Cao, Y. Q., Tian, Y., & Xu, F. (2022). NK cell immunometabolism as target for liver cancer therapy. International Immunopharmacology, 112, 13.
James, S. L., Abate, D., Abate, K. H., et al. (2018). Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet, 392(10159), 1789–1858.
Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., et al. (2021). Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 71(3), 209–249.
Gad, M. M., Saad, A. M., Al-Husseini, M. J., et al. (2019). Temporal trends, ethnic determinants, and short-term and long-term risk of cardiac death in cancer patients: A cohort study. Cardiovascular Pathology, 43, 7.
Stoltzfus, K. C., Zhang, Y., Sturgeon, K., et al. (2020). Fatal heart disease among cancer patients. Nature Communications, 11(1), 8.
Antwi, S. O., Craver, E. C., Nartey, Y. A., Sartorius, K., & Patel, T. (2022). Metabolic risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A prospective study. Cancers, 14(24), 13.
Burra, P., Becchetti, C., & Germani, G. (2020). NAFLD and liver transplantation: Disease burden, current management and future challenges. JHEP Reports, 2(6), 12.
Aimo, A., Castiglione, V., Borrelli, C., et al. (2020). Oxidative stress and inflammation in the evolution of heart failure: From pathophysiology to therapeutic strategies. European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, 27(5), 494–510.
D’Souza, S., Lau, K. C. K., Coffin, C. S., & Patel, T. R. (2020). Molecular mechanisms of viral hepatitis induced hepatocellular carcinoma. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 26(38), 5759–5783.
Remmelzwaal, S., van Oort, S., Handoko, M. L., van Empel, V., Heymans, S. R. B., & Beulens, J. W. J. (2022). Inflammation and heart failure: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine, 23(11), 728–735.
Zhou, M. Z., Liu, B. R., & Shen, J. (2022). Immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clinical and Experimental Medicine, 23(3), 569–577.
Savarese, G., Becher, P. M., Lund, L. H., Seferovic, P., Rosano, G. M. C., & Coats, A. J. S. (2022). Global burden of heart failure: A comprehensive and updated review of epidemiology. Cardiovascular Research, 118(17), 3272–3287.
Bloom, M. W., Hamo, C. E., Cardinale, D., et al. (2016). Cancer therapy-related cardiac dysfunction and heart failure: Part 1: Definitions, pathophysiology, risk factors, and imaging. Circulation: Heart Failure, 9(1), 10.
Slamon, D., Eiermann, W., Robert, N., et al. (2011). Adjuvant trastuzumab in HER2-positive breast cancer. New England Journal of Medicine, 365(14), 1273–1283.
Belzile-Dugas, E., & Eisenberg, M. J. (2021). Radiation-induced cardiovascular disease: Review of an underrecognized pathology. Journal of the American Heart Association, 10(18), 10.
Banke, A., Schou, M., Videbaek, L., et al. (2016). Incidence of cancer in patients with chronic heart failure: A long-term follow-up study. European Journal of Heart Failure, 18(3), 260–266.
Hasin, T., Gerber, Y., Weston, S. A., et al. (2016). Heart failure after myocardial infarction is associated with increased risk of cancer. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 68(3), 265–271.
Meijers, W. C., Maglione, M., Bakker, S. J. L., et al. (2018). Heart failure stimulates tumor growth by circulating factors. Circulation, 138(7), 678–691.
Ritchie, M. E., Phipson, B., Wu, D., et al. (2015). limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Research, 43(7), 13.
Langfelder, P., & Horvath, S. (2008). WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics, 9(1), 559.
Szklarczyk, D., Gable, A. L., Nastou, K. C., et al. (2021). The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Research, 49(D1), D605–D612.
Doncheva, N. T., Morris, J. H., Gorodkin, J., & Jensen, L. J. (2019). Cytoscape StringApp: Network analysis and visualization of proteomics data. Journal of Proteome Research, 18(2), 623–632.
Zhou, Y. Y., Zhou, B., Pache, L., et al. (2019). Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nature Communications, 10, 10.
Yu, G. C., Wang, L. G., Yan, G. R., & He, Q. Y. (2015). DOSE: An R/Bioconductor package for disease ontology semantic and enrichment analysis. Bioinformatics, 31(4), 608–609.
Bindea, G., Mlecnik, B., Tosolini, M., et al. (2013). Spatiotemporal dynamics of intratumoral immune cells reveal the immune landscape in human cancer. Immunity, 39(4), 782–795.
Garge, N. R., Bobashev, G., & Eggleston, B. (2013). Random forest methodology for model-based recursive partitioning: The mobForest package for R. BMC Bioinformatics, 14, 8.
