Abstract
Purpose
Bcl-2 family proteins are of great significance in the pathogenesis and development of tumors. In this study, the correlations between the expression of Bcl-2 family proteins and clinicopathological features and prognosis of neuroendocrine neoplasms (NENs) were further investigated.
Methods
105 Patients diagnosed with gastroenteropancreatic NENs (GEP-NENs) with the paraffin specimen of the tumor available were retrospectively included. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was performed to detect the expression of Bcl-2 family proteins in paraffin-embedded samples. Student’s t-test and Chi-square test were applied to compare the difference of quantitative and categorical variables, respectively. Survival analysis was conducted according to Kaplan–Meier method. Univariate and multivariate cox regression analysis were used to identify the independent prognostic factors.
Results
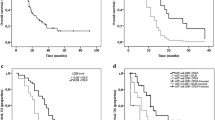
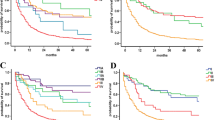
The IHC score of Bcl-2 was significantly higher in neuroendocrine carcinoma (NEC) patients (65.6%), while a higher IHC score of Noxa was more common in neuroendocrine tumor (NET) patients (49.3%). Survival analysis indicated that patients with higher Bcl-2 expression and lower Noxa expression had worse 5-year survival (39.3% vs. 75.6%, p < 0.001; 40.6% vs. 84.9%, p < 0.001). Multivariate cox analysis indicated that high Bcl-2 expression was an independent factor associated with inferior DFS (hazard ratio [HR]: 2.092; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.106–3.955; p = 0.023) and OS (HR: 2.784; 95% CI: 1.326–5.846; p = 0.007), while higher Noxa expression was associated with superior DFS (HR:0.398; 95% CI: 0.175–0.907; p = 0.028) and OS (HR: 0.274; 95% CI: 0.110–0.686; p = 0.006).
Conclusions
Higher expression of Bcl-2 and lower expression of Noxa were associated with unfavorable prognosis of GEP-NENs patients.



Similar content being viewed by others

References
A. Dasari, C. Shen, D. Halperin, B. Zhao, S. Zhou, Y. Xu et al. Trends in the incidence, prevalence, and survival outcomes in patients with neuroendocrine tumors in the United States. JAMA Oncol. 3(10), 1335–1342 (2017)
J.C. Yao, M.H. Shah, T. Ito, C.L. Bohas, E.M. Wolin, E. Van Cutsem et al. Everolimus for advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 364(6), 514–523 (2011)
E. Raymond, L. Dahan, J.L. Raoul, Y.J. Bang, I. Borbath, C. Lombard-Bohas et al. Sunitinib malate for the treatment of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 364(6), 501–513 (2011)
J.C. Yao, N. Fazio, S. Singh, R. Buzzoni, C. Carnaghi, E. Wolin et al. Everolimus for the treatment of advanced, non-functional neuroendocrine tumours of the lung or gastrointestinal tract (RADIANT-4): a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet 387(10022), 968–977 (2016)
J. Xu, L. Shen, Z. Zhou, J. Li, C. Bai, Y. Chi et al. Surufatinib in advanced extrapancreatic neuroendocrine tumours (SANET-ep): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 21(11), 1500–1512 (2020)
J.E. Guikema, M. Amiot, E. Eldering, Exploiting the pro-apoptotic function of NOXA as a therapeutic modality in cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 21(8), 767–779 (2017)
E.M. Bruckheimer, S.H. Cho, M. Sarkiss, J. Herrmann, T.J. McDonnell, The Bcl-2 gene family and apoptosis. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 62, 75–105 (1998)
J.B. Dietrich, Apoptosis and anti-apoptosis genes in the Bcl-2 family. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 105(2), 125–135 (1997)
I. Kapoor, J. Bodo, B. Hill, E. Hsi, A. Almasan, Targeting BCL-2 in B-cell malignancies and overcoming therapeutic resistance. Cell Death Dis. 11(11), 941 (2020)
J.W. Moul, Angiogenesis, p53, bcl-2 and Ki-67 in the progression of prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy. Eur. Urol. 35(5-6), 399–407 (1999)
Y. Wei, Y. Cao, R. Sun, L. Cheng, X. Xiong, X. Jin et al. Targeting Bcl-2 proteins in acute myeloid leukemia. Front. Oncol. 10, 584974 (2020)
N. Gangat, A. Tefferi, Venetoclax-based chemotherapy in acute and chronic myeloid neoplasms: literature survey and practice points. Blood Cancer J. 10(11), 122 (2020)
S. Yachida, E. Vakiani, C.M. White, Y. Zhong, T. Saunders, R. Morgan et al. Small cell and large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas of the pancreas are genetically similar and distinct from well-differentiated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 36(2), 173–184 (2012)
I.D. Nagtegaal OR, D. Klimstra, WHO classification of tumours. digestive system tumours. Fifth Edition: World Health Organization Press. 2019
S.B. Edge, AJCC cancer staging manual 8th ed: Springer; 2017.
