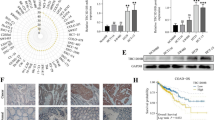
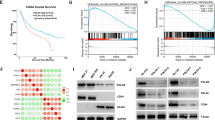
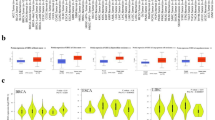
Abstract
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third leading malignancy worldwide in both new cases and deaths. Neoadjuvant radiotherapy is the standard preoperative regimens for locally advanced patients. However, approximately 50% of patients develop recurrence and metastasis after radiotherapy, which is largely due to the radiation resistance properties of the tumor, and the internal mechanism has not been elucidated. Here we found that CEMIP expression is up-regulated in a variety of tumor types, particularly in CRC. Public databases and clinical samples revealed that CEMIP expression is significantly higher in tumor tissues than in adjacent normal tissues in patients with locally advanced CRC who received neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy, and it is closely related to the poor prognosis. Functional characterization uncovered that downregulation of CEMIP expression can enhance the radiosensitivity of CRC cells, which is confirmed to be achieved by promoting DNA damage and apoptosis. In vivo studies further verified that CEMIP knockdown can significantly improve the radiosensitivity of subcutaneously implanted colorectal tumors in mice, suggesting that CEMIP may be a radiation-resistant gene in CRC. Mechanistically, EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is hypothesized to play a key role in CEMIP mediating radiation resistance. These results provide a potential new strategy targeting CEMIP gene for the comprehensive treatment of locally advanced CRC patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72(1):7–33.
Ringborg U, Bergqvist D, Brorsson B, Cavallin-Ståhl E, Ceberg J, Einhorn N, et al. The Swedish council on technology assessment in health care (SBU) systematic overview of radiotherapy for cancer including a prospective survey of radiotherapy practice in Sweden 2001–summary and conclusions. Acta Oncol. 2003;42(5–6):357–65.
Benson AB, Venook AP, Al-Hawary MM, Cederquist L, Chen YJ, Ciombor KK et al: Anal Carcinoma, Version 2.2018, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2018, 16(7):852–871.
Sauer R, Becker H, Hohenberger W, Rödel C, Wittekind C, Fietkau R, et al. Preoperative versus postoperative chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(17):1731–40.
Wang XC, Yue X, Zhang RX, Liu TY, Pan ZZ, Yang MJ, et al. Genome-wide RNAi screening identifies RFC4 as a factor that mediates radioresistance in colorectal cancer by facilitating nonhomologous end joining repair. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25(14):4567–79.
Monson JR, Probst CP, Wexner SD, Remzi FH, Fleshman JW, Garcia-Aguilar J, et al. Failure of evidence-based cancer care in the United States: the association between rectal cancer treatment, cancer center volume, and geography. Ann Surg. 2014;260(4):625–31.
Uehara K, Nagino M. Neoadjuvant treatment for locally advanced rectal cancer: a systematic review. Surg Today. 2016;46(2):161–8.
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108.
Brenner H, Kloor M, Pox CP. Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 2014;383(9927):1490–502.
Lorimer PD, Motz BM, Kirks RC, Boselli DM, Walsh KK, Prabhu RS, et al. Pathologic complete response rates after neoadjuvant treatment in rectal cancer: an analysis of the national cancer database. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017;24(8):2095–103.
Spataro S, Guerra C, Cavalli A, Sgrignani J, Sleeman J, Poulain L et al. (2022) CEMIP (HYBID, KIAA1199): structure, function and expression in health and disease. Febs J
Matsuzaki S, Tanaka F, Mimori K, Tahara K, Inoue H, Mori M. Clinicopathologic significance of KIAA1199 overexpression in human gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16(7):2042–51.
Birkenkamp-Demtroder K, Maghnouj A, Mansilla F, Thorsen K, Andersen CL, Øster B, et al. Repression of KIAA1199 attenuates Wnt-signalling and decreases the proliferation of colon cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2011;105(4):552–61.
Liu J, Han P, Gong J, Wang Y, Chen B, Liao J, et al. Knockdown of KIAA1199 attenuates growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Discov. 2018;4:102.
Kuscu C, Evensen N, Kim D, Hu YJ, Zucker S, Cao J. Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of KIAA1199 gene expression in human breast cancer. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(9):e44661.
Koga A, Sato N, Kohi S, Yabuki K, Cheng XB, Hisaoka M, et al. KIAA1199/CEMIP/HYBID overexpression predicts poor prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreatology. 2017;17(1):115–22.
Zhang P, Song Y, Sun Y, Li X, Chen L, Yang L, et al. AMPK/GSK3β/β-catenin cascade-triggered overexpression of CEMIP promotes migration and invasion in anoikis-resistant prostate cancer cells by enhancing metabolic reprogramming. Faseb j. 2018;32(7):3924–35.
