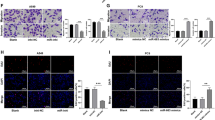
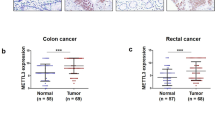
Abstract
METTL3 is an important methyltransferase in N(6)-methyladenosine (m6A) modification. Recently, METTL3 mediates methylation of pri-microRNA (miRNA) to accelerate miRNA maturation, regulating tumor development. This study explored whether METTL3 mediated miR-99a-5p to influence oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cell metastasis. MiR-99a-5p, ZBTB7A, and MATTL3 expression was measured using quantitative real-time PCR. Biological behaviors were assessed using cell counting kit-8, flow cytometry, Transwell assay, as well as western blot. Luciferase reporter assay evaluated the interaction between miR-99a-5p and ZBTB7A. METTL3-regulated pri-miR-99a-5p processing was determined by RNA binding protein immunoprecipitation (RIP) and methylated RNA immunoprecipitation (MeRIP) assays. The consequences clarified that miR-99a-5p was upregulated in OSCC cells. Downregulation of miR-99a-5p suppressed cellular viability, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and induced apoptosis. ZBTB7A acted as a miR-99a-5p target and reversed the effects on cellular behaviors induced by miR-99a-5p inhibitor. m6A content and METTL3 expression were increased in OSCC cells. METTL3 promoted the m6A modification of pri-miR-99a-5p and thereby facilitated miR-99a-5p processing. Moreover, knockdown of METTL3 inhibited OSCC metastasis by downregulating miR-99a-5p. Taken together, METTL3 promoted miR-99a-5p maturation in an m6A-dependent manner, which further targets ZBTB7A to accelerate the progression of OSCC. These findings suggest potential targets for OSCC therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Laversanne, M., Soerjomataram, I., Jemal, A., & Bray, F. (2021 May). Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. C Ca: A Cancer Journal For Clinicians, 71(3), 209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660.
Vitório, J. G., Duarte-Andrade, F. F., Dos Santos Fontes Pereira, T., Fonseca, F. P., Amorim, L. S. D., Martins-Chaves, R. R., Gomes, C. C., Canuto, G. A. B., & Gomez, R. S. Metabolic landscape of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Metabolomics 2020 Sep 30;16(10):105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-020-01727-6.
Chamoli, A., Gosavi, A. S., Shirwadkar, U. P., Wangdale, K. V., Behera, S. K., Kurrey, N. K., Kalia, K., & Mandoli, A. (2021 Oct). Overview of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: Risk factors, mechanisms, and diagnostics. Oral Oncology, 121, 105451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2021.105451.
Abdelmeguid, A. S., Silver, N. L., Boonsripitayanon, M., Glisson, B. S., Ferrarotto, R., Gunn, G. B., Phan, J., Gillenwater, A. M., & Hanna, E. Y. Role of induction chemotherapy for oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2021 Sep 1;127(17):3107–3112. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.33616.
Howard, A., Agrawal, N., & Gooi, Z. (2021 Oct). Lip and oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am, 35(5), 895–911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hoc.2021.05.003.
Yao, C. M. K. L., Chang, E. I., & Lai, S. Y. Contemporary Approach to Locally Advanced Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Curr Oncol Rep. 2019 Nov 7;21(11):99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-019-0845-8.
Montagnani, F., Fornaro, L., Frumento, P., Vivaldi, C., Falcone, A., & Fioretto, L. (2017 Jun). Multimodality treatment of locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the oesophagus: A comprehensive review and network meta-analysis. Critical Reviews In Oncology Hematology, 114, 24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.03.024.
Tomioka, H., Yamagata, Y., Oikawa, Y., Ohsako, T., Kugimoto, T., Kuroshima, T., Hirai, H., Shimamoto, H., & Harada, H. Risk factors for distant metastasis in locoregionally controlled oral squamous cell carcinoma: A retrospective study. Sci Rep 2021 Mar 4;11(1):5213. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-84704-w.
Rupaimoole, R., & Slack, F. J. (2017 Mar). MicroRNA therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery, 16(3), 203–222. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2016.246.
Hill, M., & Tran, N. miRNA interplay: mechanisms and consequences in cancer. Dis Model Mech. 2021 Apr 1;14(4):dmm047662. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.047662.
Rajan, C., Roshan, V. G. D., Khan, I., Manasa, V. G., Himal, I., Kattoor, J., Thomas, S., Kondaiah, P., & Kannan, S. MiRNA expression profiling and emergence of new prognostic signature for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 31;11(1):7298. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-86316-w.
Jadhav, K. B., Nagraj, S. K., & Arora, S. (2021 Apr). miRNA for the assessment of lymph node metastasis in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma: Systematic review and metanalysis. Journal Of Oral Pathology And Medicine, 50(4), 345–352. https://doi.org/10.1111/jop.13134.