Alhamzawi, R., & Ali, H. T. M. (2018). The Bayesian adaptive lasso regression. Mathematical Biosciences, 303, 75–82.
Parente, D. J. (2021). PolyBoost: An enhanced genomic variant classifier using extreme gradient boosting. Proteomics: Clinical Applications, 15(2–3), 5.
Liberzon, A., Birger, C., Thorvaldsdottir, H., Ghandi, M., Mesirov, J. P., & Tamayo, P. (2015). The Molecular Signatures Database hallmark gene set collection. Cell Systems, 1(6), 417–425.
Hänzelmann, S., Castelo, R., & Guinney, J. (2013). GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-Seq data. BMC Bioinformatics, 14, 15.
Chen, K. J., Liu, S., Lu, C. L., & Gu, X. F. (2022). A prognostic and therapeutic hallmark developed by the integrated profile of basement membrane and immune infiltrative landscape in lung adenocarcinoma. Frontiers in Immunology, 13, 14.
Blanche, P., Dartigues, J. F., & Jacqmin-Gadda, H. (2013). Estimating and comparing time-dependent areas under receiver operating characteristic curves for censored event times with competing risks. Statistics in Medicine, 32(30), 5381–5397.
Bian, R. T., Xu, X. G., & Li, W. Y. (2023). Uncovering the molecular mechanisms between heart failure and end-stage renal disease via a bioinformatics study. Frontiers in Genetics, 13, 13.
Dick, S. A., & Epelman, S. (2016). Chronic heart failure and inflammation what do we really know? Circulation Research, 119(1), 159–176.
Revelo, X., Parthiban, P., Chen, C., et al. (2021). Cardiac resident macrophages prevent fibrosis and stimulate angiogenesis. Circulation Research, 129(12), 1086–1101.
Shirakawa, K., & Sano, M. (2022). Neutrophils and neutrophil extracellular traps in cardiovascular disease: An overview and potential therapeutic approaches. Biomedicines, 10(8), 20.
Daseke, M. J., Valerio, F. M., Kalusche, W. J., Ma, Y. G., DeLeon-Pennell, K. Y., & Lindsey, M. L. (2019). Neutrophil proteome shifts over the myocardial infarction time continuum. Basic Research in Cardiology, 114(5), 13.
Sreejit, G., Abdel-Latif, A., Athmanathan, B., et al. (2020). Neutrophil-derived S100A8/A9 amplify granulopoiesis after myocardial infarction. Circulation, 141(13), 1080–1094.
Horckmans, M., Ring, L., Duchene, J., et al. (2017). Neutrophils orchestrate post-myocardial infarction healing by polarizing macrophages towards a reparative phenotype. European Heart Journal, 38(3), 187–197.
Daseke, M. J., Chalise, U., Becirovic-Agic, M., et al. (2021). Neutrophil signaling during myocardial infarction wound repair. Cellular Signalling, 77, 12.
Ko, T., Fujita, K., Nomura, S., et al. (2018). Quantification of DNA damage in heart tissue as a novel prediction tool for therapeutic prognosis. Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation, 37(4), S233–S233.
Siggens, L., Figg, N., Bennett, M., & Foo, R. (2012). Nutrient deprivation regulates DNA damage repair in cardiomyocytes via loss of the base-excision repair enzyme OGG1. The FASEB Journal, 26(5), 2117–2124.
Li, X., Ramadori, P., Pfister, D., Seehawer, M., Zender, L., & Heikenwalder, M. (2021). The immunological and metabolic landscape in primary and metastatic liver cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer, 21(9), 541–557.
Guil, S., & Esteller, M. (2012). Cis-acting noncoding RNAs: Friends and foes. Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, 19(11), 1068–1075.
Engreitz, J. M., Ollikainen, N., & Guttman, M. (2016). Long non-coding RNAs: Spatial amplifiers that control nuclear structure and gene expression. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 17(12), 756–770.
Gil, N., & Ulitsky, I. (2020). Regulation of gene expression by cis-acting long non-coding RNAs. Nature Reviews Genetics, 21(2), 102–117.
Gillman, R., Floro, K. L., Wankell, M., & Hebbard, L. (2021). The role of DNA damage and repair in liver cancer. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta: Reviews on Cancer, 1875(1), 12.
Tecchio, C., Scapini, P., Pizzolo, G., & Cassatella, M. A. (2013). On the cytokines produced by human neutrophils in tumors. Seminars in Cancer Biology, 23(3), 159–170.
Liu, W., Zhou, X., Yao, Q., et al. (2023). In situ expansion and reprogramming of Kupffer cells elicit potent tumoricidal immunity against liver metastasis. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 133(8), 19.
