Abstract
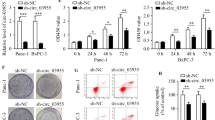
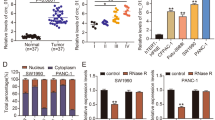
Pancreatic cancer (PC) is a malignant tumor with insidious clinical manifestations and dismal prognosis. Emerging reports have demonstrated that circRNAs exert pivotal biological function in PC. Here, we investigated the crucial biological role and underlying regulatory mechanisms of differentially expressed circ_103809 in PC. In this study, hsa_circ_103809 (hsa_circ_0072088) was identified as the research object via analyzing and screening the aberrantly expressed circRNAs in PC by GSE69362 dataset. The levels of circ_103809 in PC tissues and cells were assessed via qRT-PCR. Functional assays were conducted to monitor the impacts of circ_103809 on PC cells. Additionally, the downstream molecular targets and regulatory networks of circ_103809 were predicted by bioinformatics and validated using luciferase assays and rescue experiments. We found that circ_103809 was substantially upregulated in PC tissues and cells. Silencing circ_103809 restrained the growth viability, clonogenic rate, migration, and invasion capabilities of PC cells. Further mechanistic exploration disclosed that miR-197-3p was the downstream gene of circ_103809, while Tetraspanin-3 (TSPAN3) was a direct target of miR-197-3p. The suppressive effect of circ_103809 knockdown on malignant processes of PC cells was eliminated by miR-197-3p downregulation or TSPAN3 upregulation. Our study demonstrated that circ_103809 served as an innovative positive regulator in the growth and metastasis of PC cells. Furthermore, circ_103809 mediated the miR-197-3p/TSPAN3 axis to modulate the malignant progression of PC cells, which was prospected to be a probable biomarker and an efficient therapeutic target for PC.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Laversanne, M., Soerjomataram, I., Jemal, A., et al. (2021). Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 71(3), 209–249.
Khalaf, N., El-Serag, H. B., Abrams, H. R., & Thrift, A. P. (2021). Burden of pancreatic cancer: From epidemiology to practice. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 19(5), 876–884.
Rahib, L., Smith, B. D., Aizenberg, R., Rosenzweig, A. B., Fleshman, J. M., & Matrisian, L. M. (2014). Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Research, 74(11), 2913–21.
Klein, A. P. (2021). Pancreatic cancer epidemiology: understanding the role of lifestyle and inherited risk factors. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology Hepatology, 18(7), 493–502.
Naudin, S., Viallon, V., Hashim, D., Freisling, H., Jenab, M., Weiderpass, E., et al. (2020). Healthy lifestyle and the risk of pancreatic cancer in the EPIC study. European Journal of Epidemiology, 35(10), 975–986.
Zanini, S., Renzi, S., Limongi, A. R., Bellavite, P., Giovinazzo, F., & Bermano, G. (2021). A review of lifestyle and environment risk factors for pancreatic cancer. European Journal of Cancer, 145, 53–70.
Wu, B., & Shi, L. (2020). Cost-effectiveness of maintenance olaparib for germline BRCA-mutated metastatic pancreatic cancer. Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, 18(11), 1528–1536.
Manrai, M., Tilak, T., Dawra, S., Srivastava, S., & Singh, A. (2021). Current and emerging therapeutic strategies in pancreatic cancer: Challenges and opportunities. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 27(39), 6572–6589.
Strobel, O., Neoptolemos, J., Jager, D., & Buchler, M. W. (2019). Optimizing the outcomes of pancreatic cancer surgery. Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology, 16(1), 11–26.
Chen, L., & Shan, G. (2021). CircRNA in cancer: Fundamental mechanism and clinical potential. Cancer Letters., 505, 49–57.
Chen, G., Tang, W., Wang, S., Long, C., He, X., Yang, D., et al. (2021). Promising diagnostic and therapeutic circRNAs for skeletal and chondral disorders. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 17(5), 1428–1439.
Lauretti, E., Dabrowski, K., & Pratico, D. (2021). The neurobiology of non-coding RNAs and Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis: Pathways, mechanisms and translational opportunities. Ageing Research Reviews., 71, 101425.
Lu, D., & Thum, T. (2019). RNA-based diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for cardiovascular disease. Nature Reviews Cardiology, 16(11), 661–674.
