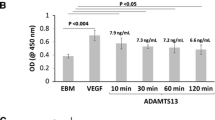
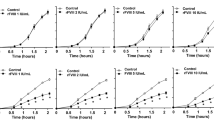
Abstract
B7-H3 is a cell surface molecule in the immunoglobulin superfamily that has been shown to perform both immunological and non-immunological functions. It has also been found that vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is an important molecule in the modulation of endothelial cell behavior. In this study, we analyzed the serum expression of B7-H3 in 113 rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematous patients using the ELISA and found a positive correlation between B7-H3 and VEGF. Next, we investigated the involvement of B7-H3 in angiogenesis using human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) with transient knockdown of B7-H3 and an in vivo Matrigel model. Data from the in vitro experiments showed that B7-H3 increased cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation, and correlated with the expression of VEGF. Furthermore, B7-H3 affected the formation of functional vascular networks in Matrigel plugs, which were dissected from mice injected with different HUVECs. Our data suggest that B7-H3 promotes angiogenesis through the enhancement of VEGF secretion. This is the first study proposing a significant role for B7-H3 in the promotion of angiogenesis and may provide further understanding of this gene’s biological function.








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
12 June 2020
The order of authors��� affiliations in the published version of this article was not consistent with the order in the submitted manuscript due to typesetting
References
Chapoval AI, Ni J, Lau JS, Wilcox RA, Flies DB, Liu D, et al. B7-H3: a costimulatory molecule for T cell activation and IFN-gamma production. Nat Immunol. 2001;2(3):269–74.
Suh WK, Wang SX, Jheon AH, Moreno L, Yoshinaga SK, Ganss B, et al. The immune regulatory protein B7-H3 promotes osteoblast differentiation and bone mineralization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(35):12969–73.
Xu L, Zhang G, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Xu W, Wu S, et al. Stimulation of B7-H3 (CD276) directs the differentiation of human marrow stromal cells to osteoblasts. Immunobiology. 2011;216(12):1311–7.
Tran CN, Thacker SG, Louie DM, Oliver J, White PT, Endres JL, et al. Interactions of T cells with fibroblast-like synoviocytes: role of the B7 family costimulatory ligand B7-H3. J Immunol. 2008;180(5):2989–98.
Calabro L, Sigalotti L, Fonsatti E, Bertocci E, Di Giacomo AM, Danielli R, et al. Expression and regulation of B7-H3 immunoregulatory receptor, in human mesothelial and mesothelioma cells: immunotherapeutic implications. J Cell Physiol. 2011;226(10):2595–600.
Lee YH, Martin-Orozco N, Zheng P, Li J, Zhang P, Tan H, et al. Inhibition of the B7-H3 immune checkpoint limits tumor growth by enhancing cytotoxic lymphocyte function. Cell Res. 2017;27(8):1034–45.
Luo L, Chapoval AI, Flies DB, Zhu G, Hirano F, Wang S, et al. B7-H3 enhances tumor immunity in vivo by costimulating rapid clonal expansion of antigen-specific CD8+ cytolytic T cells. J Immunol. 2004;173(9):5445–50.
Li Y, Yang X, Wu Y, Zhao K, Ye Z, Zhu J, et al. B7-H3 promotes gastric cancer cell migration and invasion. Oncotarget. 2017;8(42):71725–35.
Li Y, Guo G, Song J, Cai Z, Yang J, Chen Z, et al. B7-H3 promotes the migration and invasion of human bladder cancer cells via the PI3K/Akt/STAT3 signaling pathway. J Cancer. 2017;8(5):816–24.
Marrelli A, Cipriani P, Liakouli V, Carubbi F, Perricone C, Perricone R, et al. Angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis: a disease specific process or a common response to chronic inflammation? Autoimmun Rev. 2011;10(10):595–8.
Leblond A, Allanore Y, Avouac J. Targeting synovial neoangiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2017;16(6):594–601.