Gregory, R. I., Yan, K. P., Amuthan, G., Chendrimada, T., Doratotaj, B., Cooch, N., & Shiekhattar, R. The Microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs. Nature. 2004 Nov 11;432(7014):235 – 40. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03120.
Bernstein, E., Caudy, A. A., Hammond, S. M., & Hannon, G. J. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature. 2001 Jan 18;409(6818):363-6. https://doi.org/10.1038/35053110.
Jakob, M., Mattes, L. M., Küffer, S., Unger, K., Hess, J., Bertlich, M., Haubner, F., Ihler, F., Canis, M., Weiss, B. G., & Kitz, J. (2019 Oct). MicroRNA expression patterns in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Hsa-mir-99b-3p and hsa-mir-100-5p as novel prognostic markers for oral cancer. Head And Neck, 41(10), 3499–3515. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.25866.
Sun, X., & Yan, H. (2021 May). MicroRNA-99a-5p suppresses cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting isoprenylcysteine carboxylmethyltransferase in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Journal Of International Medical Research, 49(5), 300060520939031. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060520939031.
Liu, Z., & Zhang, J. Human C-to-U Coding RNA Editing Is Largely Nonadaptive. Mol Biol Evol. 2018 Jul 1;35(7):1821. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy011.
Liu, Z. X., Li, L. M., Sun, H. L., & Liu, S. M. Link between m6A modification and cancers. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2018 Jul 13;6:89. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2018.00089.
Han, X., Guo, J., & Fan, Z. Interactions between m6A modification and miRNAs in malignant tumors. Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jun 9;12(6):598. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-03868-5.
Alarcón, C. R., Lee, H., Goodarzi, H., Halberg, N., & Tavazoie, S. F. N6-methyladenosine marks primary microRNAs for processing. Nature 2015 Mar 26;519(7544):482–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14281.
Zeng, C., Huang, W., Li, Y., & Weng, H. Roles of METTL3 in cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic targeting. J Hematol Oncol 2020 Aug 27;13(1):117. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00951-w.
Gong, Y., Jiang, Q., Liu, L., Liao, Q., Yu, J., Xiang, Z., & Luo, X. (2022). METTL3-mediated m6A modification promotes processing and maturation of pri-miRNA-19a to facilitate nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation and invasion. Physiol Genomics. Sep 1;54(9):337–349. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00007.2022.
Han, J., Wang, J. Z., Yang, X., Yu, H., Zhou, R., Lu, H. C., Yuan, W. B., Lu, J. C., Zhou, Z. J., Lu, Q., Wei, J. F., & Yang, H. METTL3 promote tumor proliferation of bladder cancer by accelerating pri-miR221/222 maturation in m6A-dependent manner. Mol Cancer 2019 Jun 22;18(1):110. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1036-9.
Mishra, S., Yadav, T., & Rani, V. (2016 Feb). Exploring miRNA based approaches in cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. Critical Reviews In Oncology Hematology, 98, 12–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2015.10.003.
Li, Y., Yan, J., Wang, Y., Wang, C., Zhang, C., & Li, G. (2020 Dec). LINC00240 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration and EMT via the miR-124-3p / DNMT3B axis. Cell Biochemistry And Function, 38(8), 1079–1088. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbf.3551.
Yoshimura, A., Sawada, K., Nakamura, K., Kinose, Y., Nakatsuka, E., Kobayashi, M., Miyamoto, M., Ishida, K., Matsumoto, Y., Kodama, M., Hashimoto, K., Mabuchi, S., & Kimura, T. Exosomal miR-99a-5p is elevated in sera of ovarian cancer patients and promotes cancer cell invasion by increasing fibronectin and vitronectin expression in neighboring peritoneal mesothelial cells. BMC Cancer 2018 Nov 5;18(1):1065. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4974-5.
Garrido-Cano, I., Constâncio, V., Adam-Artigues, A., Lameirinhas, A., Simón, S., Ortega, B., Martínez, M. T., Hernando, C., Bermejo, B., Lluch, A., Lopes, P., Henrique, R., Jerónimo, C., Cejalvo, J. M., & Eroles, P. Circulating miR-99a-5p Expression in Plasma: A Potential Biomarker for Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 8;21(19):7427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197427.
Shi, J., Bao, X., Liu, Z., Zhang, Z., Chen, W., & Xu, Q. Serum miR-99a-5p and miR-5100 are Promising Prognosis Predictors for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Theranostics. 2019 Jan 25;9(4):920–931. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.30339.