Yang, B., Zhang, B., Qi, Q., & Wang, C. (2022). CircRNA has_circ_0017109 promotes lung tumor progression via activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling due to modulating miR-671-5p/FZD4 axis. BMC Pulmonary Medicine, 22(1), 443.
Li, H., Luo, F., Jiang, X., Zhang, W., Xiang, T., Pan, Q., et al. (2022). CircITGB6 promotes ovarian cancer cisplatin resistance by resetting tumor-associated macrophage polarization toward the M2 phenotype. Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer., 10(3), e004029.
Jiang, Y., Zhao, J., Li, R., Liu, Y., Zhou, L., Wang, C., et al. (2022). CircLRFN5 inhibits the progression of glioblastoma via PRRX2/GCH1 mediated ferroptosis. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 41(1), 307.
Zhang, X., Tan, P., Zhuang, Y., & Du, L. (2020). hsa_circRNA_001587 upregulates SLC4A4 expression to inhibit migration, invasion, and angiogenesis of pancreatic cancer cells via binding to microRNA-223. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 319(6), G703–G717.
Liu, M., Luo, C., Dong, J., Guo, J., Luo, Q., Ye, C., et al. (2020). CircRNA_103809 suppresses the proliferation and metastasis of breast cancer cells by sponging MicroRNA-532-3p (miR-532-3p). Frontiers in Genetics., 11, 485.
Zhan, W., Liao, X., Chen, Z., Li, L., Tian, T., Yu, L., et al. (2020). Circular RNA hsa_circRNA_103809 promoted hepatocellular carcinoma development by regulating miR-377-3p/FGFR1/ERK axis. J Cell Physiol, 235(2), 1733–1745.
Huang, W., Lu, Y., Wang, F., Huang, X., & Yu, Z. (2020). Circular RNA circRNA_103809 accelerates bladder cancer progression and enhances chemo-resistance by activation of miR-516a-5p/FBXL18 Axis. Cancer Management and Research., 12, 7561–7568.
Liu, W., Ma, W., Yuan, Y., Zhang, Y., & Sun, S. (2018). Circular RNA hsa_circRNA_103809 promotes lung cancer progression via facilitating ZNF121-dependent MYC expression by sequestering miR-4302. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communication, 500(4), 846–851.
Babu, V. S., Mallipatna, A., Sa, D., Dudeja, G., Kannan, R., Shetty, R., et al. (2022). Integrated analysis of cancer tissue and vitreous humor from retinoblastoma eyes reveals unique tumor-specific metabolic and cellular pathways in advanced and non-advanced tumors. Cells, 11(10), 1668.
Li, H., Hao, X., Wang, H., Liu, Z., He, Y., Pu, M., et al. (2016). Circular RNA expression profile of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma revealed by microarray. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 40(6), 1334–1344.
Yang, J., Xu, R., Wang, C., Qiu, J., Ren, B., & You, L. (2021). Early screening and diagnosis strategies of pancreatic cancer: a comprehensive review. Cancer Communications (London), 41(12), 1257–1274.
Yu, S., Zhang, C., & Xie, K. P. (2021). Therapeutic resistance of pancreatic cancer: Roadmap to its reversal. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Reviews on Cancer, 1875(1), 188461.
Xia, L., Song, M., Sun, M., Wang, F., & Yang, C. (2018). Circular RNAs as biomarkers for cancer. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1087, 171–187.
Rong, Z., Xu, J., Shi, S., Tan, Z., Meng, Q., Hua, J., et al. (2021). Circular RNA in pancreatic cancer: A novel avenue for the roles of diagnosis and treatment. Theranostics, 11(6), 2755–2769.
Wang, Y. Z., An, Y., Li, B. Q., Lu, J., & Guo, J. C. (2019). Research progress on circularRNAs in pancreatic cancer: Emerging but promising. Cancer Biology & Therapy, 20(9), 1163–1171.
Liu, X., Zhou, L., Chen, Y., Jiang, X., & Jiang, J. (2021). CircRNF13 promotes the malignant progression of pancreatic cancer through targeting miR-139-5p/IGF1R Axis. Journal of Oncology, 2021, 6945046.
Zhou, X., Liu, K., Cui, J., Xiong, J., Wu, H., Peng, T., et al. (2021). Circ-MBOAT2 knockdown represses tumor progression and glutamine catabolism by miR-433-3p/GOT1 axis in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 40(1), 124.
