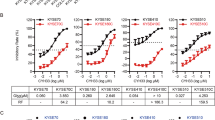
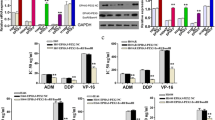
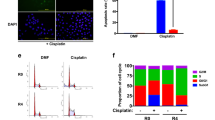
Abstract
Chemo-resistance has been identified as a crucial factor contributing to tumor recurrence and a leading cause of worse prognosis in patients with ESCC. Therefore, unravel the critical regulators and effective strategies to overcome drug resistance will have a significant clinical impact on the disease. In our study we found that RNF149 was upregulated in ESCC and high RNF149 expression was associated with poor prognosis with ESCC patients. Functionally, we have demonstrated that overexpression of RNF149 confers CDDP resistance to ESCC; however, inhibition of RNF149 reversed this phenomenon both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, we demonstrated that RNF149 interacts with PH domain and leucine rich repeat protein phosphatase 2 (PHLPP2) and induces E3 ligase-dependent protein degradation of PHLPP2, substantially activating the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in ESCC. Additionally, we found that inhibition of PI3K/AKT signalling pathway by AKT siRNA or small molecule inhibitor significantly suppressed RNF149-induced CDDP resistance. Importantly, RNF149 locus was also found to be amplified not only in ESCC but also in various human cancer types. Our data suggest that RNF149 might function as an oncogenic gene. Targeting the RNF149/PHLPP2/PI3K/Akt axis may be a promising prognostic factor and valuable therapeutic target for malignant tumours.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424.
Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ. Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(23):2241–52.
Kadian LK, Arora M, Prasad CP, Pramanik R, Chauhan SS. Signaling pathways and their potential therapeutic utility in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol. 2022;24:1014–32.
Li B, Xu WW, Lam AKY, Wang Y, Hu HF, Guan XY, Qin YR, Saremi N, Tsao SW, He QY, et al. Significance of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its potential as a target for anti-metastasis therapy. Oncotarget. 2017;8(24):38755–66.
Deng L, Wu X, Zhu X, Yu Z, Liu Z, Wang J, Zheng Y. Combination effect of curcumin with docetaxel on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway to induce autophagy and apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(1):57–72.
Wang L, Zhang Z, Yu X, Li Q, Wang Q, Chang A, Huang X, Han X, Song Y, Hu J, et al. SOX9/miR-203a axis drives PI3K/AKT signaling to promote esophageal cancer progression. Cancer Lett. 2020;468:14–26.
Wang H, Yang X, Guo Y, Shui L, Li S, Bai Y, Liu Y, Zeng M, Xia J. HERG1 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma growth and metastasis through TXNDC5 by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):324.
Yu J, Wang W, Yao W, Yang Z, Gao P, Liu M, Wang H, Chen S, Wang D, Wang W, et al. Gambogic acid affects ESCC progression through regulation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signal pathway. J Cancer. 2020;11(19):5568–77.
Wang Y, Lyu Z, Qin Y, Wang X, Sun L, Zhang Y, Gong L, Wu S, Han S, Tang Y, et al. FOXO1 promotes tumor progression by increased M2 macrophage infiltration in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Theranostics. 2020;10(25):11535–48.
Hillier LW, Graves TA, Fulton RS, Fulton LA, Pepin KH, Minx P, Wagner-McPherson C, Layman D, Wylie K, Sekhon M, et al. Generation and annotation of the DNA sequences of human chromosomes 2 and 4. Nature. 2005;434(7034):724–31.
Won S, Jung J, Park E, Kim H. Identification of genes related to intramuscular fat content of pigs using genome-wide association study. Asian Austral J Anim Sci. 2018;31(2):157–62.
Loomis SJ, Klein AP, Lee KE, Chen F, Bomotti S, Truitt B, Iyengar SK, Klein R, Klein BEK, Duggal P. Exome array analysis of nuclear lens opacity. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2018;25(3):215–9.
Beckner ME, Pollack IF, Nordberg ML, Hamilton RL. Glioblastomas with copy number gains in EGFR and RNF139 show increased expressions of carbonic anhydrase genes transformed by ENO1. BBA Clin. 2016;5:1–15.
Hong SW, Jin DH, Shin JS, Moon JH, Na YS, Jung KA, Kim SM, Kim JC, Kim KP, Hong YS, et al. Ring finger protein 149 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase active on wild-type v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1 (BRAF). J Biol Chem. 2012;287(28):24017–25.
