Abstract
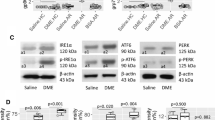
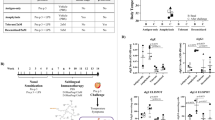
Food allergy (FA) is a common immune disorder that involves dysfunctional immune regulation. More remedies for restoring immune regulation are necessary. Semaphorin 3 A (Sema3a) is a secreted protein of the semaphorin family, which plays a role in immune responses at all stages. The objective of this study is to gain an understanding of how Sema3a can restore the immune regulatory abilities of type 1 regulatory T cells (Tr1 cells). In this study, blood samples were taken from patients with FA. Tr1 cells were purified from blood samples using flow cytometry cell sorting, using LAG3 and CD49b as surface markers. RNA sequencing was employed to examine the characteristics of Tr1 cells. We observed an exaggerated increase in ER stress in peripheral Tr1 cells of FA patients. Enforced expression of spliced X-box protein-1 (XBP1s, one of the key molecules in ER stress) resulted in suppression of interleukin (IL)-10 expression in CD4+ T cells. Eukaryotic initiation factor 2a (eIF2a) mediated the effects of XBP1 on suppressing IL-10 expression in Tr1 cells. The use of Sema3a resulted in a decrease in ER stress, and an increase in IL-10 expression in Tr1 cells of FA patients. Sema3a administration reduced experimental FA by increasing the number of Tr1 cells. In conclusion, IL-10 expression in Tr1 cells is disturbed by ER stress. Sema3a treatment restores the expression of IL-10 and the immunosuppressive capability of Tr1 cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data and materials are available upon the request.
References
Seumois G, Ramírez-Suástegui C, Schmiedel BJ, Liang S, Peters B, Sette A, et al. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of allergen-specific T cells in allergy and Asthma. Sci Immunol. 2020;5(48):eaba6087. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.aba6087.
Turner JA, Stephen-Victor E, Wang S, Rivas MN, Abdel-Gadir A, Harb H, et al. Regulatory T cell-derived TGF-β1 controls multiple checkpoints governing Allergy and Autoimmunity. Immunity. 2020;53(6):1202–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2020.10.002.
Josefowicz SZ, Lu LF, Rudensky AY. Regulatory T cells: mechanisms of differentiation and function. Annu Rev Immunol. 2012;30:531–64. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141623.
Bertolini TB, Biswas M, Terhorst C, Daniell H, Herzog RW, Piñeros AR. Role of orally induced regulatory T cells in immunotherapy and tolerance. Cell Immunol. 2021;359:104251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellimm.2020.104251.
Saidova A, Hershkop AM, Ponce M, Eiwegger T, Allergen-Specific T. Cells in IgE-Mediated Food Allergy. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2018;66(3):161–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-017-0501-7.
Walter P, Ron D. The unfolded protein response: from stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science. 2011;334(6059):1081–6. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1209038.
You K, Wang L, Chou CH, Liu K, Nakata T, Jaiswal A, et al. QRICH1 dictates the outcome of ER stress through transcriptional control of proteostasis. Science. 2021;371(6524):eabb6896. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abb6896.
Lotfi R, Zamanimehr N. Semaphorin-3A: a promising therapeutic tool in allergic rhinitis. Immunol Res. 2022;70(2):135–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-022-09264-1.
Kiseleva EP, Rutto KV. Semaphorin 3A in the Immune System: twenty years of study. Biochem (Mosc). 2022;87(7):640–57. https://doi.org/10.1134/s0006297922070069.
Delaire S, Billard C, Tordjman R, Chédotal A, Elhabazi A, Bensussan A, et al. Biological activity of soluble CD100. II. Soluble CD100, similarly to H-SemaIII, inhibits immune cell migration. J Immunol. 2001;166(7):4348–54. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.166.7.4348.
Vadasz Z, Toubi E. Semaphorin3A: a potential therapeutic tool in immune-mediated Diseases. Eur J Rheumatol. 2018;5(1):58–61. https://doi.org/10.5152/eurjrheum.2017.17076.