Cui, S. H., Hu, X. D., & Yan, Y. (2021 Nov). Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway participates in the effect of miR-99a-5p on oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting RASSF4. Journal Of Oral Pathology And Medicine, 50(10), 1005–1017. https://doi.org/10.1111/jop.13216.
Singh, A. K., Verma, S., Kushwaha, P. P., Prajapati, K. S., Shuaib, M., Kumar, S., & Gupta, S. Role of ZBTB7A zinc finger in tumorigenesis and metastasis. Mol Biol Rep 2021 May;48(5):4703–4719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06405-x.
Wang, G., Lunardi, A., Zhang, J., Chen, Z., Ala, U., Webster, K. A., Tay, Y., Gonzalez-Billalabeitia, E., Egia, A., Shaffer, D. R., Carver, B., Liu, X. S., Taulli, R., Kuo, W. P., Nardella, C., Signoretti, S., Cordon-Cardo, C., Gerald, W. L., & Pandolfi, P. P. (2013 Jul). Zbtb7a suppresses prostate cancer through repression of a Sox9-dependent pathway for cellular senescence bypass and tumor invasion. Nature Genetics, 45(7), 739–746. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2654.
Liu, X. S., Haines, J. E., Mehanna, E. K., Genet, M. D., Ben-Sahra, I., Asara, J. M., Manning, B. D., & Yuan, Z. M. ZBTB7A acts as a tumor suppressor through the transcriptional repression of glycolysis. Genes Dev. 2014 Sep 1;28(17):1917-28. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.245910.114.
Yeh, L. Y., Yang, C. C., Wu, H. L., Kao, S. Y., Liu, C. J., Chen, Y. F., Lin, S. C., & Chang, K. W. The miR-372-ZBTB7A Oncogenic Axis suppresses TRAIL-R2 Associated Drug Sensitivity in oral carcinoma. Front Oncol 2020 Jan 31;10:47. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.00047.
Liu, S., Zhuo, L., Wang, J., Zhang, Q., Li, Q., Li, G., Yan, L., Jin, T., Pan, T., Sui, X., Lv, Q., & Xie, T. METTL3 plays multiple functions in biological processes. Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Jun 1;10(6):1631–1646.
Yi, Y. C., Chen, X. Y., Zhang, J., & Zhu, J. S. Novel insights into the interplay between m6A modification and noncoding RNAs in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020 Aug 7;19(1):121. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01233-2.
Nogami, M., Miyamoto, K., Hayakawa-Yano, Y., Nakanishi, A., Yano, M., & Okano, H. DGCR8-dependent efficient pri-miRNA processing of human pri-miR-9-2. J Biol Chem 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100409.
Bi, X., Lv, X., Liu, D., Guo, H., Yao, G., Wang, L., Liang, X., & Yang, Y. METTL3-mediated maturation of mir-126-5p promotes ovarian cancer progression via PTEN-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Cancer Gene Ther 2021 Apr;28(3–4):335–349. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00222-3.
Peng, W., Li, J., Chen, R., Gu, Q., Yang, P., Qian, W., Ji, D., Wang, Q., Zhang, Z., Tang, J., & Sun, Y. Upregulated METTL3 promotes metastasis of colorectal Cancer via miR-1246/SPRED2/MAPK signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Sep 6;38(1):393. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1408-4.
Liu, L., Wu, Y., Li, Q., Liang, J., He, Q., Zhao, L., Chen, J., Cheng, M., Huang, Z., Ren, H., Chen, J., Peng, L., Gao, F., Chen, D., & Wang, A. METTL3 Promotes Tumorigenesis and Metastasis through BMI1 m6A Methylation in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Mol Ther. 2020 Oct 7;28(10):2177–2190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.06.024.
Zhao, W., Cui, Y., Liu, L., Ma, X., Qi, X., Wang, Y., Liu, Z., Ma, S., Liu, J., & Wu, J. METTL3 facilitates oral squamous cell Carcinoma Tumorigenesis by enhancing c-Myc Stability via YTHDF1-Mediated m6A modification. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2020 Jun 5;20:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2020.01.033.
Funding
This study was supported by Research Project of TCM Bureau of Guangdong Province(Project name: Study on the mechanism of inhibiting invasion and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma by reducing the m6A modification level of miR-99a-5p by downregulating METTL3, Project number: 20222084).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12033_2023_815_MOESM4_ESM.jpg
Supplementary Material 4: Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of miR-99a-5p on the biological functions of HOK cells. After HOK cells were transfected with miR-99a-5p mimic and mimic nc, (A) cell viability was evaluated using CCK-8; (B,C) cell migration and (D,E) invasion were evaluated by Transwell assay.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Guan, Y. & Zhang, X. METTL3-Mediated Maturation of miR-99a-5p Promotes Cell Migration and Invasion in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Targeting ZBTB7A. Mol Biotechnol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-00815-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-00815-x