Abstract
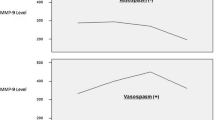
Delayed cerebral ischemia (DCI) is one of the major causes of a poor neurological outcome following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH). Several biomarkers, including matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), have been evaluated to predict the development of DCI for timely management. This prospective cohort study was done on 98 patients with aSAH presenting within 72 h of the ictus. Serum samples were collected preoperatively, 7 days after ictus, 10 days after ictus, or when the patient developed DCI, whichever was earlier. The primary objective was to correlate the serum MMP-9 levels with the development of DCI. The secondary objectives were to correlate the serum MMP-9 levels with sonographic vasospasm and the neurological outcome. There was no correlation between the serum MMP-9 levels and the development of DCI (p = 0.37). Similarly, there was no correlation between the serum MMP-9 levels and the sonographic vasospasm (0.05) nor with the modified Rankin Scale (mRS) at discharge (p = 0.27), mRS at 3 months (p = 0.22), and Glasgow Outcome Scale Extended (GOSE) at 3 months (p = 0.15). Serum MMP-9 levels do not predict the development of DCI following aSAH.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Available by reasonable request from the corresponding author.
References
Akpinar A, Ucler N, Erdogan U, Baydin SS, Gungor A, Tugcu B (2016) Measuring serum matrix metalloproteinase-9 levels in peripheral blood after subarachnoid hemorrhage to predict cerebral vasospasm. Springerplus 22:1153. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-2837-6
Chan V, Lindsay P, McQuiggan J, Zagorski B, Hill MD, O’Kelly C (2019) Declining admission and mortality rates for subarachnoid hemorrhage in Canada between 2004 and 2015. Stroke 50(1):181–184. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.022332. Epub 2018 Nov 21. PMID: 30580710
Chang JJ, Triano M, Corbin MJ, Desale S, Liu AH, Felbaum DR et al (2020) Transcranial Doppler velocity and associations with delayed cerebral ischemia in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurol Sci 15(415):116934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2020.116934
Chou SHY, Feske SK, Simmons SL, Konisberg GJ, Orzell SC (2011) Elevated peripheral neutrophils and matrix metalloproteinase 9 as biomarkers of functional outcome following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Transl Stroke Res 2:600–607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-011-0117-x
Dang B, Shen H, Li H, Zhu M, Guo C, He W (2016) Matrix metalloproteinase 9 may be involved in contraction of vascular smooth muscle cells in an in vitro rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Mol Med Rep 14:4279–4284. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5736
Feigin VL, Lawes CM, Bennett DA, Barker-Collo SL, Parag V (2009) Worldwide stroke incidence and early case fatality reported in 56 population-based studies: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol 8:355–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70025-0
Fischer M, Dietmann A, Beer R, Broessner G, Helbok R, Pfausler B et al (2013) Differential regulation of matrix-metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. PLoS ONE 8:e59952. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059952
Kiiski H, Långsjö J, Tenhunen J, Ala-Peijari M, Huhtala H, Hämäläinend M et al (2018) S100B, NSE and MMP-9 fail to predict neurologic outcome while elevated S100B associates with milder initial clinical presentation after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurol Sci 15(390):129–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2018.04.030
Mc Girt MJ, Lynch JR, Blessing R, Warner DS, Friedman AH, Laskowitx DT (2002) Serum von Willebrand factor, matrix metalloproteinase 9, and vascular endothelial growth factor levels predict the onset of cerebral vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 51:1128–1134. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-200211000-00005
Mehta V, Russin J, Spirtos A, He S, Adamczyk P, Amar AP, Mack WJ (2013) Matrix metalloproteinases in cerebral vasospasm following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurol Res Int 2013:943761. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/943761. Epub 2013 Apr 3. PMID: 23691315; PMCID: PMC3649803
Rosenberg GA (1995) Matrix metalloproteinases in brain injury. J Neurotrauma 12:833–842. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.1995.12.833
Rowland MJ, Hsdjipavlou G, Kelly M, Westbrook J, Pattinson KTS (2012) Delayed cerebral ischaemia after subarachnoid haemorrhage: looking beyond vasospasm. Br J Anaesth 109:315–329. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aes264
Samagh N, Bhagat H, Jangra K (2019) Monitoring cerebral vasospasm: how much can we rely on transcranial Doppler. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol 35:12–18. https://doi.org/10.4103/joacp.JOACP_192_17
Sharma T, Datta KK, Kumar M, Dey G, Khan AA, Mangalaparthi KK et al (2020) Intracranial aneurysm biomarker candidates identified by a proteome-wide study. OMICS 24:483–492. https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2020.0057
Triglia T, Mezzapesa A, Martin JC, Verdier M, Lagier D (2016) Early matrix metalloproteinase-9 concentration in the first 48h after aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage predicts delayed cerebral ischaemia. Eur J Anaesthesiol 33:662–669. https://doi.org/10.1097/EJA.0000000000000494
Vergouwen MDI, Vermeulen M, van Gijn J, Rinkel GJE, Wijdicks EF et al (2010) Definition of delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage as an outcome event in clinical trials and observational studies: proposal of a multidisciplinary research group. Stroke 41:2391–2395. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.589275
Wang Z, Fang Q, Dang BQ, Shen XM, Shu Z, Zuo G, He WC, Chen G (2012) Potential contribution of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (mmp-9) to cerebral vasospasm after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Ann Clin Lab Sci 42(1):14–20 PMID: 22371905
Funding
Received institutional research grant for the purchase of the ELSIA kits.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. The data collection was done by V.N. and A.D. The biochemical analysis was performed by M.K. and the data analysis was performed by V.G. and H.B. The first draft of the manuscript was written by V.N. and S.M. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Ethical clearance was received from the Institutional Ethical Committee, approval number: INT/IEC/2021/712.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Narayan, V., Kumar, M., Mahajan, S. et al. The Role of Serum Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 as a Predictor of Delayed Cerebral Ischemia in Patients with Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. J Mol Neurosci 74, 18 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-024-02194-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-024-02194-7