Toledano S, Nir-Zvi I, Engelman R, Kessler O, Neufeld G. Class-3 semaphorins and their receptors: potent multifunctional modulators of Tumor Progression. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(3):556. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030556.
Kalmarzi RN, Rajabinejad M, Lotfi R. Immune semaphorins: crucial regulatory signals and novel therapeutic targets in Asthma and allergic Diseases. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;881:173209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173209.
Sicherer SH, Sampson HA. Food allergy: a review and update on epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, prevention, and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141(1):41–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2017.11.003.
Powell MJ, Thompson SA, Tone Y, Waldmann H, Tone M. Posttranscriptional regulation of IL-10 gene expression through sequences in the 3’-untranslated region. J Immunol. 2000;165(1):292–6. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.165.1.292.
Wang Q, Li L, Li C, Cao H, Chen Y, Zhou W, et al. Circadian protein CLOCK modulates regulatory B cell functions of nurses engaging day-night shift rotation. Cell Signal. 2022;96:110362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2022.110362.
Gabryšová L, Alvarez-Martinez M, Luisier R, Cox LS, Sodenkamp J, Hosking C, et al. c-Maf controls immune responses by regulating disease-specific gene networks and repressing IL-2 in CD4(+) T cells. Nat Immunol. 2018;19(5):497–507. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-018-0083-5.
Stöckl S, Reichart J, Zborilova M, Johnstone B, Grässel S. Semaphorin 3A-Neuropilin-1 signaling modulates MMP13 expression in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(22):14180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214180.
Luo X, Mo L, Wang X, Zhang S, Liu H, Wu G, et al. Rnf20 inhibition enhances immunotherapy by improving regulatory T cell generation. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022;79(12):588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-022-04613-7.
Zeng HT, Liu JQ, Zhao M, Yu D, Yang G, Mo LH, et al. Exosomes carry IL-10 and antigen/MHC II complexes to induce antigen-specific oral tolerance. Cytokine. 2020;133:155176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155176.
Cubillos-Ruiz JR, Silberman PC, Rutkowski MR, Chopra S, Perales-Puchalt A, Song M, et al. ER stress sensor XBP1 controls anti-tumor immunity by disrupting dendritic cell homeostasis. Cell. 2015;161(7):1527–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.025.
Zeng X, Xiao X, Hu S, He W, Wu G, Geng X, et al. XBP1 is required in Th2 polarization induction in airway allergy. Theranostics. 2022;12(12):5337–49. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.75100.
Yoshida H, Matsui T, Yamamoto A, Okada T, Mori K. XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor. Cell. 2001;107(7):881–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00611-0.
Harding HP, Zhang Y, Ron D. Protein translation and folding are coupled by an endoplasmic-reticulum-resident kinase. Nature. 1999;397(6716):271–4. https://doi.org/10.1038/16729.
Huang H, Liu Y, Wang Y, Liu H, Xie B, Zheng MBW, et al. Semaphorin-3 promotes specific Immunotherapy effects on Experimental Food Allergy. J Immunol Res. 2022;2022:5414993. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5414993.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported by research grants of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (8197033399, 32090052), Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Regional Immunity and Diseases (2019B030301009) and Shenzhen science, technology and innovation committee (KQTD20170331145453160, SGDX20201103095609027, KCXFZ20201221173208023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Gao P, Song S, Wang Y, Liu H, Wang X and Shu Q performed experiments, analyzed data and reviewed the manuscript. Yang P and Zheng P organized the project and supervised experiments. Yang P designed the project and prepared the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The experimental protocols were reviewed and approved by the human ethics committee and animal ethics committee at Zhengzhou University.
Competing interests
None to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, P., Song, S., Wang, Y. et al. Semaphorin 3 a restores the ability of type 1 regulatory T cells to suppress food allergy. Immunol Res 72, 320–330 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-023-09437-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-023-09437-6