Lu, Y., Zhou, S., Cheng, G., Ruan, Y., Tian, Y., Lv, K., et al. (2022). CircLMTK2 silencing attenuates gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer by sponging miR-485-5p and to target PAK1. Journal of Oncology, 2022, 1911592.
Kristensen, L. S., Andersen, M. S., Stagsted, L. V. W., Ebbesen, K. K., Hansen, T. B., & Kjems, J. (2019). The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet, 20(11), 675–691.
Wang, Y., Zhang, J., Jia, J., Qian, B., & Tian, X. (2022). Circ_0008768 suppresses the pancreatic cancer progression via miR-330- 3p/PTEN Axis. Protein Pept Lett, 29(9), 796–805.
Shi, Y., Shen, M., Yang, Y., & Qiu, J. (2022). CircDUSP22 overexpression restrains pancreatic cancer development via modulating miR-1178-3p and downstream BNIP3. Biochemical Genetics., 61(2), 651–668.
Huang, Q., Ma, B., Su, Y., Chan, K., Qu, H., Huang, J., et al. (2020). miR-197-3p represses the proliferation of prostate cancer by regulating the VDAC1/AKT/beta-catenin signaling axis. Int J Biol Sci, 16(8), 1417–1426.
Xie, W., Shui, C., Fang, X., Peng, Y., & Qin, L. (2020). miR-197-3p reduces epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting ABCA7 in ovarian cancer cells. 3 Biotech., 10(8), 375.
Yuan, J., Liu, Z., Liu, J., & Fan, R. (2022). Circ_0060055 promotes the growth, invasion, and radioresistance of glioblastoma by targeting MiR-197-3p/API5 Axis. Neurotox Res, 40(5), 1292–1303.
Zhang, J., Wang, S., Bai, Y., Ali, A. M., Deng, J., Chen, Y., et al. (2023). miR-197-3p promotes osteosarcoma stemness and chemoresistance by inhibiting SPOPL. Journal of Clinical Medicine., 12(3), 1177.
Kumar, S., Saikia, J., Sharawat, S. K., Malik, P. S., Kumar, S., & Mohan, A. (2022). Analysis of miR-375-3p, miR-197-3p, and miR-15a-5p expression and their clinical relevance as biomarkers in lung cancer. Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment, 21, 15330338221080980.
Wang, Y. Y., Wu, Z. Y., Wang, G. C., Liu, K., Niu, X. B., Gu, S., et al. (2016). LINC00312 inhibits the migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells by targeting miR-197-3p. Tumour Biol, 37(11), 14553–14563.
Kwon, H. Y., Bajaj, J., Ito, T., Blevins, A., Konuma, T., Weeks, J., et al. (2015). Tetraspanin 3 is required for the development and propagation of acute myelogenous leukemia. Cell Stem Cell, 17(2), 152–164.
Zhang, R., Tang, P., Wang, F., Xing, Y., Jiang, Z., Chen, S., et al. (2019). Tumor suppressor miR-139-5p targets Tspan3 and regulates the progression of acute myeloid leukemia through the PI3K/Akt pathway. J Cell Biochem, 120(3), 4423–4432.
Lei, W., Lin, J., Liu, F., & Chen, N. (2021). Long noncoding RNA GAS6 antisense RNA1 silencing attenuates the tumorigenesis of acute myeloid leukemia cells through targeting microRNA-370-3p/Tetraspanin3 axis. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc, 78(1), 69–81.
Funding
This study was supported by Ningbo Digestive System Cancer Clinical Medicine Research Center (2019A21003), and Medical and Health Science and Technology Program of Zhejiang Province (2023KY239).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XW and SZ: designed the experiments, and drafted the manuscript. LW and JM: collected the clinical samples and processed statistical data. YR, YZ and HS: performed the experiments and analyzed the data. XZ: designed, and supervised the study. HL: designed, supervised the study and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Ningbo Medical Center Li Huili Hospital. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for this study. All experiments were performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations and in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Zhou, S., Wang, L. et al. Circ_103809 Aggravates the Malignant Phenotype of Pancreatic Cancer Through Modulating miR-197-3p/TSPAN3 Axis. Mol Biotechnol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-00874-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-00874-0