Nair VS, Gevaert O, Davidzon G, Napel S, Graves EE, Hoang CD, Shrager JB, Quon A, Rubin DL, Plevritis SK. Prognostic PET 18F-FDG uptake imaging features are associated with major oncogenomic alterations in patients with resected non-small cell lung cancer. Can Res. 2012;72(15):3725–34.
Shimada Y, Imamura M, Wagata T, Yamaguchi N, Tobe T. Characterization of 21 newly established esophageal cancer cell lines. Cancer. 1992;69(2):277–84.
He S, Niu G, Shang J, Deng Y, Wan Z, Zhang C, You Z, Shen H. The oncogenic Golgi phosphoprotein 3 like overexpression is associated with cisplatin resistance in ovarian carcinoma and activating the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017;36(1):137.
Zhu J, Wu Y, Lao S, Shen J, Yu Y, Fang C, Zhang N, Li Y, Zhang R. Targeting TRIM54/Axin1/beta-catenin axis prohibits proliferation and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2021;11: 759842.
Lin C, Liu A, Zhu J, Zhang X, Wu G, Ren P, Wu J, Li M, Li J, Song L. miR-508 sustains phosphoinositide signalling and promotes aggressive phenotype of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4620.
Cha JH, Jeong Y, Oh AR, Lee SB, Hong SS, Kim K. Emerging roles of PHLPP phosphatases in metabolism. BMB Rep. 2021;54(9):451–7.
Hribal ML, Mancuso E, Spiga R, Mannino GC, Fiorentino TV, Andreozzi F, Sesti G. PHLPP phosphatases as a therapeutic target in insulin resistance-related diseases. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2016;20(6):663–75.
Newton AC, Trotman LC. Turning off AKT: PHLPP as a drug target. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014;54:537–58.
Grzechnik AT, Newton AC. PHLPPing through history: a decade in the life of PHLPP phosphatases. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016;44(6):1675–82.
Baffi TR, Cohen-Katsenelson K, Newton AC. PHLPPing the script: emerging roles of PHLPP phosphatases in cell signaling. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021;61:723–43.
Fruman DA, Chiu H, Hopkins BD, Bagrodia S, Cantley LC, Abraham RT. The PI3K pathway in human disease. Cell. 2017;170(4):605–35.
Fresno Vara JA, Casado E, de Castro J, Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C, González-Barón M. PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2004;30(2):193–204.
Xie Y, Shi X, Sheng K, Han G, Li W, Zhao Q, Jiang B, Feng J, Li J, Gu Y. PI3K/Akt signaling transduction pathway, erythropoiesis and glycolysis in hypoxia (review). Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(2):783–91.
Thorpe LM, Yuzugullu H, Zhao JJ. PI3K in cancer: divergent roles of isoforms, modes of activation and therapeutic targeting. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15(1):7–24.
Revathidevi S, Munirajan AK. Akt in cancer: mediator and more. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019;59:80–91.
Yang Q, Jiang W, Hou P. Emerging role of PI3K/AKT in tumor-related epigenetic regulation. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019;59:112–24.
Shi N, Yu H, Chen T. Inhibition of esophageal cancer growth through the suppression of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:7637–47.
Zhou S, Guo Z, Zhou C, Zhang Y, Wang S. Circ_NRIP1 is oncogenic in malignant development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) via miR-595/SEMA4D axis and PI3K/AKT pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21(1):250.
Xu JC, Chen TY, Liao LT, Chen T, Li QL, Xu JX, Hu JW, Zhou PH, Zhang YQ. NETO2 promotes esophageal cancer progression by inducing proliferation and metastasis via PI3K/AKT and ERK pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(1):259–70.
Liu S, Jiang H, Min L, Ning T, Xu J, Wang T, Wang X, Zhang Q, Cao R, Zhang S, et al. Lysophosphatidic acid mediated PI3K/Akt activation contributed to esophageal squamous cell cancer progression. Carcinogenesis. 2021;42(4):611–20.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82103637).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JZ and RZ designed all experiments, supervised the project, and wrote the manuscript. YW and XQ conducted the molecular cloning and performed all the in vitro experiments. JT and XJ performed the in vivo experiments.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Tang, J., Wu, Y. et al. RNF149 confers cisplatin resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via destabilization of PHLPP2 and activating PI3K/AKT signalling. Med Oncol 40, 290 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-023-02137-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-023-02137-z