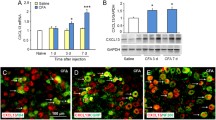
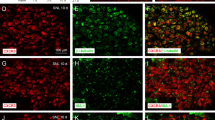
Abstract
Tissue injury, pathogen infection, and diseases are often accompanied by inflammation to release mediators that sensitize nociceptors and further recruit immune cells, which can lead to chronic hyperalgesia and inflammation. Tissue acidosis, occurring at the inflammatory site, is a major factor contributing to pain and hyperalgesia. The receptor G2 accumulation (G2A), expressed in neurons and immune cells, responds to protons or oxidized free fatty acids such as 9-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid produced by injured cells or oxidative stresses. We previously found increased G2A expression in mouse dorsal root ganglia (DRG) at 90 min after complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA)-induced inflammatory pain, but whether G2A is involved in the inflammation or hyperalgesia remained unclear. In this study, we overexpressed or knocked-down G2A gene expression in DRG to explore the roles of G2A. G2A overexpression reduced the infiltration of acute immune cells (granulocytes) and attenuated hyperalgesia at 90 to 240 min after CFA injection. G2A knockdown increased the number of immune cells before CFA injection and prolonged the inflammatory hyperalgesia after CFA injection. G2A may serve as a threshold regulator in neurons to attenuate the initial nociceptive and inflammatory signals, modulating the chronic state of hyperalgesia.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolick DT, Whetzel AM, Skaflen M, Deem TL, Lee J, Hedrick CC (2007) Absence of the G protein-coupled receptor G2A in mice promotes monocyte/endothelial interactions in aorta. Circ Res 100(4):572–580. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000258877.57836.d2
Chen YJ, Huang CH, Lin CS, Chang WH, Sun WH (2009) Expression and function of proton-sensing G-protein-coupled receptors in inflammatory pain. Mol Pain 5:39. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-5-39
Courtright LJ, Kuzell WC (1965) Sparing effect of neurological deficit and trauma on the course of adjuvant arthritis in the rat. Ann Rheum Dis 24(4):360–368. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.24.4.360
Colpaert FC, Donnerer J, Lembeck F (1983) Effects of capsaicin on inflammation and on the substance P content of nervous tissues in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Life Sci 32(16):1827–1834. https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-3205(83)90060-7
Dai SP, Huang YH, Chang CJ, Huang YF, Hsieh WS, Tabata Y, Ishii S, Sun WH (2017) TDAG8 involved in initiating inflammatory hyperalgesia and establishing hyperalgesic priming in mice. Sci Rep 7:41415. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41415
Frasch SC, Fernandez-Boyanapalli RF, Berry KZ, Leslie CC, Bonventre JV, Murphy RC, Henson PM, Bratton DL (2011) Signaling via macrophage G2A enhances efferocytosis of dying neutrophils by augmentation of Rac activity. J Biol Chem 286(14):12108–12122. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.181800
Frasch SC, Fernandez-Boyanapalli RF, Berry KA, Murphy RC, Leslie CC, Nick JA, Henson PM, Bratton DL (2013) Neutrophils regulate tissue neutrophilia in inflammation via the oxidant-modified lipid lysophosphatidylserine. J Biol Chem 288(7):4583–4593. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.438507
Frasch SC, McNamee EN, Kominsky D, Jedlicka P, Jakubzick C, Berry KZ, Mack M, Furuta GT, Lee JJ, Henson PM, Colgan SP, Bratton DL (2016) G2A signaling dampens colitic inflammation via production of IFN-γ. J Immunol 197(4):1425–1434. https://doi.org/10.4049/ jimmunol.1600264
Geering B, Stoeckle C, Conus S, Simon HU (2013) Living and dying for inflammation: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils. Trends Immunol 34(8):398–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2013.04.002
Hattori T, Obinata H, Ogawa A, Kishi M, Tatei K, Ishikawa O, Izumi T (2008) G2A plays proinflammatory roles in human keratinocytes under oxidative stress as a receptor for 9-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid. J Investig Dermatol 128(5):1123–1133. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jid.5701172
Hohmann SW, Angioni C, Tunaru S, Lee S, Woolf C, Offermanns S, Geisslinger G, Scholich K, Sisignano M (2017) The G2A receptor (GPR132) contributes to oxaliplatin-induced mechanical pain hyperalsnesitivity. Sci Rep 7(1):446. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00591-0
Huang CH, Tzeng JN, Chen YJ, Tsai WF, Chen CC, Sun WH (2007) Nociceptors of dorsal root ganglion express proton-sensing G-protein-coupled receptors. Mol Cell Neurosci 36(2):195–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2007.06.010
Huang WY, Dai SP, Chang YC, Sun WH (2015) Acidosis mediates the switching of Gs-PKA and Gi-PKCε dependence in prolonged hyperalgesia induced by inflammation. PLoS One 10(5):e0125022. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0125022
Huang YH, Su YS, Chang CJ, and Sun, WH. (2016) Heteromerization of OGR1 and G2A enhance proton signaling. J receptor & signal transduction 6:1–12
Kabarowski JH, Feramisco JD, Le LQ, Gu JL, Luoh SW, Simon MI, Witte ON (2000) Direct genetic demonstration of G alpha 13 coupling to the orphan G protein-coupled receptor G2A leading to RhoA-dependent actin rearrangement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:12109–12114
Kabarowski JH (2009) G2A and LPC: regulatory function in immunity. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 89(3-4):73–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2009.04.007