Nagashima M, Yoshino S, Ishiwata T, Asano G. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in angiogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1995;22(9):1624–30.
Zhang J, Li C, Zheng Y, Lin Z, Zhang Y, Zhang Z. Inhibition of angiogenesis by arsenic trioxide via TSP-1-TGF-beta1-CTGF-VEGF functional module in rheumatoid arthritis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(43):73529–46.
Jiang S, Li Y, Lin T, Yuan L, Wu S, Xia L, et al. IL-35 inhibits angiogenesis through VEGF/Ang2/Tie2 pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;40(5):1105–16.
Clavel G, Bessis N, Boissier MC. Recent data on the role for angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2003;70(5):321–6.
Efremova M, Rieder D, Klepsch V, Charoentong P, Finotello F, Hackl H, et al. Targeting immune checkpoints potentiates immunoediting and changes the dynamics of tumor evolution. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):32.
Karin N. Chemokines and cancer: new immune checkpoints for cancer therapy. Curr Opin Immunol. 2018;51:140–5.
Hofmeyer KA, Ray A, Zang X. The contrasting role of B7-H3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(30):10277–8.
Sun J, Lai H, Shen D, Wu P, Yang J, Sun Z, et al. Reduced sB7-H3 expression in the peripheral blood of systemic lupus erythematosus patients. J Immunol Res. 2017;2017:5728512.
Sun J, Liu C, Gao L, Guo Y, Zhang Y, Wu P, et al. Correlation between B7-H3 expression and rheumatoid arthritis: a new polymorphism haplotype is associated with increased disease risk. Clin Immunol. 2015;159(1):23–32.
Jiang J, Liu C, Zhang G, Gao L, Chen Y, Zhu R, et al. Enhancement of membrane B7-H3 costimulatory molecule but reduction of its soluble form in multiple sclerosis. J Clin Immunol. 2013;33(1):118–26.
Zhao JL, Chen FL, Zhou Q, Pan W, Wang XH, Xu J, et al. B7-H3 protein expression in a murine model of osteosarcoma. Oncol Lett. 2016;12(1):383–6.
Yan R, Yang S, Sun J, Chen X, Zhang G, Feng P, et al. A novel monoclonal antibody against mouse B7-H3 developed in rats. Hybridoma (Larchmt). 2012;31(4):267–71.
Feng P, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Dai X, Mao T, Fan Y, et al. The interaction of MMP-2/B7-H3 in human osteoporosis. Clin Immunol. 2016;162:118–24.
Li D, Wang J, Zhou J, Zhan S, Huang Y, Wang F, et al. B7-H3 combats apoptosis induced by chemotherapy by delivering signals to pancreatic cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2017;8(43):74856–68.
Seaman S, Zhu Z, Saha S, Zhang XM, Yang MY, Hilton MB, et al. Eradication of tumors through simultaneous ablation of CD276/B7-H3-positive tumor cells and tumor vasculature. Cancer Cell. 2017;31(4):501–15.
Qin X, Zhang H, Ye D, Dai B, Zhu Y, Shi G. B7-H3 is a new cancer-specific endothelial marker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2013;6:1667–73.
Nowak-Sliwinska P, Alitalo K, Allen E, Anisimov A, Aplin AC, Auerbach R, et al. Consensus guidelines for the use and interpretation of angiogenesis assays. Angiogenesis. 2018;21(3):425–532.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Jiangsu Province University Outstanding Science and Technology Innovation Team (Grant no. 2015023), Qinglan Project (Sunjing, Sunzhongwen), and Jiangsu Provincial Medical Talent (Sunjing). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experiments were approved by the Ethics Review Board of Suzhou Vocational Health College, and written informed consent was obtained from each blood donor.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, H., Sun, Z., Yang, J. et al. B7-H3 modulates endothelial cell angiogenesis through the VEGF cytokine. Immunol Res 67, 202–211 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-019-09084-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-019-09084-w