D. Creytens, NKX2.2 immunohistochemistry in the distinction of Ewing sarcoma from cytomorphologic mimics: Diagnostic utility and pitfalls-Comment on Russell-Goldman et al. Cancer Cytopathol. 127(3), 202 (2019)
Z. Guo, X. Zhang, H. Zhu, N. Zhong, X. Luo, Y. Zhang et al. TELO2 induced progression of colorectal cancer by binding with RICTOR through mTORC2. Oncol. Rep. 45(2), 523–534 (2021)
W. Chen, J. Peng, Q. Ou, Y. Wen, W. Jiang, Y. Deng et al. Expression of NDRG2 in human colorectal cancer and its association with prognosis. J. Cancer 10(15), 3373–3380 (2019)
J. Peng, Y. Zhao, Q. Luo, H. Chen, W. Fan, Z. Pan et al. High WNT6 expression indicates unfavorable survival outcome for patients with colorectal liver metastasis after liver resection. J. Cancer 10(12), 2619–2627 (2019)
A.S. Ebrahim, H. Sabbagh, A. Liddane, A. Raufi, M. Kandouz, A. Al-Katib, Hematologic malignancies: newer strategies to counter the BCL-2 protein. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 142(9), 2013–2022 (2016)
D.G. Wang, C.F. Johnston, J.M. Sloan, K.D. Buchanan, Expression of Bcl-2 in lung neuroendocrine tumours: comparison with p53. J. Pathol. 184(3), 247–251 (1998)
M. Rahmani, J. Nkwocha, E. Hawkins, X. Pei, R.E. Parker, M. Kmieciak et al. Cotargeting BCL-2 and PI3K induces BAX-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis in AML cells. Cancer Res. 78(11), 3075–3086 (2018)
D. Trisciuoglio, M. Desideri, L. Ciuffreda, M. Mottolese, D. Ribatti, A. Vacca et al. Bcl-2 overexpression in melanoma cells increases tumor progression-associated properties and in vivo tumor growth. J. Cell Physiol. 205(3), 414–421 (2005)
A.A. Gal, M.N. Sheppard, J.D. Nolen, C. Cohen, p53, cellular proliferation, and apoptosis-related factors in thymic neuroendocrine tumors. Mod. Pathol. 17(1), 33–39 (2004)
T.C. Fisher, A.E. Milner, C.D. Gregory, A.L. Jackman, G.W. Aherne, J.A. Hartley et al. bcl-2 modulation of apoptosis induced by anticancer drugs: resistance to thymidylate stress is independent of classical resistance pathways. Cancer Res. 53(14), 3321–3326 (1993)
U.A. Sartorius, P.H. Krammer, Upregulation of Bcl-2 is involved in the mediation of chemotherapy resistance in human small cell lung cancer cell lines. Int J. Cancer 97(5), 584–592 (2002)
S. Hafezi, M. Rahmani, Targeting BCL-2 in cancer: advances, challenges, and perspectives. Cancers. 2021;13
T.L. Lochmann, K.V. Floros, M. Naseri, K.M. Powell, W. Cook, R.J. March et al. Venetoclax Is Effective in Small-Cell Lung Cancers with High BCL-2 Expression. Clin. Cancer Res. 24(2), 360–369 (2018)
D.A. Pollyea, Venetoclax in AML: where we are and where we are headed. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 20(Suppl 1), S25–S26 (2020)
P. Gomez-Bougie, S. Wuilleme-Toumi, E. Menoret, V. Trichet, N. Robillard, M. Philippe et al. Noxa up-regulation and Mcl-1 cleavage are associated to apoptosis induction by bortezomib in multiple myeloma. Cancer Res. 67(11), 5418–5424 (2007)
K.G. Ponder, S.M. Matulis, S. Hitosugi, V.A. Gupta, C. Sharp, F. Burrows et al. Dual inhibition of Mcl-1 by the combination of carfilzomib and TG02 in multiple myeloma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 17(7), 769–777 (2016)
M.C. Albert, K. Brinkmann, H. Kashkar, Noxa and cancer therapy: Tuning up the mitochondrial death machinery in response to chemotherapy. Mol. Cell Oncol. 1(1), e29906 (2014)
W.J. Mackus, A.P. Kater, A. Grummels, L.M. Evers, B. Hooijbrink, M.H. Kramer et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells display p53-dependent drug-induced Puma upregulation. Leukemia 19(3), 427–434 (2005)
K.M. Lucas, N. Mohana-Kumaran, D. Lau, X.D. Zhang, P. Hersey, D.C. Huang et al. Modulation of NOXA and MCL-1 as a strategy for sensitizing melanoma cells to the BH3-mimetic ABT-737. Clin. Cancer Res. 18(3), 783–795 (2012)
C. Seveno, D. Loussouarn, S. Brechet, M. Campone, P. Juin, S. Barille-Nion, gamma-Secretase inhibition promotes cell death, Noxa upregulation, and sensitization to BH3 mimetic ABT-737 in human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 14(3), R96 (2012)
Author contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Data collection and analysis were performed by Y.G., L.Z., and N.Z. Experiments design: D.J.Y. and J.C. Immunohistochemical staining and analysis: M.L., Q.Y.L. Manuscript writing: Y.G., L.Z., N.Z., and L.C. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82141104); Guangzhou Science and Technology Plan (201804010078); Province Natural Science Fund of Guangdong (2019A1515011373); National Natural Science Foundation of China (82003268).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These author contributed equally: Yu Guo, Lin Zhang and Ning Zhang.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Zhang, L., Zhang, N. et al. Bcl-2 and Noxa are potential prognostic indicators for patients with gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Endocrine 78, 159–168 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-022-03114-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-022-03114-8