Le LQ, Karbarowski JH, Weng SAB, Harvill ET, Jensen ER, Miller JF, Witte ON (2001) Mice lacking the orphan G protein-coupled receptor G2A develop a late-onset autoimmune syndrome. Immunity 14(5):561–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1074-7613(01)00145-5
Lin P, Ye RD (2003) The lysophospholipid receptor G2A activates a specific combination of G proteins and promotes apotosis. J Biol Chem 278(16):14379–14386. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M209101200
Marchand F, Perretti M, McMahon SB (2005) Role of the immune system in chronic pain. Nat Rev Neurosci 6(7):521–532. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1700
Matsumoto G, Kushibiki T, Kinoshita Y, Lee U, Omi Y, Kubota E, Tabata Y (2006) Cationized gelatin delivery of a plasmid DNA expressing small interference RNA for VEGF inhibits murine squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci 97(4):313–321. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00174.x
McMahon SB, Russa FL, Bennett DLH (2015) Crosstalk between the nociceptive and immune systems in host defence and disease. Nat Rev 16(7):389–402. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3946
Metcalf D, Robb L, Dunn AR, Mifsud S, Rago LD (1996) Role of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in the development of an acute neutrophil inflammatory response in mice. Blood 88(10):3755–3764
Murakami N, Yokomizo T, Okuno T, Shimizu T (2004) G2A is a proton-sensing G-protein-coupled receptor antagonized by lysophosphatidylcholine. J Biol Chem 279(41):42484–42491. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M406561200
Navegantes KC, de Souza Gomes R, Pereira PAT, Czaikoski PG, Azevedo CHM, Monteiro MC. 2017 Immune modulation of some autoimmune diseases: the critical role of macrophages and neutrophils in the innate and adaptive immunity. J Transl Med. 15(1):36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-017-1141-8
Obinata H, Hattori T, Nakane S, Tatei K, Izumi T (2005) Identification of 9-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid and other oxidized free fatty acids as ligands of the G protein-coupled receptor G2A. J Biol Chem 280(49):40676–40683. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M507787200
Radu CG, Nijagal A, McLaughlin J, Wang L, Witte ON (2005) Differential proton sensitivity of related G protein-coupled receptors T cell death-associated gene 8 and G2A expressed in immune cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(5):1632–1637. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0409415102
Peter C, Waibel M, Radu CG, Yang LV, Witte ON, Schulze-Osthoff K, Wesselborg S, Lauber K (2008) Migration to apoptotic “find-me” signals is mediated via the phagocyte receptor G2A. J Biol Chem 283(9):5296–5305. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M706586200
Soehnlein O, Steffens S, Hidalgo A, Weber C (2017) Neutrophils as protagonists and targets in chronic inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 17(4):248–261. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2017.10
Summers C, Rankin SM, Condliffe AM, Singh N, Peters AM, Chilvers ER (2010) Neutrophil kinetics in health and disease. Trends Immunol 31(8):318–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2010.05.006
Thakor D, Spigelman I, Tabata Y, Nishimura I (2007) Subcutaneous peripheral injection of cationized gelatin/DNA polyplexes as a platform for non-viral gene transfer to sensory neurons. Mol Therapy 15(12):2124–2131. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mt.6300256
Thomas RM, Schmedt C, Novelli M, Choi BK, Skok J, Tarakhovsky A, Roes J (2004) C-terminal Src kinase controls acute inflammation and granulocyte adhesion. Immunity 20(2):181–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1074-7613(04)00023-8
Zhuge Y, Yuan Y, Breemen RV, Degrand M, Holian O, Yoder M, Hazel L (2014) Stimulated bronchial epithelial cells release bioactive lysophosphatidylcholine 16:0, 18:0, and 18:1. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res 6(1):66–74. https://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2014.6.1.66
Weng Z, Fluckiger AC, Nisitani S, Wahl MI, Le LQ, Hunter CA, Fernal AA, le Beau MM, Witte ON (1998) A DNA damage and stress inducible G protein-coupled receptor blocks cells in G2/M. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(21):12334–12339. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.21.12334
Acknowledgements
We thank the Taiwan Mouse Clinic (MOST 105-2325-B-001-010), which is funded by the National Research Program for Biopharmaceuticals (NRPB) at the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) of Taiwan, for technical support in H&E staining. We also thank Dr. Yasuhiko Tabata (Kyoto University, Japan) for providing CG.
Funding
This work was supported by the funds from MOST (MOST 105-2320-B-008-003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YSS participated in the data interpretation and coordination of the study and is the primary author of the manuscript. YFH performed the animal experiments and cAMP assays. JH performed the animal experiments. CWL performed the qPCR experiments. WSH performed the H&E staining experiments. WHS conceived the study and participated in its design and coordination and contributed to writing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, YS., Huang, YF., Wong, J. et al. G2A as a Threshold Regulator of Inflammatory Hyperalgesia Modulates Chronic Hyperalgesia. J Mol Neurosci 64, 39–50 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-017-1000-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-017-1000-3