Shen F, Zong ZH, Liu Y, Chen S, Sheng XJ, Zhao Y. CEMIP promotes ovarian cancer development and progression via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;114:108787.
Evensen NA, Li Y, Kuscu C, Liu J, Cathcart J, Banach A, et al. Hypoxia promotes colon cancer dissemination through up-regulation of cell migration-inducing protein (CEMIP). Oncotarget. 2015;6(24):20723–39.
Qian J, Rankin EB. Hypoxia-induced phenotypes that mediate tumor heterogeneity. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1136:43–55.
Semenza GL. Intratumoral hypoxia, radiation resistance, and HIF-1. Cancer Cell. 2004;5(5):405–6.
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y, He QY. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS. 2012;16(5):284–7.
Zhang Y, Zheng L, Ding Y, Li Q, Wang R, Liu T, et al. MiR-20a induces cell radioresistance by activating the PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015;92(5):1132–40.
Monson JR, Weiser MR, Buie WD, Chang GJ, Rafferty JF, Buie WD, et al. Practice parameters for the management of rectal cancer (revised). Dis Colon Rectum. 2013;56(5):535–50.
Ngan SY, Burmeister B, Fisher RJ, Solomon M, Goldstein D, Joseph D, et al. Randomized trial of short-course radiotherapy versus long-course chemoradiation comparing rates of local recurrence in patients with T3 rectal cancer: trans-Tasman radiation oncology group trial 01.04. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(31):3827–33.
Evensen NA, Kuscu C, Nguyen HL, Zarrabi K, Dufour A, Kadam P, et al. Unraveling the role of KIAA1199, a novel endoplasmic reticulum protein, in cancer cell migration. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105(18):1402–16.
Tang L, Wei F, Wu Y, He Y, Shi L, Xiong F, et al. Role of metabolism in cancer cell radioresistance and radiosensitization methods. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37(1):87.
Zhao L, Zhang D, Shen Q, Jin M, Lin Z, Ma H, et al. KIAA1199 promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer cells via microtubule destabilization regulated by a PP2A/stathmin pathway. Oncogene. 2019;38(7):935–49.
Chen Y, Zhou H, Jiang WJ, Wang JF, Tian Y, Jiang Y, et al. The role of CEMIP in tumors: an update based on cellular and molecular insights. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;146:112504.
Cabrera-Licona A, Pérez-Añorve IX, Flores-Fortis M, Moral-Hernández OD, la González-de RCH, Suárez-Sánchez R, et al. Deciphering the epigenetic network in cancer radioresistance. Radiother Oncol. 2021;159:48–59.
Shrivastava S, Mansure JJ, Almajed W, Cury F, Ferbeyre G, Popovic M, et al. The role of HMGB1 in radioresistance of bladder cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016;15(3):471–9.
Eder S, Arndt A, Lamkowski A, Daskalaki W, Rump A, Priller M, et al. Baseline MAPK signaling activity confers intrinsic radioresistance to KRAS-mutant colorectal carcinoma cells by rapid upregulation of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K). Cancer Lett. 2017;385:160–7.
Delaney G, Jacob S, Featherstone C, Barton M. The role of radiotherapy in cancer treatment: estimating optimal utilization from a review of evidence-based clinical guidelines. Cancer. 2005;104(6):1129–37.
Haustermans K, Debucquoy A, Lambrecht M. The ESTRO Breur Lecture 2010: toward a tailored patient approach in rectal cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2011;100(1):15–21.
Leiker AJ, DeGraff W, Choudhuri R, Sowers AL, Thetford A, Cook JA, et al. Radiation enhancement of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by the dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor PF-05212384. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(12):2792–801.
Tang Z, Ding Y, Shen Q, Zhang C, Li J, Nazar M, et al. KIAA1199 promotes invasion and migration in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) via PI3K-Akt mediated EMT. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019;97(1):127–40.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China 81803063 to Yiyi Li, 82273564, 82073342, 81872470 to Yi Ding, 81903125 to Yuqin Zhang, and 82170647 to Kai Wang, the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong, China 2018030310297 to Yiyi Li, and 2020A1515011205 to Kai Wang, the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou, China 202102020976 to Yiyi Li, and 202206010045 to Yi Ding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by JW, YZ, WL, YX, KW and QX. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YL and YD. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
The protocol was approved by the institutional ethics committee (Identifier: NFEC-2022-367), and all patients provided written informed consent.
Consent for publication
N/A.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Weng, J., Zhang, Y., Liang, W. et al. Downregulation of CEMIP enhances radiosensitivity by promoting DNA damage and apoptosis in colorectal cancer. Med Oncol 40, 73 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-022-01940-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-022-01940-4