Wang, S. M., Song, Z. L., Tan, B., Zhang, J. J., Zhang, J. D., & Liu, S. Y. (2021). Identification and validation of hub genes associated with hepatocellular carcinoma via integrated bioinformatics analysis. Frontiers in Oncology, 11, 12.
Shen, S. L., Peng, H., Wang, Y., et al. (2018). Screening for immune-potentiating antigens from hepatocellular carcinoma patients after radiofrequency ablation by serum proteomic analysis. BMC Cancer, 18, 8.
Sun, L., Yu, S., Dong, C. R., et al. (2022). Comprehensive analysis of prognostic value and immune infiltration of ficolin family members in hepatocellular carcinoma. Frontiers in Genetics, 13, 14.
Cao, J., Liu, Z. Y., Liu, J., Li, C., Zhang, G. G., & Shi, R. Z. (2021). Bioinformatics analysis and identification of genes and pathways in ischemic cardiomyopathy. International Journal of General Medicine, 14, 5927–5937.
Prohászka, Z., Munthe-Fog, L., Ueland, T., et al. (2013). Association of ficolin-3 with severity and outcome of chronic heart failure. PLoS ONE, 8(4), e60976.
Bromberg-White, J. L., Andersen, N. J., & Duesbery, N. S. (2012). MEK genomics in development and disease. Briefings in Functional Genomics, 11(4), 300–310.
Duran, P., Sandoval, A., Gonzalez-Ramirez, R., Zarco, N., & Felix, R. (2020). Regulation of the Ca2+ channel alpha(2)delta-1 subunit expression by epidermal growth factor via the ERK/ELK-1 signaling pathway. American Journal of Physiology: Endocrinology and Metabolism, 319(1), E232–E244.
Wang, J., & Guo, T. (2013). Metabolic remodeling in chronic heart failure. Journal of Zhejiang University Science B, 14(8), 688–695.
Zamora, M., & Villena, J. A. (2019). Contribution of impaired insulin signaling to the pathogenesis of diabetic cardiomyopathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(11), 16.
Shi, Y., Han, T., & Liu, C. (2021). CircRNA hsa_circ_0006220 acts as a tumor suppressor gene by regulating miR-197-5p/CDH19 in triple-negative breast cancer. Annals of Translational Medicine, 9(15), 13.
Peiseler, M., Schwabe, R. F., Hampe, J., Kubes, P., Heikenwaelder, M., & Tacke, F. (2022). Immune mechanisms linking metabolic injury to inflammation and fibrosis in fatty liver disease—Novel insights into cellular communication circuits. Journal of Hepatology, 77(4), 1136–1160.
Gyorfi, A. H., Matei, A. E., & Distler, J. H. W. (2018). Targeting TGF-beta signaling for the treatment of fibrosis. Matrix Biology, 68–69, 8–27.
Murphy-Ullrich, J. E., & Suto, M. J. (2018). Thrombospondin-1 regulation of latent TGF-beta activation: A therapeutic target for fibrotic disease. Matrix Biology, 68–69, 28–43.
Dobaczewski, M., Chen, W., & Frangogiannis, N. G. (2011). Transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta signaling in cardiac remodeling. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, 51(4), 600–606.
Frangogiannis, N. G. (2017). The role of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta in the infarcted myocardium. Journal of Thoracic Disease, 9, S52–S63.
Chen, J., Gingold, J. A., & Su, X. P. (2019). Immunomodulatory TGF-beta signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Trends in Molecular Medicine, 25(11), 1010–1023.
Xu, X., Lei, Y. M., Chen, L. J., et al. (2021). Phosphorylation of NF-kappa Bp65 drives inflammation-mediated hepatocellular carcinogenesis and is a novel therapeutic target. Journal of Experimental and Clinical Cancer Research, 40(1), 17.
Hanna, A., & Frangogiannis, N. G. (2020). Inflammatory cytokines and chemokines as therapeutic targets in heart failure. Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy, 34(6), 849–863.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Innovative Team of Intelligent Inspection and Active Health (ITIH) for supporting this study.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Biomedical Science and Technology Support Special Project of Shanghai Science and Technology Innovation Action Plan in 2021 (21S11901700) and Shanghai Shanghai Pudong New Area Clinical Medicine Summit Fund Project (PWYgf2021-04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. LC, YL, and LM designed the study. LC, XW, and XL wrote the initial version of the manuscript and revised the final version. LC, XW, and XL performed data collection and analyzed the data. YL and LM supervised the work. All authors contributed to the manuscript and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, L., Wang, X., Li, X. et al. Identification of Co-diagnostic Genes for Heart Failure and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Through WGCNA and Machine Learning Algorithms. Mol Biotechnol 66, 1229–1245 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-01025-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-01025-1